Explore the workings of reed switches, their types, advantages, applications across industries, limitations, and importance in modern technology.
Understanding Reed Switches
A reed switch is an electrical switch that is operated by an applied magnetic field. Designed by Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1936, this unique device plays an integral role in a wide range of appliances and systems, from simple household items to complex industrial machinery.
Components of a Reed Switch
A reed switch primarily consists of two or three thin metal reeds, sealed within a glass envelope, creating an airtight space to prevent any degradation of the switch’s performance due to environmental factors.
-
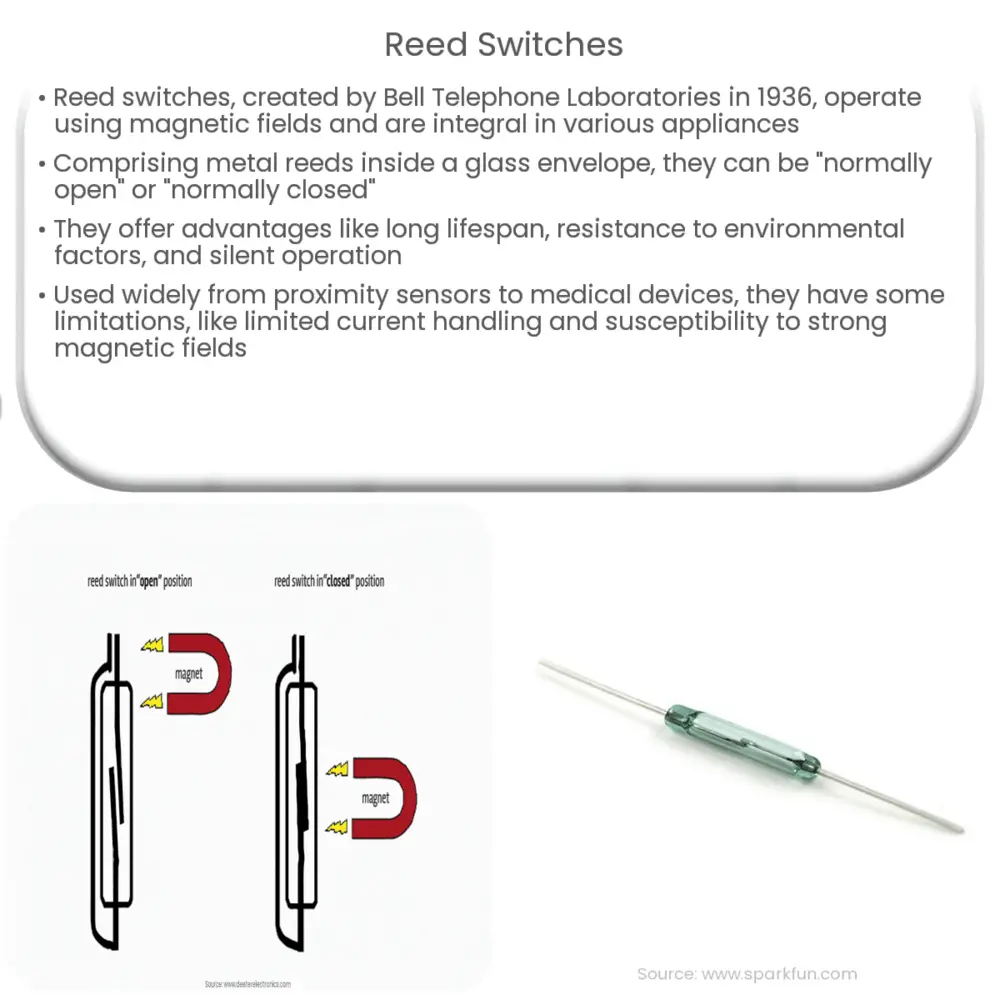
The reed blades are typically made from a ferromagnetic material. They act as both magnetic and electrical contacts. When a magnetic field is applied, the reeds magnetize and move towards each other, closing the switch.
-
The glass envelope encapsulates the reed blades, shielding them from external contaminants. It also has an almost perfect vacuum or is filled with an inert gas to enhance switch reliability.
Types of Reed Switches
There are generally two types of reed switches: normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC).
-
Normally Open (NO): In a NO reed switch, the reed contacts are usually open until a magnetic field is applied, which pulls them together and closes the switch, allowing current to pass through.
-
Normally Closed (NC): An NC reed switch operates oppositely. The contacts are usually closed, allowing current to pass. When a magnetic field is applied, it forces the contacts apart, breaking the circuit.
Advantages of Reed Switches
Reed switches offer several advantages over traditional mechanical switches. They operate without any physical contact between components, resulting in low wear and tear and a significantly longer lifespan. Additionally, the sealed design of the switch provides excellent resistance against environmental factors such as moisture and dust. Their operation is silent, and they can be made extremely small, making them ideal for applications where size is a constraint.
Applications of Reed Switches
Given their unique properties and benefits, reed switches find use in a plethora of applications across different industries.
-
Proximity Sensing: Reed switches are frequently used in proximity sensors due to their ability to function without direct contact. They detect the presence of a magnetic field, often integrated into doors and windows for security alarm systems.
-
Telecommunications: In telecommunications, reed switches are used in telephone exchanges, signaling, and other communication devices.
-
Automotive Industry: These switches are vital in various automotive applications, such as speed sensors, fluid level indicators, and gear position sensors.
-
Medical Devices: Reed switches are also used in medical equipment, such as infusion pumps and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their many advantages, reed switches have some limitations. They have a limited switching capacity and can’t handle high currents or voltages. Exposure to strong magnetic fields can also cause the reeds to stick together. Lastly, while they are generally reliable, reed switches can fail due to mechanical shock or if subjected to many frequent operating cycles. Therefore, careful consideration should be taken when deciding to use reed switches in any design.
Conclusion
In conclusion, reed switches are an essential component in many of today’s devices and applications, thanks to their unique operating principle and the advantages they offer. Despite some limitations, they continue to be a reliable and efficient choice for a variety of applications, from security systems to medical devices. The understanding of reed switches and their effective integration into systems is vital for engineers and designers in various fields. As technology advances, the utilization of reed switches is likely to evolve, providing new opportunities and applications.

