Explore the fundamentals of synchronous AC motors, their types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications in various industries.
Introduction to Synchronous AC Motors
Synchronous AC motors are a type of electric motor where the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current. In simpler terms, the motor’s speed is consistent with the rate of the alternating current (AC) that powers it. Synchronous AC motors offer an array of benefits, making them a choice of preference for certain applications.
Working Principle of Synchronous AC Motors
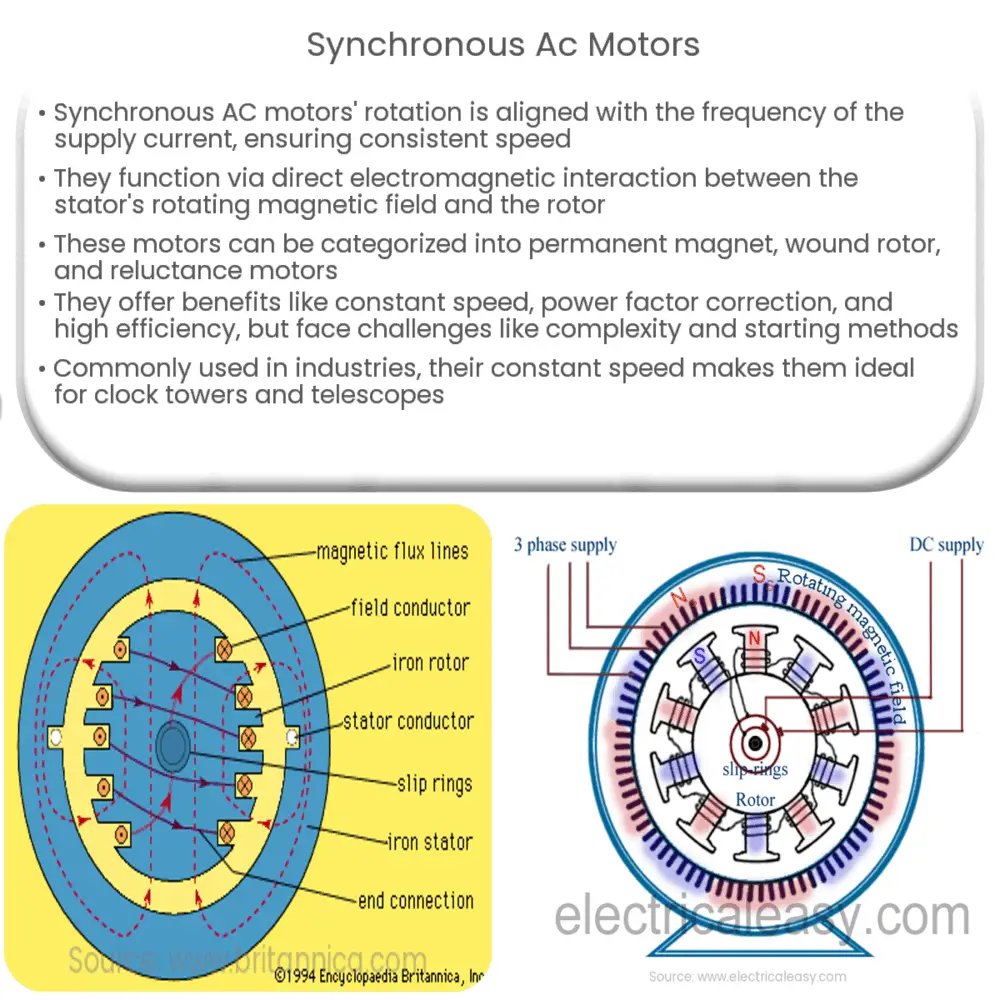
Unlike induction motors, synchronous motors do not rely on a generated magnetic field to create torque. Instead, they employ direct electromagnetic interaction. The stator, or stationary part of the motor, creates a rotating magnetic field, while the rotor, or the moving part of the motor, follows this rotation synchronously.
The Construction of a Synchronous AC Motor
-
Stator: The stator, similar to other types of AC motors, is composed of laminated cores with slots, which carry the armature windings. These windings are supplied with three-phase alternating current, which produces a rotating magnetic field.
-
Rotor: The rotor design varies depending upon the method of starting. It can either be a salient pole type (where poles are projecting out) or a cylindrical type (also known as non-salient pole). It contains field windings, which are supplied with DC current to produce the required magnetic field.
Types of Synchronous AC Motors
There are three primary types of synchronous AC motors, namely:
-
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM): These motors use permanent magnets on the rotor to create the necessary magnetic field. They are highly efficient, compact, and can operate at high speeds.
-
Wound rotor synchronous motors: In this type, the rotor winding is excited by an external DC source. These motors can manage heavy start loads and are typically used in high power applications.
-
Reluctance motors: In reluctance motors, the rotor is designed to follow the magnetic field created by the stator, but without any conductors on the rotor itself. They are commonly used for their high-speed capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous AC Motors
There are several reasons why synchronous AC motors are popular in many industries. Some of their key advantages include:
-
Constant speed operation: Synchronous motors maintain a constant speed irrespective of the load. The speed is proportional to the frequency of the power source, making them ideal for precision operations.
-
Power factor correction: They can operate under leading power factors, thereby improving the overall power factor of the system. This is beneficial in industrial settings where reactive power is a concern.
-
High efficiency and power: These motors offer high power output and efficiency, especially in low-speed, high-torque applications.
However, synchronous AC motors also have certain limitations, including:
-
Complexity: They are more complex in construction and operation compared to induction motors. This increases the overall cost and necessitates expert handling.
-
Starting methods: These motors require a separate starting mechanism, as they cannot self-start like induction motors.
Applications of Synchronous AC Motors
Synchronous AC motors find extensive applications in a variety of fields due to their unique properties. They are widely used in industries such as paper and pulp, metal, cement, and chemicals. They are also commonly used in pumps, compressors, fans, extruders, and mills. Additionally, due to their constant speed operation, they are beneficial in applications like clock towers and telescopes.
Conclusion
In summary, synchronous AC motors offer significant benefits, including high efficiency, power factor correction, and constant speed operation. Although they come with their share of challenges such as complexity and starting issues, their advantages often outweigh these drawbacks in many applications. By understanding their construction, operation, and types, we can better appreciate their role in our everyday lives and industrial applications. It is important to select the right type of motor for the specific application to reap the maximum benefits that these motors offer.


