Radar level sensors provide accurate, non-contact level measurements for liquids and solids in various industries, handling challenging environments.
Radar Level Sensor: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Radar level sensors, also known as radar level transmitters, are cutting-edge devices that provide reliable and accurate measurements of liquid and solid levels in various industries. These sensors have rapidly become the preferred choice for level measurement due to their non-contact nature, immunity to environmental conditions, and ability to perform in challenging scenarios. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of radar level sensors, their working principles, types, and applications across industries.
Working Principle of Radar Level Sensors
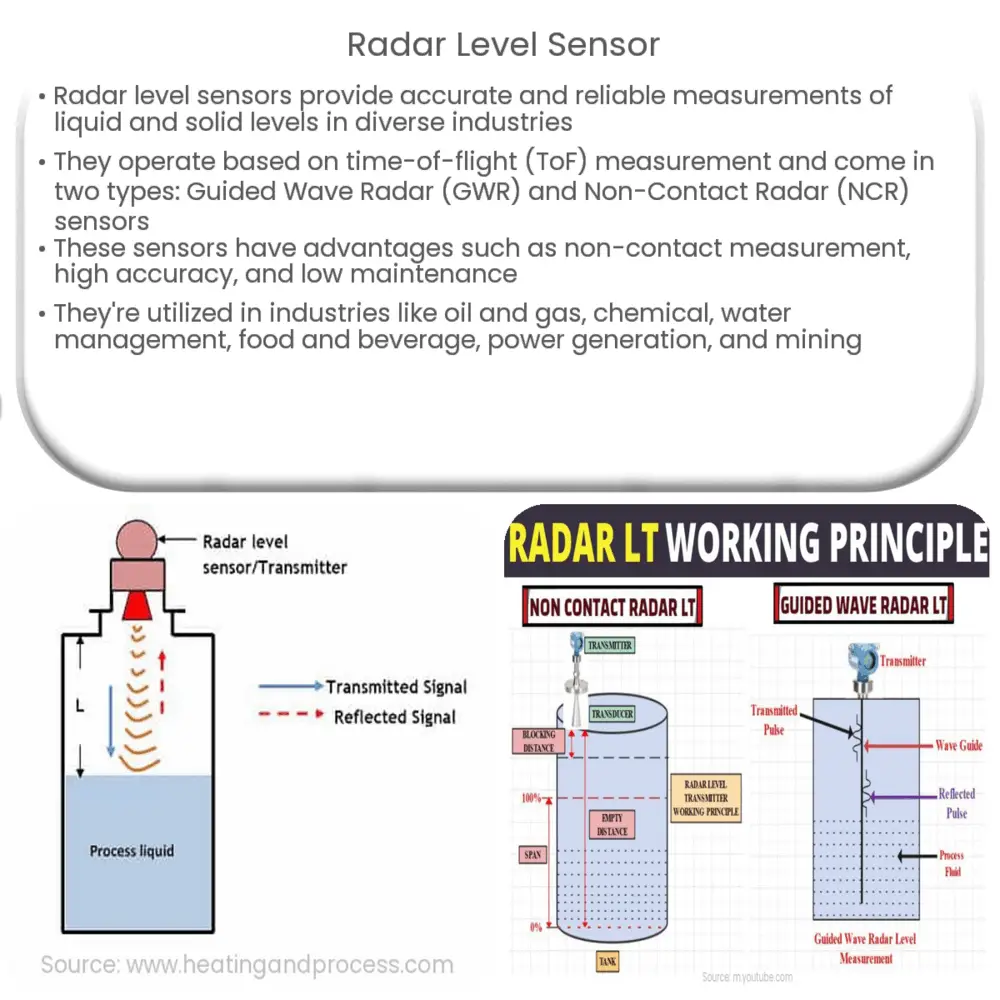
Radar level sensors operate on the principle of time-of-flight (ToF) measurement. They emit electromagnetic waves towards the surface of the material being measured, which then reflect back to the sensor. The time taken for the waves to travel to the surface and back is directly proportional to the distance between the sensor and the material surface. By calculating the time difference and knowing the speed of light, the sensor can accurately determine the level of the substance.
