Explore the world of shunt resistors: their purpose, working principle, types, applications, and selection considerations.
Introduction to Shunt Resistors
Shunt resistors, often referred to as current shunt resistors or simply shunts, are specialized resistors designed for measuring electric current. They are key components in various electrical systems and are highly appreciated for their precision and reliability. In this article, we delve into the fascinating world of shunt resistors, exploring their purpose, working principle, and applications in different fields.
The Purpose of Shunt Resistors
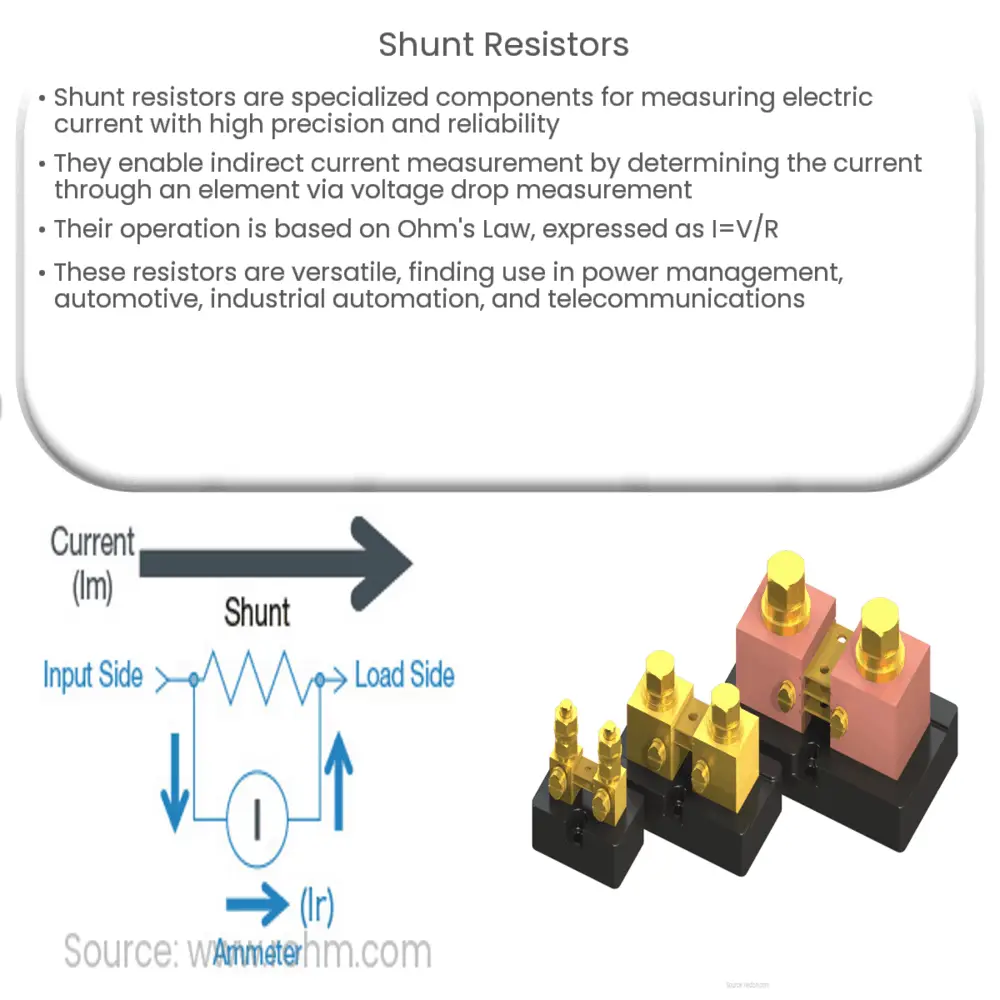
Electric current, the flow of electric charge, is a fundamental parameter in any electrical system. However, it can be challenging to measure directly. Shunt resistors solve this problem by enabling indirect current measurement. When a shunt resistor is placed in parallel with a circuit element, the current through that element can be determined by measuring the voltage drop across the shunt resistor.
Working Principle
The operation of a shunt resistor is grounded in Ohm’s Law, which states that the current (I) through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points, and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) between them. Mathematically, this relationship is expressed as I=V/R.
- I represents the current through the conductor in units of amperes.
- V denotes the voltage measured across the conductor in volts.
- R symbolizes the resistance of the conductor in ohms (Ω).
Therefore, when a known resistance (the shunt resistor) is placed in a circuit, the current flowing through it can be calculated by measuring the voltage drop across the resistor.
Types of Shunt Resistors
Shunt resistors come in various types, each designed to cater to specific requirements. The three major types are:
- Low-side shunt resistors
- High-side shunt resistors
- Four-terminal shunt resistors
Low-side shunt resistors are placed at the ground or common side of the load. They offer ease of implementation and simplicity in measurement. High-side shunt resistors are connected at the supply side, providing a more accurate current measurement, especially in systems with variable common-mode voltage. Four-terminal shunt resistors, also known as Kelvin resistors, are designed to reduce the impact of contact resistance, offering highly precise current measurement.
Applications of Shunt Resistors
Shunt resistors find usage in a wide array of applications due to their versatility and precision in current measurement. Some key applications include:
- Power Management: Shunt resistors play a vital role in power management systems, including power supplies and battery management, where they aid in monitoring and regulating the current flow.
- Automotive: In the automotive industry, shunts are used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) for battery management and power control systems.
- Industrial Automation: Industrial machinery and automation systems often use shunt resistors to ensure safety and efficiency in operations.
- Telecommunication: Shunt resistors are used in telecommunications equipment for current sensing and power management.
Considerations When Choosing Shunt Resistors
Selecting the right shunt resistor for a specific application requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Current Rating: The shunt resistor must be able to handle the maximum current it is expected to measure.
- Resistance Value: The resistance value affects the voltage drop, which in turn influences the measurement accuracy. A lower resistance results in a smaller voltage drop and less power dissipation, but may compromise accuracy.
- Power Rating: The power rating determines the maximum amount of power the shunt resistor can safely dissipate as heat.
- Temperature Coefficient: The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) indicates how much the resistance value will change with temperature, which can affect measurement accuracy.
Conclusion
Shunt resistors are indispensable components in a wide range of electrical and electronic systems, providing accurate current measurement, essential for optimal performance and safety. Their functionality, grounded in the basic principle of Ohm’s Law, and their versatility in design and application, make them a cornerstone of modern electrical engineering. As technology continues to evolve and the demand for more efficient and precise electrical systems grows, the significance of shunt resistors is set to increase even more.



