Explore the functionality of switching voltage regulators, their types, advantages, challenges, applications, and future trends in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Switching Voltage Regulators
As technology advances, the need for effective power management in electronic devices has become increasingly crucial. This is where a Switching Voltage Regulator comes in. This device is essential for maintaining the stability of a system’s power supply and ensuring the efficient utilization of energy.
Understanding the Basics
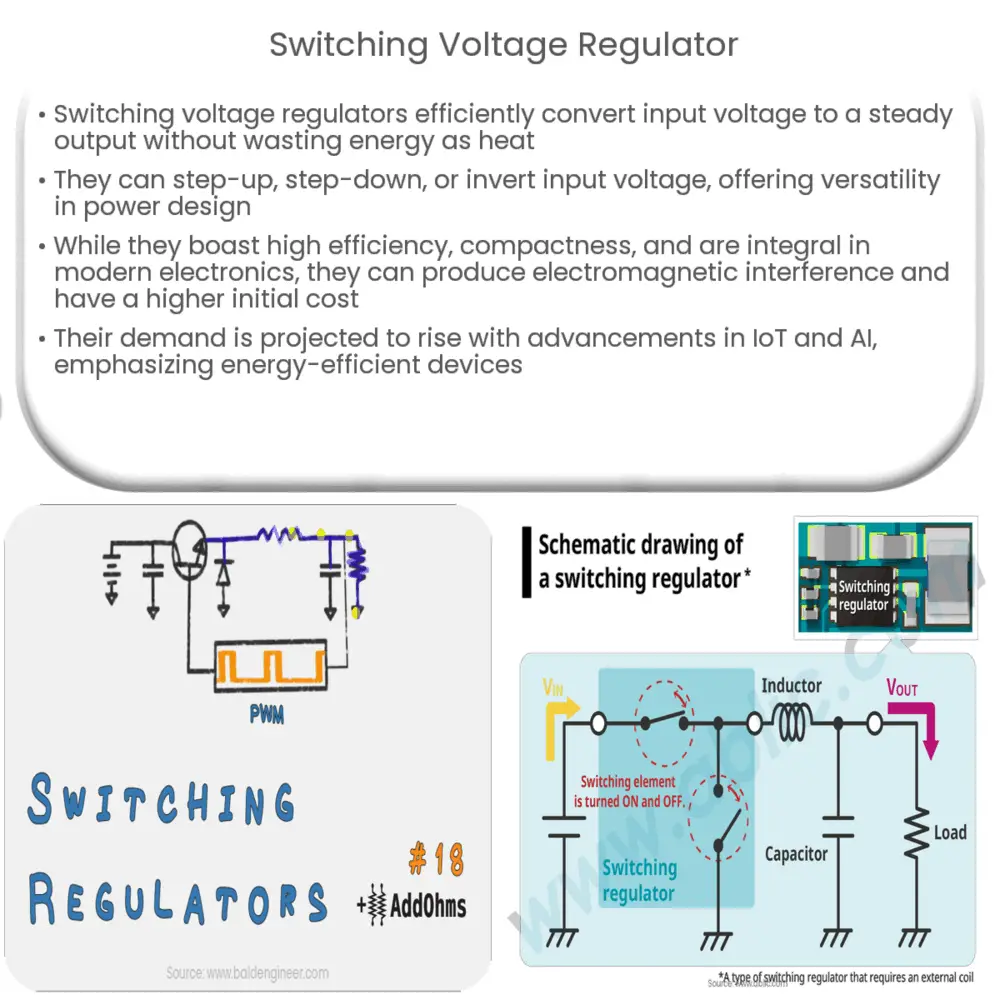
A switching voltage regulator is a type of power supply that efficiently converts an input voltage into a steady output voltage. Unlike linear regulators that dissipate excess voltage as heat, switching regulators use a different technique to achieve the same goal, thus minimizing energy waste. They operate by rapidly switching a series element on and off, hence their name.
Types of Switching Voltage Regulators
- Buck Regulators: Also known as step-down regulators, they convert a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage.
- Boost Regulators: Conversely, boost regulators, also known as step-up regulators, transform a lower input voltage to a higher output voltage.
- Buck-Boost Regulators: These versatile regulators can either step-up or step-down the input voltage as required.
Working Mechanism
Switching voltage regulators work on the principle of Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). The series element is switched on and off at a high frequency, with the duration of the “on” state (the duty cycle) adjusted to control the amount of energy transferred to the output. This rapid switching, combined with energy storage elements like inductors and capacitors, ensures a stable output voltage despite variations in input voltage or load.
Key Advantages
- High Efficiency: As energy isn’t dissipated as heat, switching regulators typically offer efficiencies of 85-95%, making them ideal for battery-powered devices.
- Flexibility: With the ability to step-up, step-down, or invert the input voltage, they offer a wide range of power design solutions.
- Small Size: Due to high switching frequencies, the associated inductors and capacitors can be small, resulting in compact designs.
Despite these advantages, switching regulators do have some challenges, which we will discuss in the next part of this article, along with a deep-dive into applications and future trends in this field.
Challenges with Switching Voltage Regulators
Although switching voltage regulators have distinct advantages, they also have some challenges. One of the major issues is noise. The high-frequency switching operation can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can affect other electronic components in the circuit. Additionally, due to the complex design, they require more external components than their linear counterparts. Furthermore, they have a higher initial cost, making them less desirable for low-cost applications.
Applications of Switching Voltage Regulators
Switching voltage regulators are widely used in various applications due to their high efficiency and versatility. They are found in:
- Consumer Electronics: In devices such as laptops, smartphones, and televisions to manage power efficiency.
- Automotive Industry: In electronic control units, LED headlights, and infotainment systems.
- Industrial Applications: In automation systems, power tools, and renewable energy systems.
Future Trends
The demand for switching voltage regulators is expected to increase in the future, driven by the growing need for energy-efficient devices. The advent of IoT (Internet of Things) and advancements in AI (Artificial Intelligence) will further push the boundaries of power management, leading to more compact and efficient switching regulators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, switching voltage regulators play a pivotal role in power management in modern electronic devices. Their ability to convert voltages efficiently, along with their flexibility and compactness, make them an integral part of various industries. Despite the challenges such as noise and design complexity, their demand is set to rise, largely due to the increasing need for energy-efficient and miniaturized devices. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in switching voltage regulator designs and capabilities, ultimately leading to more efficient power management solutions in our electronics.