These sensors can be designed to work at different frequency ranges, depending on the specific application requirements. The most common frequency ranges for radar level sensors are:
- Low-frequency radar: 6 GHz to 10 GHz
- High-frequency radar: 24 GHz to 26 GHz
- Ultra-high-frequency radar: 77 GHz to 79 GHz
Types of Radar Level Sensors
Radar level sensors can be broadly classified into two types based on their technology:
1. Guided Wave Radar (GWR) Level Sensors
Guided Wave Radar level sensors utilize a probe, also known as a waveguide, that is immersed in the process material. The electromagnetic waves emitted by the sensor travel along the probe and are reflected by the material surface back to the sensor. GWR sensors are suitable for a wide range of applications, including those with high temperatures, pressures, and varying material characteristics. These sensors can measure both liquid and solid levels with high accuracy and reliability.
2. Non-Contact Radar (NCR) Level Sensors
Non-Contact Radar level sensors, also known as free-space radar sensors, do not require a waveguide or direct contact with the material being measured. The electromagnetic waves are emitted directly towards the material surface and are reflected back to the sensor. NCR sensors are ideal for applications where contact with the process material is not desired or possible, such as corrosive, toxic, or volatile substances. They can also handle a wide range of process conditions, including turbulence, foam, and vapors.
Key Advantages of Radar Level Sensors
Radar level sensors offer several benefits compared to traditional level measurement technologies, such as ultrasonic, capacitive, or hydrostatic sensors. Some of the key advantages include:
- Non-contact measurement: Radar level sensors do not require contact with the process material, reducing the risk of contamination and corrosion.
- High accuracy: Radar level sensors provide highly accurate level measurements, typically within a few millimeters.
- Wide measurement range: These sensors can measure levels over a wide range of distances, from a few centimeters to several hundred meters.
- Unaffected by environmental conditions: Radar level sensors can perform reliably in various environmental conditions, including dust, humidity, temperature changes, and vapors.
- Low maintenance: Due to their non-contact nature and robust design, radar
level sensors require minimal maintenance, making them cost-effective in the long run. - Easy integration: These sensors can be easily integrated with various communication protocols, such as HART, Modbus, and Profibus, for seamless communication with control systems.
Applications of Radar Level Sensors
Radar level sensors have a wide range of applications across various industries, including:
1. Oil and Gas Industry
In the oil and gas industry, radar level sensors are used for level measurements in storage tanks, separators, and other process vessels. They provide accurate and reliable measurements in challenging conditions, such as high temperatures, pressures, and the presence of corrosive and volatile substances.
2. Chemical Industry
Radar level sensors are extensively used in the chemical industry to measure levels of various chemicals in storage tanks, reactors, and other process equipment. Their non-contact nature and ability to handle corrosive materials make them ideal for this industry.
3. Water and Wastewater Management
These sensors are widely used for level measurement in water treatment plants, sewage treatment facilities, and pumping stations. They provide accurate level measurements in various conditions, such as turbulent water surfaces, foam, and vapor, ensuring efficient water management.
4. Food and Beverage Industry
Radar level sensors are employed in the food and beverage industry for level measurement of various liquids, such as milk, juice, and beer. Their non-contact nature ensures hygienic measurements and reduces the risk of contamination.
5. Power Generation
In the power generation sector, these sensors are used for level measurement in boilers, steam drums, and feedwater tanks. They provide accurate measurements in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, ensuring safe and efficient operation of power plants.
6. Mining and Bulk Solids Handling
Radar level sensors are also used for level measurement of bulk solids, such as coal, cement, and grains, in silos, hoppers, and other storage vessels. Their ability to perform in dusty environments and provide accurate measurements of uneven surfaces makes them ideal for this application.
Conclusion
Radar level sensors have revolutionized the level measurement industry with their numerous advantages and wide range of applications. Their high accuracy, non-contact nature, and ability to handle challenging environments make them the preferred choice for level measurement across various industries. By understanding the working principles, types, and applications of radar level sensors, businesses can make informed decisions and select the best-suited sensor for their specific needs.

