Explore the world of resistors, their types, operation principles, and vital role in electronics, from basic circuits to modern devices.
Understanding Resistors: The Unsung Heroes of Electronics
Resistors, a vital component in electronic circuits, are passive two-terminal electrical devices that apply resistance to the flow of electric current. They’re arguably the most widely used electronic components, playing a crucial role in controlling and regulating current flow. This article delves into the intricacies of resistors, their types, and their applications in electronic circuitry.
Principles of Operation
At its core, a resistor operates on Ohm’s Law, a fundamental principle in electricity and electronics. This law, stated as V = I * R where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance, governs how resistors function in a circuit. The resistor’s main job is to regulate the current and voltage levels within a circuit by providing a specified resistance.
Types of Resistors
Resistors come in numerous forms, each designed for a specific application or environment. The two major types are:
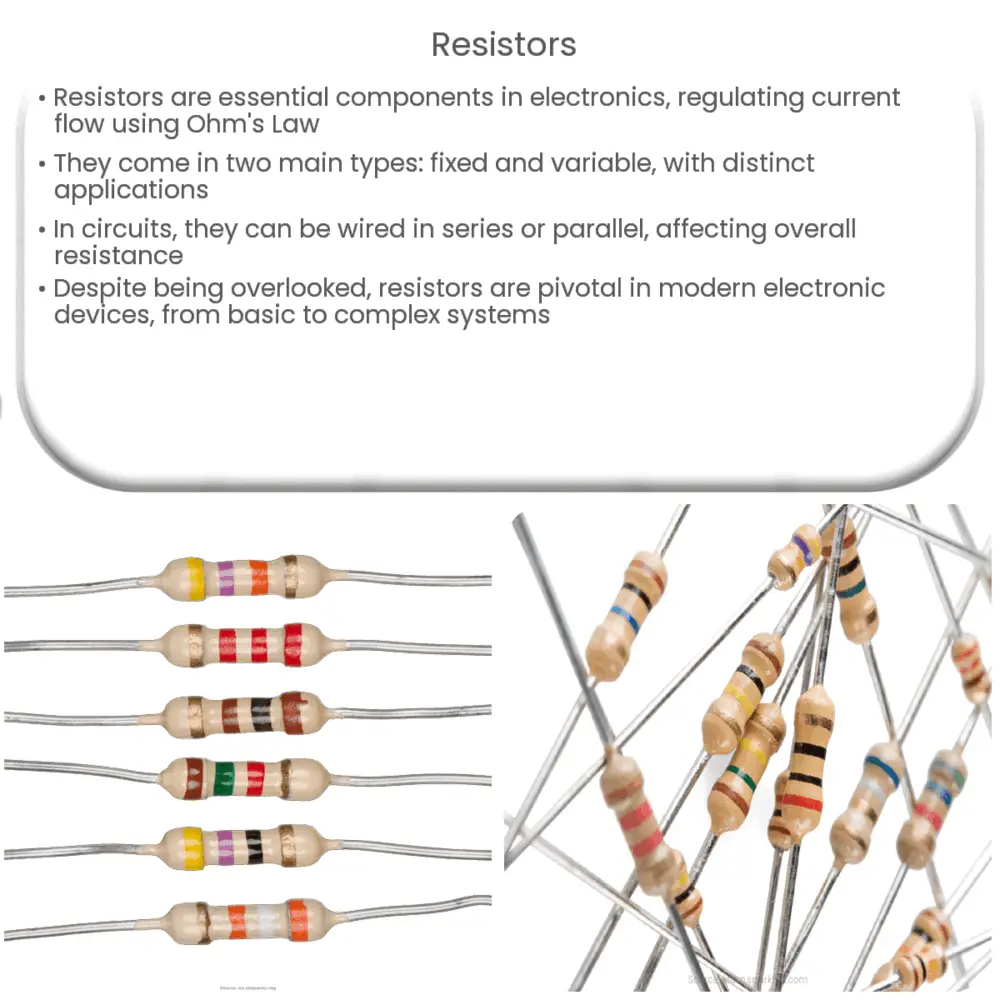
- Fixed Resistors: These are resistors with a fixed resistance value. They are the most common type of resistor and come in many varieties such as carbon composition, metal film, and wirewound resistors.
- Variable Resistors: These are resistors whose resistance value can be adjusted. This group includes potentiometers and rheostats, often used for tuning and calibration in electronic circuits.
Resistors in a Circuit
Resistors can be wired in two primary ways within a circuit: series and parallel configurations. In a series circuit, the total resistance (RTOT) is simply the sum of all individual resistances. In a parallel circuit, the reciprocal of the total resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of each individual resistance. These configurations enable fine-tuning of the overall resistance in a circuit, thereby controlling the current flow more accurately.
Color Coding and Ohmic Values
Resistors often come with color bands on their bodies to denote their resistance values. This color coding system uses a standard set of colors to represent numbers, which when translated using a color chart, reveal the resistor’s resistance value, tolerance, and sometimes its reliability or failure rate. This allows users to identify the resistance value at a glance without needing to measure it.
Applications of Resistors
Resistors are ubiquitous in electronic circuits, serving a variety of functions based on their inherent properties. Here are some of their main applications:
- Current Limiting: Resistors are commonly used to limit the current flowing to other components in a circuit to prevent them from damage.
- Voltage Division: A series of resistors can be used to divide voltage into predictable amounts in a circuit, a function essential in many electronic devices.
- Heat Generation: Certain types of resistors, like heating elements and filament bulbs, utilize the heat dissipation property of resistors.
- Signal Conditioning: Resistors play a crucial role in signal conditioning, such as filtering and attenuation, to ensure proper signal integrity.
Resistors in Modern Electronics
With the advent of miniaturized electronics, surface-mount technology (SMT) resistors have become commonplace. These tiny components are designed for automated assembly and are soldered directly onto printed circuit boards. SMT resistors are an integral part of modern electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and sophisticated medical equipment.
The Impact of Resistors
While often overlooked, resistors play a significant role in our technologically driven lives. From the simplest flashlight to the most complex supercomputer, the humble resistor is a key player, ensuring electronic devices function correctly and reliably.
Conclusion
Resistors are foundational elements in the field of electronics. They implement the principles of Ohm’s Law in practical applications, allowing us to control and manage the flow of electricity in our devices. From fixed and variable types to their role in current limiting, voltage division, and signal conditioning, resistors significantly influence the design and functionality of electronic circuits. Their presence in the miniature world of surface-mount technology exemplifies their importance in the modern electronics era. Whether we recognize it or not, our technologically enriched lives owe much to these humble, yet powerful components – the resistors.

