Explore the workings, advantages, and applications of Switched Reluctance Motors, along with the challenges and future research directions.
Introduction to Switched Reluctance Motors
Switched Reluctance Motors (SRMs) represent a unique category of electric motors, which are rapidly gaining popularity due to their unique benefits. These robust motors differ from the more traditional induction motors in many ways, particularly their simplicity and reliability.
The Principle of Operation
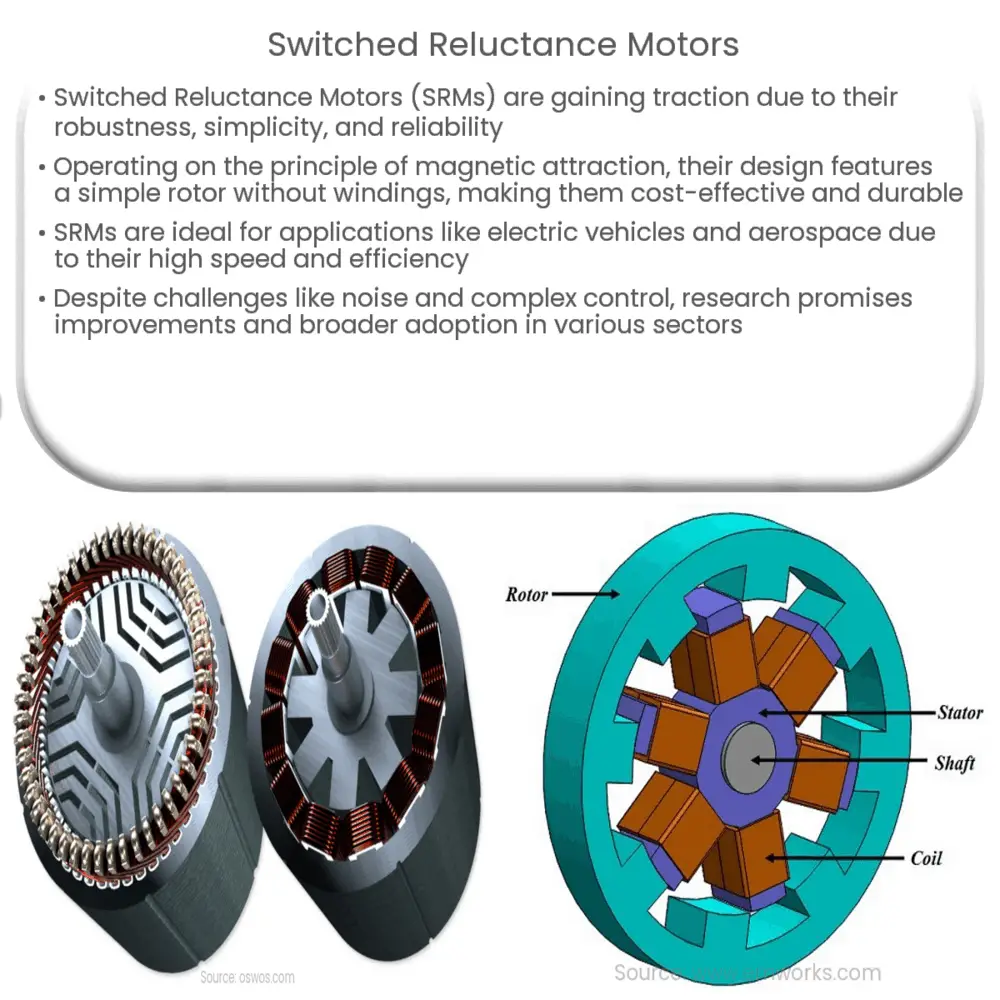
The operation of a Switched Reluctance Motor is based on the principle of magnetic attraction. The stator and rotor in these motors have salient poles, but unlike other motors, the rotor is made of soft magnetic material with no windings, magnets, or squirrel cages. It’s the simplicity of the rotor that provides a number of advantages, including cost-effectiveness and durability.
In an SRM, the magnetic reluctance of the path varies with the position of the rotor. When a particular stator winding is energized, the rotor moves to align itself with the excited stator pole to minimize the magnetic reluctance, thus producing torque. This principle of operation is known as variable reluctance.
Construction of a Switched Reluctance Motor
Switched Reluctance Motors consist of two main parts: a stator and a rotor. The stator is similar to that of a conventional motor, composed of multiple coils wound around laminated iron cores. However, the rotor is simply a piece of laminated iron with salient poles. The design of the rotor, without windings or permanent magnets, contributes to the ruggedness and low cost of the motor.
Control of Switched Reluctance Motors
Control strategies for SRMs are significantly different from other types of motors. The stator windings are excited in a sequential manner, based on the rotor position. This is typically accomplished using a rotor position sensor, although sensorless control techniques are also being developed. The power electronic converter used for this purpose is often a simple asymmetric bridge converter, which adds to the overall robustness and efficiency of the system.
Applications of Switched Reluctance Motors
The unique characteristics of SRMs, such as high torque-to-inertia ratio, high efficiency, and robust construction, make them suitable for a wide range of applications. These include electric vehicles, aerospace applications, and industrial drives. The ability of SRMs to operate at very high speeds is particularly advantageous in applications such as pumps and compressors.
Advantages of Switched Reluctance Motors
The key advantages of Switched Reluctance Motors can be attributed to their distinct design and control mechanism. The major benefits include:
- Robustness: The absence of brushes, slip rings, permanent magnets, or rotor windings contributes to the ruggedness of the SRM design. This robustness allows for the motor’s use in extreme environments and ensures longevity.
- High Speed: SRMs are capable of reaching very high speeds, limited primarily by the mechanical stress on the rotor, providing a significant advantage in applications requiring high rotational speeds.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The simplicity of the SRM design leads to a lower manufacturing cost compared to other types of motors.
- Efficiency: SRMs typically have high efficiency, especially at high speeds and loads.
Challenges and Research Directions
Despite the advantages, there are certain challenges associated with Switched Reluctance Motors. For instance, SRMs are known to produce more acoustic noise and vibration compared to other motors. This is due to the abrupt change in magnetic forces during switching. Additionally, the control of SRMs is more complex due to the non-linear relationship between the torque and the current and rotor position.
These challenges have led to significant research efforts. Areas of focus include advanced control techniques, novel designs to reduce noise and vibration, and methods to improve efficiency further. Sensorless control strategies are also an active area of research, aiming to eliminate the need for rotor position sensors and further improve the reliability of SRMs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Switched Reluctance Motors offer a cost-effective, robust, and efficient solution for many applications. Their inherent advantages, including the capability of high-speed operation and minimal maintenance, make them an attractive choice in numerous fields. Although challenges like acoustic noise, vibration, and control complexity persist, ongoing research holds promising potential for overcoming these hurdles. As technology advances, we can expect to see an increasing adoption of SRMs in various sectors such as automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications.

