Explore the functionality, applications, and future trends of dual voltage induction motors in this comprehensive article.
Understanding Dual Voltage Induction Motors
An induction motor, also referred to as an asynchronous motor, is a type of AC electric motor that primarily relies on electromagnetic induction to generate its working torque. A specific category within this broad range is the dual voltage induction motor, which offers versatile applications due to its distinct capability of operating at two different voltages.
Construction and Working Principle
The fundamental construction of a dual voltage induction motor is not vastly different from a standard induction motor. It consists of two primary parts: a stator and a rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor, which carries the winding where voltage is applied. The rotor, on the other hand, is the rotating part.
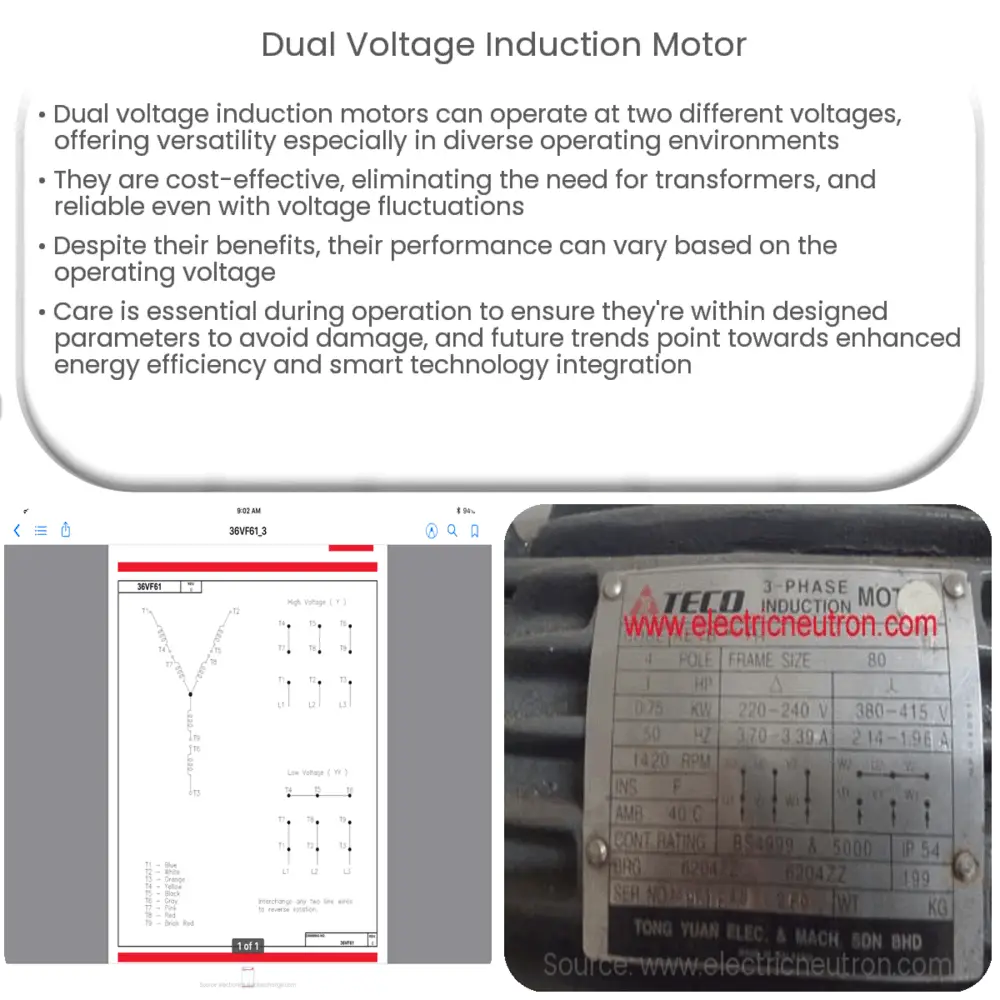
The dual voltage motor is uniquely designed with a specific winding arrangement that allows it to operate at two distinct voltages. The stator winding can be connected in parallel for low voltage operation and in series for high voltage operation. This is achieved by a switch or connector that changes the configuration of the windings.
Applications and Advantages
Dual voltage motors have a broad range of applications. These motors are highly suitable for industrial and commercial settings, where power supply voltage can vary. They are also particularly useful in scenarios where equipment is relocated to different regions with different power supply standards.
- Flexibility: The main advantage of a dual voltage motor is its versatility. It can operate at two different voltages, which provides flexibility in diverse operating environments.
- Cost-Effective: These motors reduce the need for transformers or special equipment to accommodate different voltage levels. This makes them a cost-effective choice.
- Reliability: Dual voltage motors are reliable and can operate effectively despite fluctuations in voltage supply.
Considerations and Limitations
Despite the numerous advantages, there are considerations to keep in mind when using dual voltage motors. One primary concern is that the motor’s power output is dependent on the voltage and frequency of the power supply. Therefore, the performance of the motor can vary based on the voltage it is operating at. For instance, when operating at a lower voltage, the motor will not produce the same torque as it would at a higher voltage.
Practical Implications and Precautions
While dual voltage motors offer significant flexibility and convenience, it is crucial to ensure they are operated within their designed voltage and frequency parameters. Overloading or operating the motor outside of these specified parameters can result in motor failure or damage. Hence, it is of utmost importance to correctly set the winding configuration based on the voltage of the power supply.
Connection and Installation
Connecting and installing a dual voltage motor requires a basic understanding of electrical systems and motor wiring. The motor typically comes with a wiring diagram that illustrates how to connect the windings for both low and high voltage operation. In addition, the motor’s nameplate will usually provide the necessary details for the voltage, frequency, and current ratings at both the low and high voltage configurations. Any discrepancies or uncertainties should be clarified with a qualified technician to prevent mishandling or potential damage.
Future Trends
As the world moves towards more energy-efficient and versatile industrial solutions, the demand for dual voltage motors is likely to increase. Advancements in motor design and technology promise to enhance the performance and reliability of these motors. This would further increase their applicability across various industries, from manufacturing and processing to HVAC and transportation.
- Energy Efficiency: Future design modifications aim to increase the energy efficiency of these motors, contributing to more sustainable industrial practices.
- Smart Motors: The integration of smart technologies into motor systems can provide real-time data, enhancing monitoring capabilities and predictive maintenance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dual voltage induction motors are a versatile and reliable solution in various industrial and commercial scenarios. Their ability to operate at two different voltages offers significant flexibility and cost-effectiveness. However, careful attention must be paid to their operation, ensuring they are used within their specified parameters to avoid damage or failure. With advancements in technology and design, the future of dual voltage motors is promising, with an increasing focus on energy efficiency and intelligent systems.

