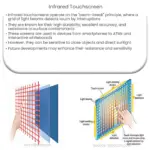
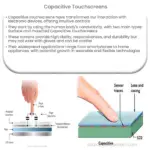
Explore the workings, types, advantages, and applications of resistive touchscreens in our comprehensive guide.
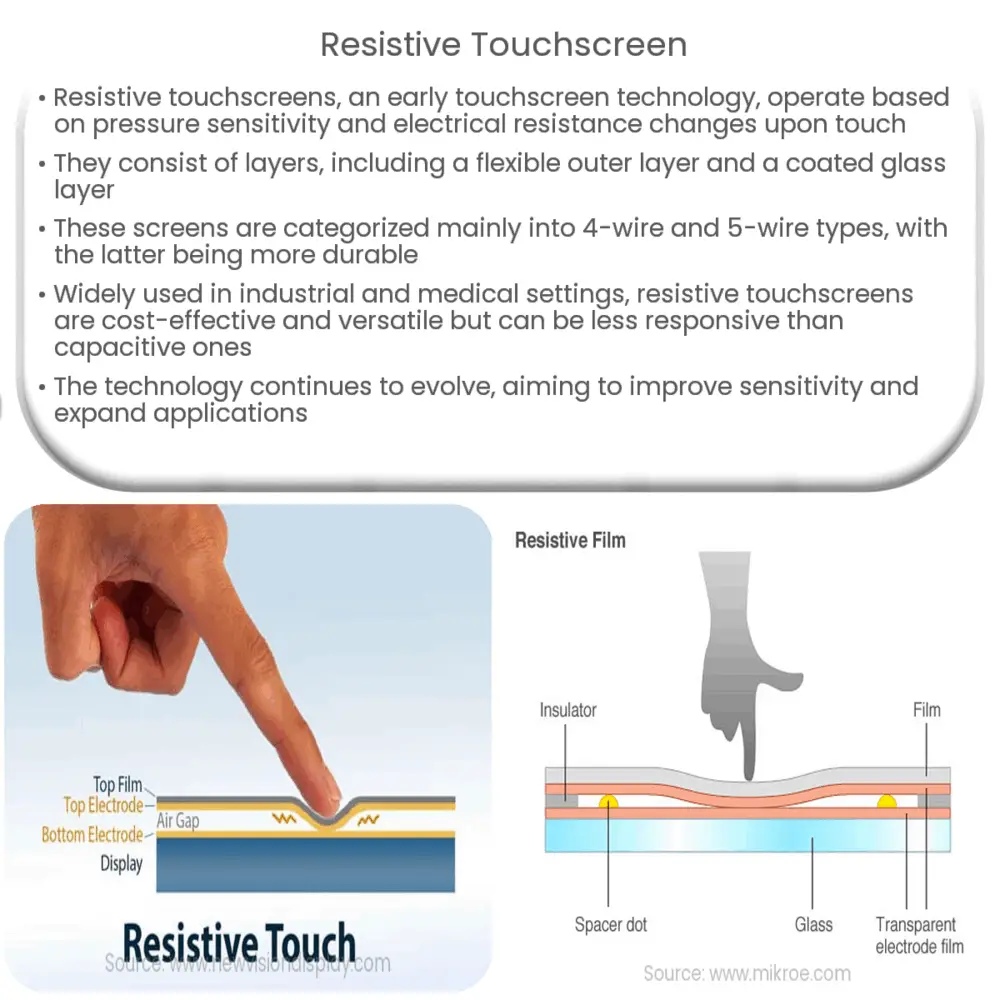
Introduction to Resistive Touchscreen Technology
Touchscreen technology has rapidly advanced in the past few decades, enhancing user experiences in various devices ranging from mobile phones to interactive kiosks. One of the earliest and most widely used forms of this technology is the resistive touchscreen. Despite the advent of more advanced touchscreen types like capacitive and infrared, resistive touchscreens still have their unique niche due to their distinctive features and benefits.
Understanding the Basics
The fundamental principle of resistive touchscreens is pressure sensitivity. They operate based on the electrical resistance changes that occur when the screen is touched. This is made possible by several layers that compose the resistive touchscreen.
- Outermost Layer: This is typically a flexible plastic layer that users interact with directly.
- Spacer Dots: These are non-conductive dots that separate the outermost layer from the next layer.
- Coated Glass Layer: This is a rigid layer coated with a transparent, resistive material.
These layers create a voltage gradient across the screen by applying a small voltage across one of the layers. When a user touches the screen, the layers come into contact at that point, which changes the resistance and, consequently, the voltage. The device then identifies the touch location based on this voltage change.
Resistive Touchscreen Types
Resistive touchscreens are generally categorized into two main types:
- 4-Wire Resistive: This is the simplest and most common type of resistive touchscreen. It uses only four interface wires: two for the X-axis and two for the Y-axis.
- 5-Wire Resistive: This is a more durable and accurate version that uses five interface wires. The extra wire is used to continuously monitor the voltage of the top layer, providing more accurate readings and longer lifespan.
Each type has its strengths and weaknesses, which influence the choice of touchscreen for different applications.
Applications of Resistive Touchscreens
Resistive touchscreens are widely used due to their durability, cost-effectiveness, and ability to work with various input methods. They are commonly found in point-of-sale systems, medical devices, and industrial control panels.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Resistive Touchscreens
Like any technology, resistive touchscreens come with a unique set of advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Resistive touchscreens are typically cheaper to produce than capacitive touchscreens, making them an affordable choice for many applications.
- Versatile Input: Unlike capacitive touchscreens, resistive touchscreens can respond to any object, including a stylus, gloved hand, or fingertip, making them useful in various environments.
- Durability: Resistive screens, especially the 5-wire type, are durable and can withstand harsh conditions, which is why they are favored in industrial and medical settings.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower Clarity: The additional layers in resistive touchscreens can reduce the screen’s clarity and brightness compared to capacitive touchscreens.
- Less Responsive: They require more pressure to register a touch and generally don’t support multi-touch, which can affect the user experience.
The Future of Resistive Touchscreens
While capacitive touchscreens have become the norm for consumer electronics due to their superior sensitivity and support for multi-touch gestures, resistive touchscreens still hold a firm place in specific sectors. The ongoing development in resistive touchscreen technology aims to enhance their sensitivity and multi-touch capabilities, potentially expanding their range of applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, resistive touchscreen technology is a robust and versatile input method that has significantly contributed to the development of interactive devices. Although it faces competition from newer technologies, its unique advantages ensure it remains relevant and widely used. The future of resistive touchscreens seems to be evolving, with potential advancements on the horizon that could enhance their capabilities and applications. Regardless of the advent of new technologies, resistive touchscreens will continue to play a crucial role in the touchscreen ecosystem.