Explore the world of sensors: their types, working principles, applications in industries, role in IoT, and the promising future they hold.
Introduction to Sensors
Sensors play a fundamental role in the technological world, acting as the primary interface between the physical world and electronic systems. As crucial components in various applications, they enable devices to interact with their surroundings by converting physical phenomena into electronic signals.
Types of Sensors
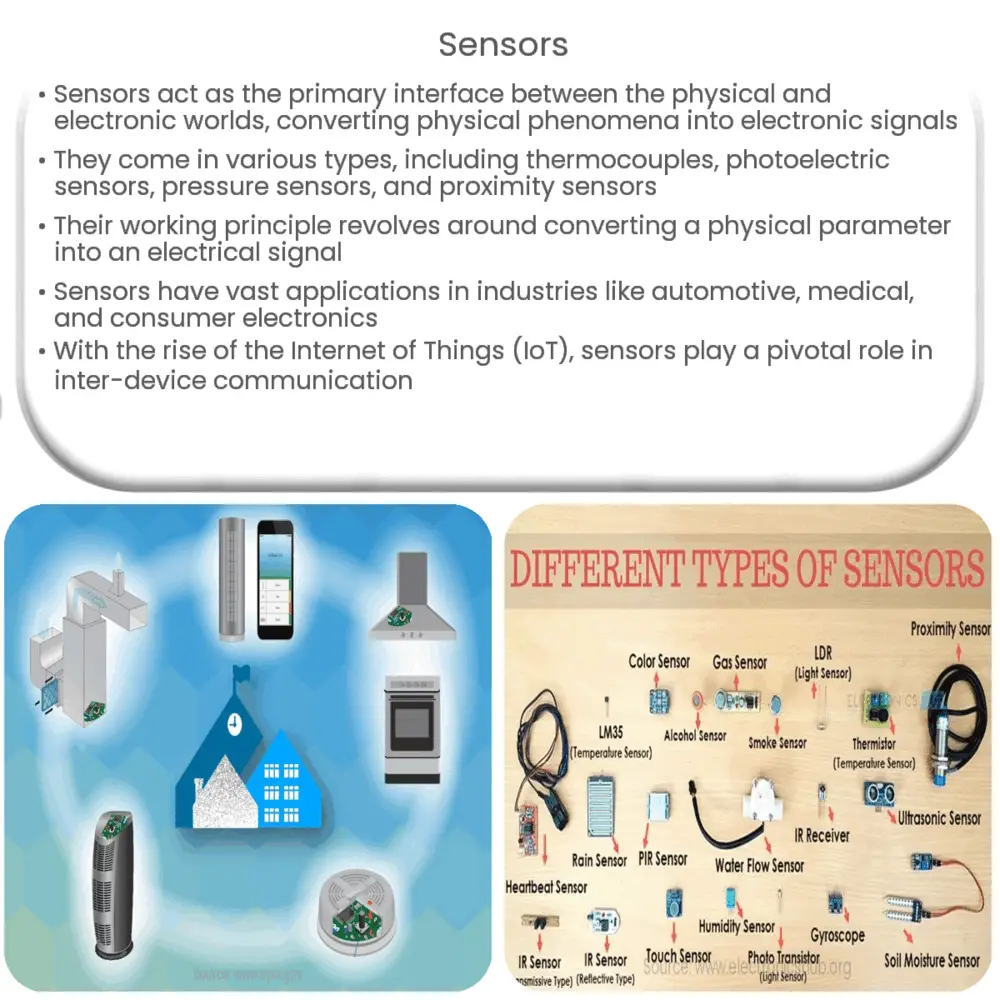
- Thermocouples: These sensors measure temperature through the variance in voltage between two different types of metal.
- Photoelectric Sensors: They convert light rays into electrical signals and are largely used in lighting systems and security devices.
- Pressure Sensors: Pressure sensors detect the force exerted on a surface and are widely used in weather instrumentation and aircraft systems.
- Proximity Sensors: These sensors detect the presence or absence of objects without physical contact. Applications include mobile phones and car parking systems.
Working Principle of Sensors
The working principle of sensors typically involves the conversion of a physical parameter into a corresponding electrical signal. The process starts with the physical phenomenon – like temperature, light, or pressure – interacting with the sensing element of the sensor. This interaction induces a change in the properties of the sensing element. The sensor’s transducer then transforms this change into an electrical signal. It’s important to note that the accuracy and precision of a sensor are critical aspects of its performance.
Applications of Sensors
Sensors have found their way into myriad applications, with their versatility and robustness being highly appreciated in diverse industries.
- Automotive Industry: Sensors are extensively used in the automotive industry, aiding in various functionalities, from fuel injection systems to anti-lock braking systems (ABS).
- Medical Field: In the healthcare sector, sensors are indispensable for equipment like digital thermometers, MRI machines, and various types of scanners.
- Consumer Electronics: Almost every consumer electronic device has some kind of sensor. They’re used in mobile phones, laptops, gaming consoles, and many more devices to enhance user interaction.
The above-listed applications merely scratch the surface of how sensors are integrated into our daily lives. Sensors are set to play an even more significant role in the future, with the advent of technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), where they will be key in enabling communication between devices.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensors
IoT represents a significant leap forward in the way we utilize sensors. The term refers to the network of interconnected devices and appliances, each embedded with sensors, that communicate and exchange data with each other. These devices could range from everyday household items, like refrigerators and thermostats, to more complex systems, like autonomous vehicles and smart factories. The sensors enable these devices to collect data about their environment, with the collected information being used to improve efficiency, safety, and convenience.
Sensor Technology and the Future
The future of sensor technology holds immense promise, with advances in nanotechnology and materials science driving the development of new, more efficient sensors. In the future, we may see sensors that can detect much finer changes in their surroundings, providing higher accuracy and precision than ever before. Furthermore, as technology advances, we can expect to see an increased integration of sensors in various areas of our lives, from environmental monitoring to personalized healthcare and beyond.
- Smart Homes: Sensors are increasingly being integrated into homes, where they can monitor temperature, humidity, and even security, making our homes safer and more comfortable.
- Environmental Monitoring: Sensors are becoming vital tools for monitoring environmental conditions, helping to track climate change and pollution levels.
- Personalized Healthcare: With the advent of wearable technology, sensors can track our health and wellbeing in real-time, allowing for personalized healthcare solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sensors are an integral part of the modern world, facilitating a seamless interaction between the physical and digital realms. With advancements in technology and an increasing demand for interconnected devices, the future of sensors is expected to be characterized by more accurate, versatile, and sophisticated devices. Whether it’s enhancing our day-to-day lives or paving the way for breakthroughs in industries like healthcare and environmental science, the possibilities with sensors are boundless, making them an essential element of our future technological landscape.

