Explore the workings, advantages, and applications of Projected Capacitive Touchscreen technology that’s revolutionizing device interaction.
Understanding Projected Capacitive Touchscreen
Projected Capacitive Touchscreen (PCT) is a cutting-edge technology that has transformed the way we interact with digital devices. This type of touch technology can be found in smartphones, tablets, and many other devices, making them more user-friendly and intuitive to use.
Working Principle of Projected Capacitive Touchscreen
Projected Capacitive Touchscreen technology operates on the principle of capacitance. This is an electrical property that allows for the storage of energy in an electric field. The screen is embedded with a grid of tiny, transparent electrodes. When a finger comes into contact with the screen, it alters the electrostatic field and changes the capacitance at that point. This change is detected by the system, which then calculates the coordinates of the touch.
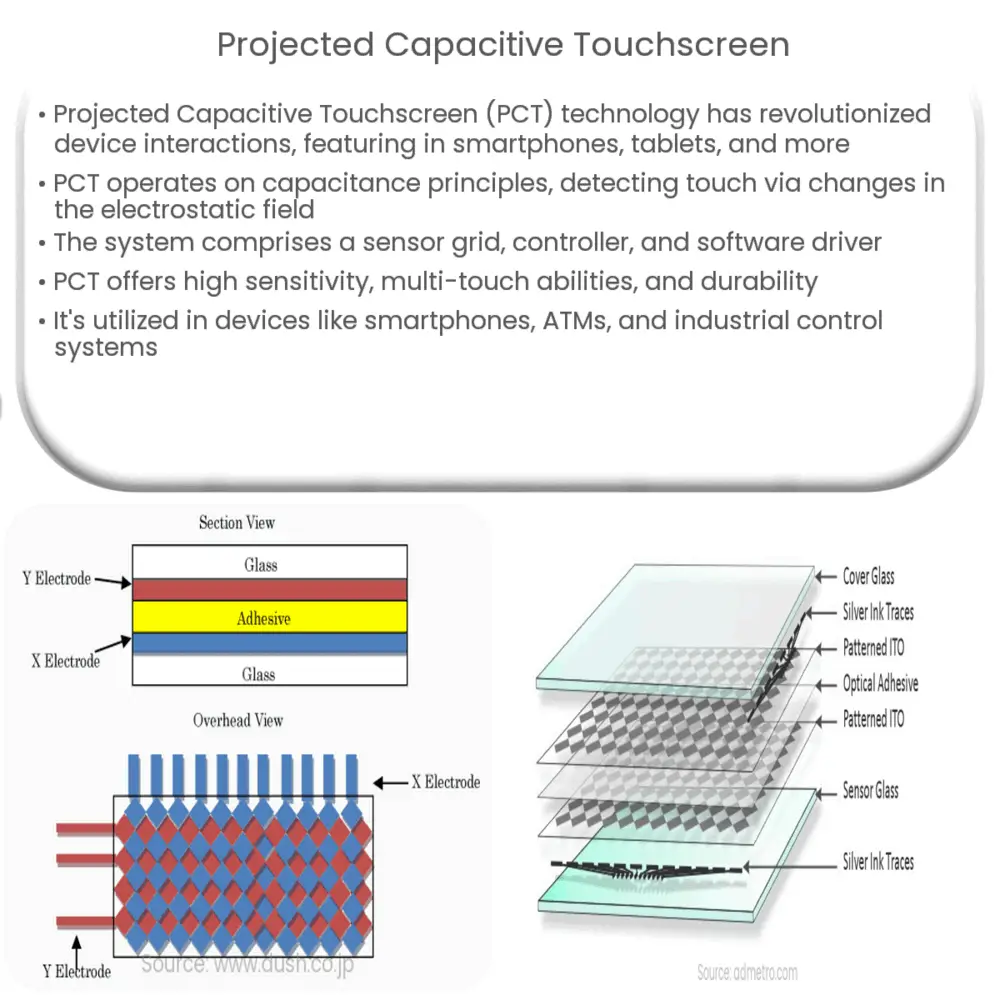
Components of Projected Capacitive Touchscreen
- Sensor Grid: The sensor grid is composed of microscopic capacitors arranged in rows and columns. This grid detects changes in capacitance when a finger or conductive stylus comes into contact with the screen.
- Controller: The controller is an electronic component that processes the signal from the sensor grid. It interprets the change in capacitance to determine the precise location of the touch.
- Software Driver: This software communicates the touch event information to the operating system or application. It translates the touch coordinates into a language that the device’s operating system can understand.
Types of Projected Capacitive Touchscreen
The two main types of PCT technology are Self-Capacitance and Mutual Capacitance.
- Self-Capacitance: In this type, each point on the grid operates independently, registering its own state of capacitance. This allows for the detection of multiple touch points at the same time, but it lacks the precision of mutual capacitance.
- Mutual Capacitance: In mutual capacitance, each point on the grid is dependent on the others. This allows for a more precise determination of touch location, but it’s less capable of multi-touch detection.
Both types of PCT offer their own unique advantages and are chosen based on the specific requirements of the application.
Advantages of Projected Capacitive Touchscreens
Projected Capacitive Touchscreens are a popular choice due to their various advantages. These include:
- High Sensitivity: PCT screens can detect a touch even without direct contact, making them ideal for use with gloves or a stylus.
- Multi-Touch Capability: PCT screens can detect multiple touches simultaneously, allowing for complex gestures and interactions.
- Durability: As the components are sealed behind a layer of glass, PCT screens are resistant to dust, water, and scratches, making them suitable for use in harsh conditions.
Applications of Projected Capacitive Touchscreens
PCT technology is versatile and can be found in a wide range of applications. This includes:
- Smartphones and Tablets: The majority of modern smartphones and tablets utilize PCT technology due to its sensitivity and multi-touch capabilities.
- ATMs and Information Kiosks: Its durability and ease of use make PCT a preferred choice for public touch screen interfaces like ATMs and information kiosks.
- Industrial Control Systems: The ruggedness of PCT screens makes them ideal for industrial control systems that require reliable operation in harsh conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of Projected Capacitive Touchscreen technology has revolutionized the way we interact with our devices. From smartphones to tablets, ATMs, and industrial control systems, PCT has made our interactions more intuitive and efficient. Its unique advantages, such as high sensitivity, multi-touch capability, and durability, have made it a popular choice in a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect PCT to play an even more significant role in shaping our digital experiences.



