Explore the population inversion formula, its factors, applications in lasers, quantum computing & spectroscopy, with a calculation example.
Understanding Population Inversion Formula
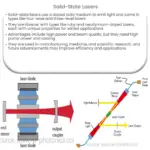
Population inversion is a crucial concept in laser physics and quantum mechanics, describing the scenario in which the number of atoms in a higher energy state exceeds the number in a lower energy state. This phenomenon is essential for the amplification of light in lasers, as it allows for stimulated emission to dominate over absorption. In this article, we will explore the population inversion formula and its significance in various fields.
The Population Inversion Formula
The population inversion formula quantifies the difference between the populations of two energy levels in a given medium. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
ΔN = N2 – N1
Where:
- ΔN is the population inversion;
- N2 is the number of atoms in the higher energy state;
- N1 is the number of atoms in the lower energy state.
When ΔN is positive, population inversion is achieved, allowing for the occurrence of stimulated emission and the generation of coherent light in laser systems.
Factors Influencing Population Inversion
Various factors can affect the population inversion between energy levels. Some of these factors include:
- Pumping Mechanism: The process by which energy is supplied to the system plays a critical role in achieving population inversion. Different pumping mechanisms, such as optical, electrical, or chemical, can be employed to achieve the desired effect.
- Energy Levels: The energy gap between the levels involved in the inversion process is significant in determining the likelihood of achieving population inversion. Generally, a larger energy gap requires a more efficient pumping mechanism to maintain the inversion.
- Decay Rates: The decay rates of the involved energy states impact the population inversion. If the decay rate of the higher energy state is much slower than the lower energy state, maintaining a population inversion becomes easier.
Applications of Population Inversion
Population inversion is a fundamental concept with numerous applications in various fields, such as:
- Laser Technology: Lasers rely on the population inversion phenomenon to generate a coherent and amplified light beam through stimulated emission.
- Quantum Computing: In quantum computing, population inversion plays a crucial role in the manipulation and control of quantum bits (qubits), which are the fundamental units of information in quantum computers.
- Spectroscopy: Population inversion is also relevant in certain spectroscopy techniques, such as saturation absorption spectroscopy, where it can be used to study the properties and interactions of atoms and molecules.
In conclusion, the population inversion formula is a simple yet essential equation that describes the conditions necessary for achieving population inversion in a given system. Understanding this formula and its implications is crucial for various scientific and technological applications, including laser technology, quantum computing, and spectroscopy.
Example of Population Inversion Calculation
Let’s consider a hypothetical two-level system where we want to calculate the population inversion. We’ll provide the number of atoms in both the higher and lower energy states.
Suppose we have:
- N2 = 700 atoms in the higher energy state;
- N1 = 300 atoms in the lower energy state.
Using the population inversion formula:
ΔN = N2 – N1
We can plug in the values:
ΔN = 700 – 300
Calculating the population inversion, we get:
ΔN = 400
In this example, the population inversion is positive (ΔN = 400), indicating that the higher energy state has more atoms than the lower energy state. This condition is necessary for stimulated emission and the generation of coherent light in laser systems.