Explore the fundamentals of switching voltage regulators, their importance in electronics, types, working principles, and future developments.
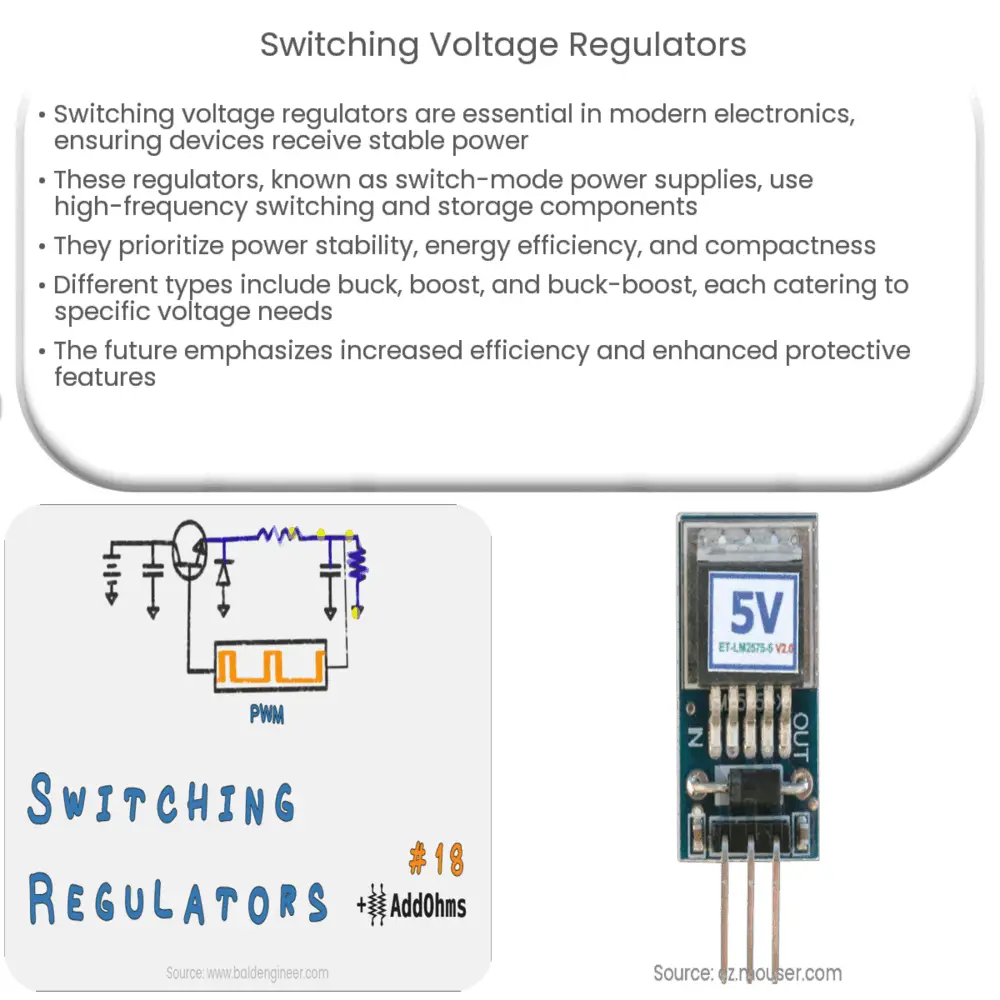
Introduction to Switching Voltage Regulators
Switching voltage regulators have become a ubiquitous component in modern electronics, and understanding their function is critical to those interested in electrical engineering or anyone building electronic devices. These regulators play an instrumental role in delivering stable, constant voltage to electronic devices, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding the Basics
At the most fundamental level, a switching voltage regulator, also known as a switch-mode power supply (SMPS), is an electronic circuit that converts power using switching devices that are turned on and off at high frequencies, and storage components like inductors or capacitors to supply power when the switching device is in its non-conduction state.
The Need for Voltage Regulation
-
Power Stability: Most electronic devices require a constant voltage supply to function optimally. Variations in voltage can cause fluctuations in the device’s performance, and in some cases, damage the device.
-
Energy Efficiency: Switching voltage regulators are more energy efficient compared to linear regulators because they avoid dissipating excess power as heat.
-
Size and Weight: Switching regulators are compact and lightweight, which makes them suitable for use in portable devices.
Types of Switching Voltage Regulators
-
Buck Regulator: Also known as a step-down converter, it’s used when the output voltage needs to be less than the input voltage.
-
Boost Regulator: The opposite of the buck regulator, this is used when the output voltage needs to be higher than the input voltage.
-
Buck-Boost Regulator: This type is utilized when the output voltage can be either higher or lower than the input voltage.
Regardless of the type, the main goal of a switching voltage regulator is to efficiently regulate voltage, providing stable power supply to various electronic devices.
Working Principle of Switching Voltage Regulators
Switching voltage regulators operate using a simple principle: they switch the input voltage on and off rapidly, creating a “pulsed” voltage. This pulsed voltage is then averaged out to achieve the desired output voltage. If the output voltage is too high, the regulator decreases the pulse width, reducing the average voltage. Conversely, if the output voltage is too low, it increases the pulse width, increasing the average voltage.
Designing with Switching Voltage Regulators
When designing electronic devices, choosing the right switching voltage regulator can make a difference in the device’s performance, size, and battery life. Some of the factors to consider include:
-
Input and Output Voltage: The input and output voltages help determine the type of regulator needed – buck, boost, or buck-boost.
-
Load Current: This is the maximum current the regulator needs to provide to the device. It’s crucial to choose a regulator that can handle the maximum load current without overheating.
-
Switching Frequency: Higher frequencies result in smaller components but can produce more noise, which may interfere with other parts of the device.
The Future of Switching Voltage Regulators
With the growth in portable and wireless electronics, the demand for more efficient and smaller switching voltage regulators is ever-increasing. The continued evolution of switching voltage regulators will likely focus on increasing efficiency, reducing size, and adding functionality such as overvoltage and overcurrent protection.
Conclusion
Switching voltage regulators serve as an integral part of modern electronics, enabling devices to function optimally under varying power conditions. Their ability to efficiently regulate power while minimizing heat dissipation makes them the preferred choice for many applications. Understanding their working principle and various types helps in better designing and selecting the appropriate regulator for electronic devices. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the capabilities and functionality of switching voltage regulators, paving the way for more advanced, efficient, and compact electronic devices.

