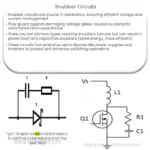
Explore the role, types, and applications of snubbers in electronics, and understand their importance in protecting circuits from transients.

Understanding Snubbers: An Essential Component
Electronic circuits are complex networks, comprising various components with diverse functionalities. One such integral component is a ‘snubber’. Snubbers are used across numerous applications, from power electronic circuits to communication systems. They play a crucial role in circuit protection, stability, and reliability.
Role of Snubbers
Snubbers, fundamentally, are energy dissipation devices or circuits. They are employed in electronic systems to safeguard other components from voltage spikes, transients, and to limit the rate of change of current and voltage (di/dt and dv/dt).
Types of Snubbers
- RC Snubber: An RC (resistor-capacitor) snubber uses a resistor (R) and capacitor (C) in series to absorb the energy from voltage spikes.
- RCD Snubber: An RCD (resistor-capacitor-diode) snubber is similar to an RC snubber, but also includes a diode. The diode ensures that the energy is absorbed only during certain conditions, making it more effective for some specific applications.
- Diode Snubber: A diode snubber uses a diode to prevent back electromotive force (EMF) from causing harm to the circuit. They’re typically found in inductive circuits, such as those with motors and relays.
Application of Snubbers
Snubbers have a wide range of applications, primarily in the field of power electronics and telecommunications. They are commonly found in switch mode power supplies (SMPS), motor drivers, and relays, where they help protect the circuit components from potentially harmful transient voltages. Other significant applications of snubbers include radio frequency (RF) power amplifiers, power grids, and semiconductor devices.
How Snubbers Work
The working principle of snubbers involves the fundamental physics of RLC circuits. During a transient event, such as a voltage spike, the snubber circuitry absorbs and dissipates the excess energy, thus protecting the rest of the circuit. Different types of snubbers, such as RC, RCD, and diode snubbers, operate on similar principles but employ different elements to achieve the desired results.
Snubbers in Real-World Applications
Let’s look at how snubbers are used in the real world. A common application is in the field of power electronics, particularly in switch mode power supplies (SMPS). During the switching operation, high-frequency voltage and current spikes can be detrimental to the solid-state switches. Snubbers are used to safeguard these switches by absorbing and dissipating the excess energy.
In telecommunications, snubbers can protect sensitive equipment from transients caused by lightning strikes or power surges. They act as a line of defense, absorbing the energy and preventing it from reaching and damaging critical parts of the system.
Design Considerations for Snubbers
While snubbers are critical to the longevity and reliability of many electronic systems, it’s important to consider several factors while incorporating them into circuit design. These include the nature and magnitude of the expected transients, the specific characteristics of the circuit elements involved, and the required performance standards of the system.
- Magnitude and Frequency of Transients: These will dictate the energy dissipation capacity required of the snubber.
- Circuit Characteristics: Different components respond differently to transient events, and so the choice of snubber type must be compatible with these components.
- Performance Standards: These define the acceptable limits of voltage and current change, thus shaping the design of the snubber.
Conclusion
In conclusion, snubbers are a vital part of electronic circuitry. Their primary function is to protect other circuit components from transient voltages and currents. By absorbing and dissipating the excess energy, they ensure the stability and reliability of electronic systems, from power supplies to telecommunications infrastructure. With a range of types available, including RC, RCD, and diode snubbers, there’s a solution to suit every application. The design and selection of snubbers require a deep understanding of circuit behavior and characteristics, making them a fascinating area of study for electronic engineers and enthusiasts alike.