RFID proximity sensors revolutionize asset tracking and security, offering increased efficiency, enhanced security, and real-time data for various industries.
RFID Proximity Sensors: Revolutionizing Asset Tracking and Security
Introduction
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology has come a long way since its inception in the 1940s. As a tool for tracking and identifying objects, RFID has evolved into a versatile and efficient technology that is now commonly used across a multitude of industries. One of the most innovative applications of RFID is the development of RFID proximity sensors. These sensors have transformed asset tracking and security in various sectors, from retail to logistics and beyond.
What are RFID Proximity Sensors?
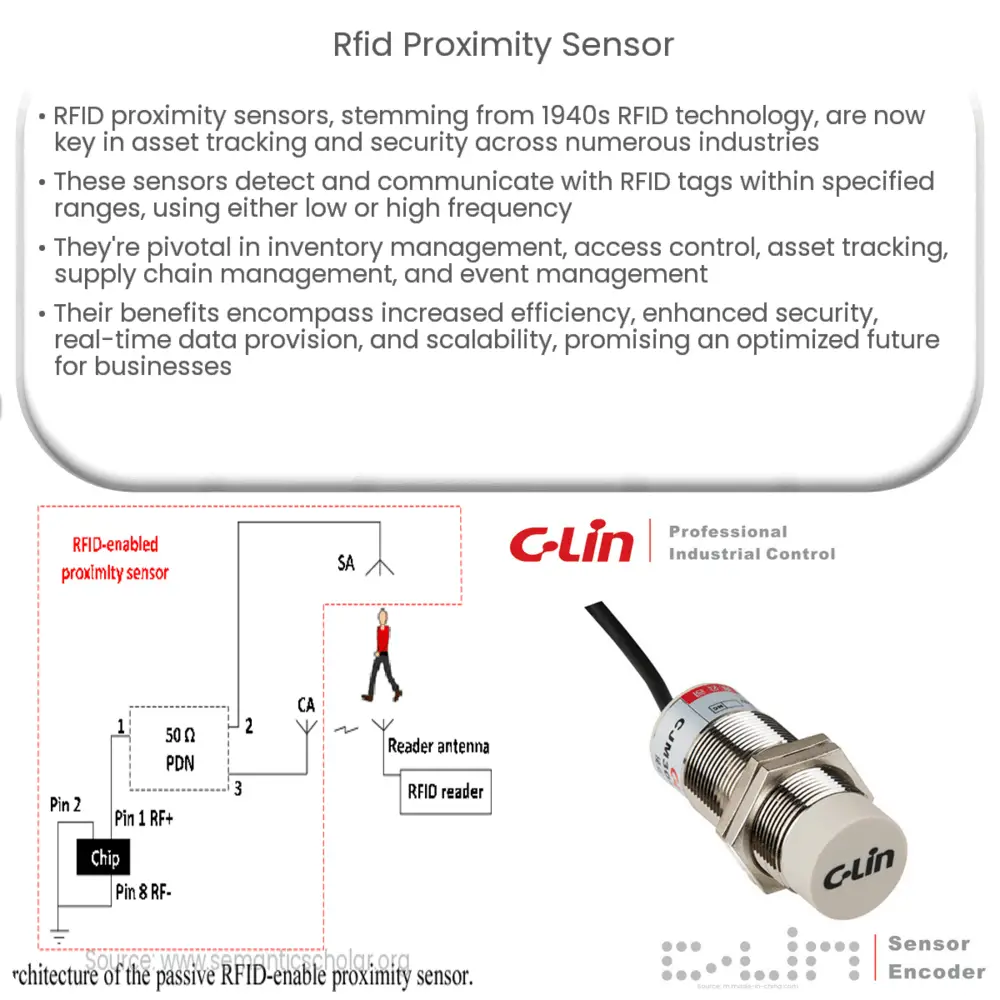
RFID proximity sensors are devices that detect and communicate with RFID tags within a certain range. The sensors are composed of an RFID reader and an antenna that emit radio frequency waves to communicate with the RFID tags. The tags, in turn, consist of a microchip and an antenna that store and transmit information. When an RFID tag comes within the specified range of an RFID proximity sensor, the sensor detects the tag, reads the information stored on it, and sends that data to a connected system.
How RFID Proximity Sensors Work
RFID proximity sensors operate using one of two frequency ranges: low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF). LF RFID proximity sensors work within a frequency range of 125 kHz to 134 kHz, while HF sensors operate within a range of 13.56 MHz. The primary difference between these two types of sensors is the read range and the type of RFID tags they can communicate with. LF RFID sensors have a shorter read range, typically up to 10 cm, and are better suited for applications that require close proximity detection. On the other hand, HF RFID sensors can detect tags from a greater distance, up to 1 meter, making them ideal for applications that require a longer detection range.
Applications of RFID Proximity Sensors
RFID proximity sensors have a wide range of applications, with asset tracking and security being two of the most prominent use cases. Some of the key applications include:
- Inventory Management: Retailers, warehouses, and other businesses can use RFID proximity sensors to track the movement of goods and monitor inventory levels. The sensors can be installed at various points within a facility to automatically detect and update the location of RFID-tagged items.
- Access Control: RFID proximity sensors can be used to control access to secure areas, such as office buildings, laboratories, or data centers. By requiring an RFID-tagged ID card or key fob to be presented within range of the sensor, authorized personnel can gain entry while keeping unauthorized individuals out.
- Asset Tracking: Companies can use RFID proximity sensors to track valuable assets, such as equipment, tools, or vehicles, throughout their facilities. By attaching RFID tags to these assets and installing sensors in strategic locations, businesses can monitor the movement and usage of their assets, helping to prevent theft and improve resource allocation.
- Supply Chain Management: RFID proximity sensors can be used to enhance visibility and control over goods moving through the supply chain. By tracking the movement of RFID-tagged products from manufacturing to distribution centers and retail outlets, businesses can gain real-time insights into their supply chain, enabling them to optimize processes and reduce operational costs.
- Event Management: Event organizers can use RFID proximity sensors to monitor attendee movement and manage access to specific areas within an event venue. By providing RFID-tagged wristbands or badges to attendees, event organizers can track attendance, control access to restricted areas, and gather valuable data to improve future events.
Benefits of RFID Proximity Sensors
Implementing RFID proximity sensors offers numerous benefits for businesses and organizations, including:
- Increased Efficiency: RFID proximity sensors automate the process of tracking and identifying items, reducing manual labor and human error. This increased efficiency can result in significant cost savings and improved productivity.
- Enhanced Security: By controlling access to secure areas and tracking valuable assets, RFID proximity sensors help prevent unauthorized access, theft, and tampering, ultimately enhancing the security of a facility or event.
- Real-time Data: RFID proximity sensors provide real-time data on the movement and location of tagged items, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and respond quickly to changing circumstances.
- Scalability: RFID proximity sensor systems can easily be expanded or reconfigured to accommodate changes in business needs, such as adding new sensors, increasing the detection range, or updating the information stored on RFID tags.
Conclusion
RFID proximity sensors have revolutionized asset tracking and security in a variety of industries, offering increased efficiency, enhanced security, and valuable real-time data. As the technology continues to evolve and improve, it is likely that RFID proximity sensors will become an even more integral part of modern business operations, helping organizations to streamline processes and optimize resources for a more efficient and secure future.

