Explore the workings, types, and applications of single-phase induction motors, a key component in household and industrial appliances.
Understanding the Single-Phase Induction Motor
Single-phase induction motors are one of the simplest, most robust, and reliable electric motors available, making them a popular choice for many applications. Unlike their three-phase counterparts, these motors operate on a single phase power supply, which is widely available in residential and commercial settings.
The primary principle behind the single-phase induction motor involves the generation of a rotating magnetic field. However, a single-phase power supply cannot create this rotating field directly. Instead, it creates a pulsating field, which is not sufficient to keep the motor running. Therefore, a unique mechanism is required, which is achieved through auxiliary winding or a capacitor.
Components and Working
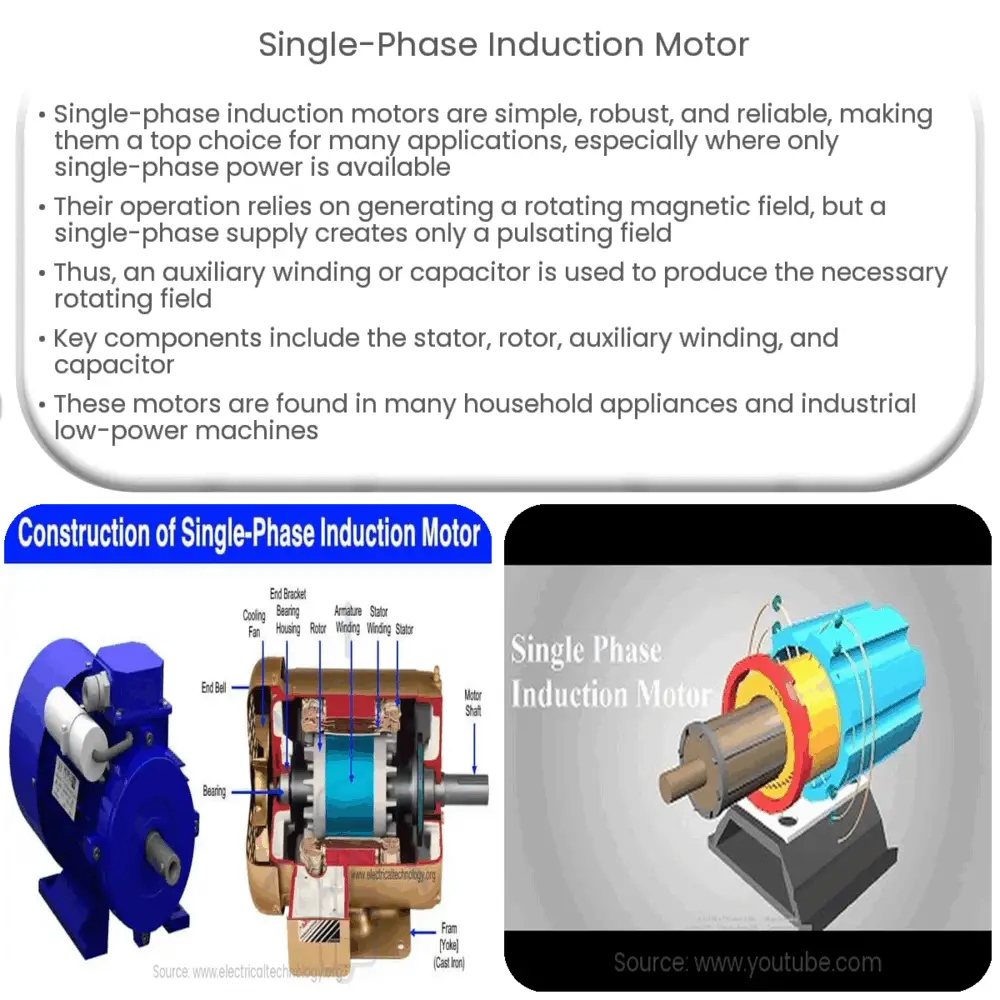
Key components of a single-phase induction motor include the stator, rotor, auxiliary winding, and capacitor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor that carries the main winding. The rotor is the rotating part, which can either be a squirrel cage or a wound type. The auxiliary winding and capacitor are responsible for creating a phase shift in the current to generate the necessary rotating magnetic field.
- Stator: The stator of a single-phase induction motor is similar to a three-phase stator, but with only one winding instead of three. This winding is placed in slots on the inner circumference of the stator. The stator core is built with high-permeability, low-loss silicon steel laminations to minimize energy loss and heat generation.
- Rotor: The rotor is typically of the squirrel cage type, made of laminated iron cores with shorted ends. The rotor bars are skewed to reduce magnetic noise and to improve the motor’s smooth operation.
Starting Mechanism
The starting mechanism of a single-phase induction motor is a crucial aspect of its operation. When the motor is switched on, the single-phase supply produces a pulsating magnetic field. However, this is not sufficient to start the motor. Instead, the auxiliary winding, usually smaller than the main winding, comes into play. The capacitor creates a phase shift, leading to the formation of a rotating magnetic field necessary to start the motor. The motor continues to run on the single-phase supply after the initial start.
Types of Single-Phase Induction Motors
Single-phase induction motors are classified into various types based on the method used to create the rotating magnetic field. The most common types include the split-phase, capacitor start, capacitor start-capacitor run, and shaded pole motors.
- Split-Phase Motors: These motors employ a resistance-start inductor-run mechanism. They have two windings – the start and run winding. The start winding has a higher resistance but lower reactance, while the run winding has a lower resistance but higher reactance. The motor disconnects the start winding from the power source once it gains momentum.
- Capacitor Start Motors: In these motors, a capacitor is connected in series with the start winding, creating a phase shift between the currents in the start and run windings. This phase shift results in a rotating magnetic field that starts the motor.
- Capacitor Start-Capacitor Run Motors: These motors have two capacitors. One capacitor is used for starting the motor, and the other is used for running the motor. This type provides better efficiency and performance.
- Shaded Pole Motors: The stator in these motors has a salient pole with a coil around it. Part of each pole is surrounded by a short-circuited, copper ring called a shading coil, creating a phase shift and hence, a rotating magnetic field.
Applications of Single-Phase Induction Motors
Single-phase induction motors are extensively used in many appliances due to their simplicity, reliability, and low cost. You can find them in refrigerators, washing machines, water pumps, fans, air-conditioners, electric clocks, drills, and other home appliances. They are also used in various industries for driving low power machines.
Conclusion
In summary, the single-phase induction motor is a critical component in many household appliances and industrial applications due to its easy operation and robustness. Despite its simplicity, the underlying principles and components involved in its operation are fascinating. These motors have proven to be an efficient solution, especially in areas where only single-phase power supply is available. Their varied types, each with unique starting mechanisms, offer a versatile range of solutions for diverse needs.

