A step recovery diode is a fast-switching semiconductor device used in high-frequency applications like frequency multipliers and pulse generators.
Understanding the Step Recovery Diode
Introduction
The step recovery diode, also known as the snap-off diode or charge-storage diode, is a high-speed semiconductor device used in various applications, such as frequency multipliers, pulse generators, and fast-switching circuits. This unique diode exhibits a rapid transition from its ON to OFF state, which enables it to operate effectively in high-frequency electronic systems. In this article, we will explore the working principle, construction, and applications of step recovery diodes.
Construction and Working Principle
A step recovery diode is typically made from silicon, although other materials like gallium arsenide (GaAs) can also be used. Its structure is similar to a conventional PN junction diode, with a lightly doped P-region and a heavily doped N-region. The crucial difference is in the charge storage characteristics of the device, which allow it to switch off rapidly.
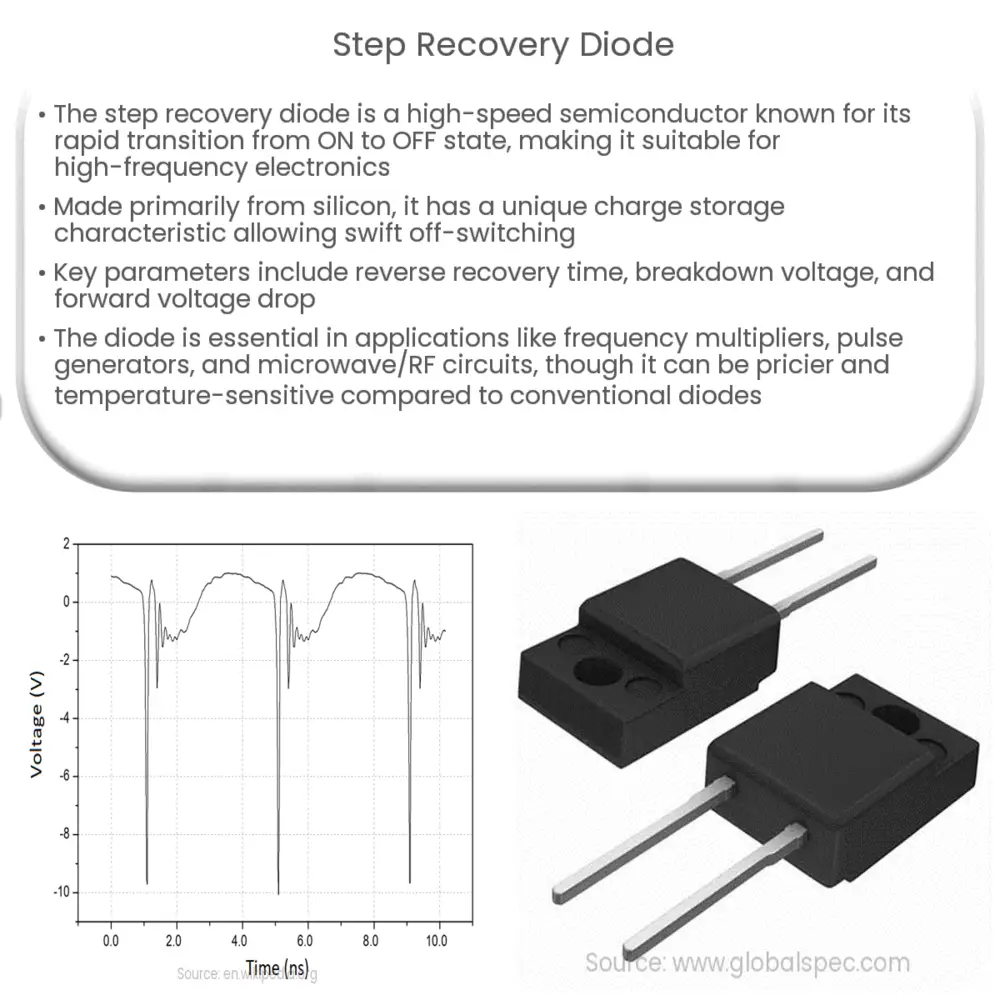
When a forward bias is applied to a step recovery diode, current flows through the device, and charge carriers (holes and electrons) accumulate at the PN junction. As the forward current continues to flow, the charge carriers form a “charge storage region” at the junction. When the diode is reverse-biased, the charge carriers in the charge storage region are removed quickly, resulting in a rapid decrease in the reverse current.
The step recovery diode’s unique characteristic is its ability to transition from the forward-biased (conducting) state to the reverse-biased (non-conducting) state with minimal delay. This rapid transition is due to the abrupt removal of charge carriers from the charge storage region when the diode is reverse-biased, causing a sudden “step” in the diode’s current-voltage (I-V) curve.
Key Specifications
Some essential parameters of step recovery diodes are:
- Reverse Recovery Time (trr): The time it takes for the diode to switch from its ON state to its OFF state. This parameter is crucial in high-frequency applications, as shorter reverse recovery times enable faster switching and higher operating frequencies.
- Breakdown Voltage (VBR): The maximum reverse voltage that can be applied to the diode without causing it to break down and conduct in the reverse direction. A higher breakdown voltage indicates a more robust device, capable of handling higher voltage levels.
- Forward Voltage Drop (VF): The voltage drop across the diode when it is in the ON state. Lower forward voltage drops result in reduced power losses and improved overall efficiency.
Applications of Step Recovery Diodes
Due to their fast-switching characteristics and unique charge storage properties, step recovery diodes find use in various applications:
- Frequency Multipliers: Step recovery diodes are widely used in frequency multiplier circuits, where an input signal is multiplied by an integer factor to produce a higher-frequency output signal. The diode’s rapid transition time allows it to generate harmonic frequencies efficiently, which can then be filtered and amplified to achieve the desired output frequency.
- Pulse Generators: The fast-switching capabilities of step recovery diodes make them suitable for generating narrow pulses in electronic circuits. They can be used to create pulse generators for time-domain reflectometry (TDR) and other high-speed applications, where precise timing and sharp pulse edges are required.
- Sampling Gates: Step recovery diodes can be employed in high-speed sampling gates to sample analog signals at specific intervals. The rapid ON to OFF transition time of the diode ensures accurate sampling of the input signal, with minimal distortion.
- Microwave and RF Applications: In microwave and radio frequency (RF) applications, step recovery diodes can be used for frequency synthesis, signal mixing, and parametric amplification. Their high-frequency performance and low capacitance make them ideal for these purposes.
Advantages and Limitations
Step recovery diodes offer several advantages, such as:
- Fast-switching capabilities, enabling high-frequency operation and rapid transition from the ON to OFF state.
- Low capacitance, which improves performance in high-frequency applications.
- Ability to generate precise pulses with minimal distortion.
However, there are also some limitations:
- Step recovery diodes are more expensive than conventional diodes due to their specialized construction and materials.
- Their performance can be sensitive to temperature variations, which may necessitate temperature compensation in some applications.
Conclusion
Step recovery diodes are high-speed semiconductor devices that offer rapid switching capabilities and unique charge storage properties. They are essential components in various applications, including frequency multipliers, pulse generators, sampling gates, and microwave and RF circuits. While their specialized construction makes them more expensive than conventional diodes, their advantages in high-frequency applications make them a valuable addition to many electronic systems.

