A polarized relay is an electromagnetic device sensitive to current direction, used for precise control in various applications like automation, telecommunications, and automotive systems.
Polarized Relay: An Introduction to the Technology and Its Applications
As we continue to witness the rapid evolution of technology, one specific development that has been gaining significant attention is the polarized relay. This electrical device is designed to control a circuit by using a low-power signal to switch a high-power circuit on or off. It has a variety of applications, ranging from industrial automation to consumer electronics. In this article, we will delve into the basics of polarized relays, their working principles, and their practical applications.
Understanding the Basics of Polarized Relays
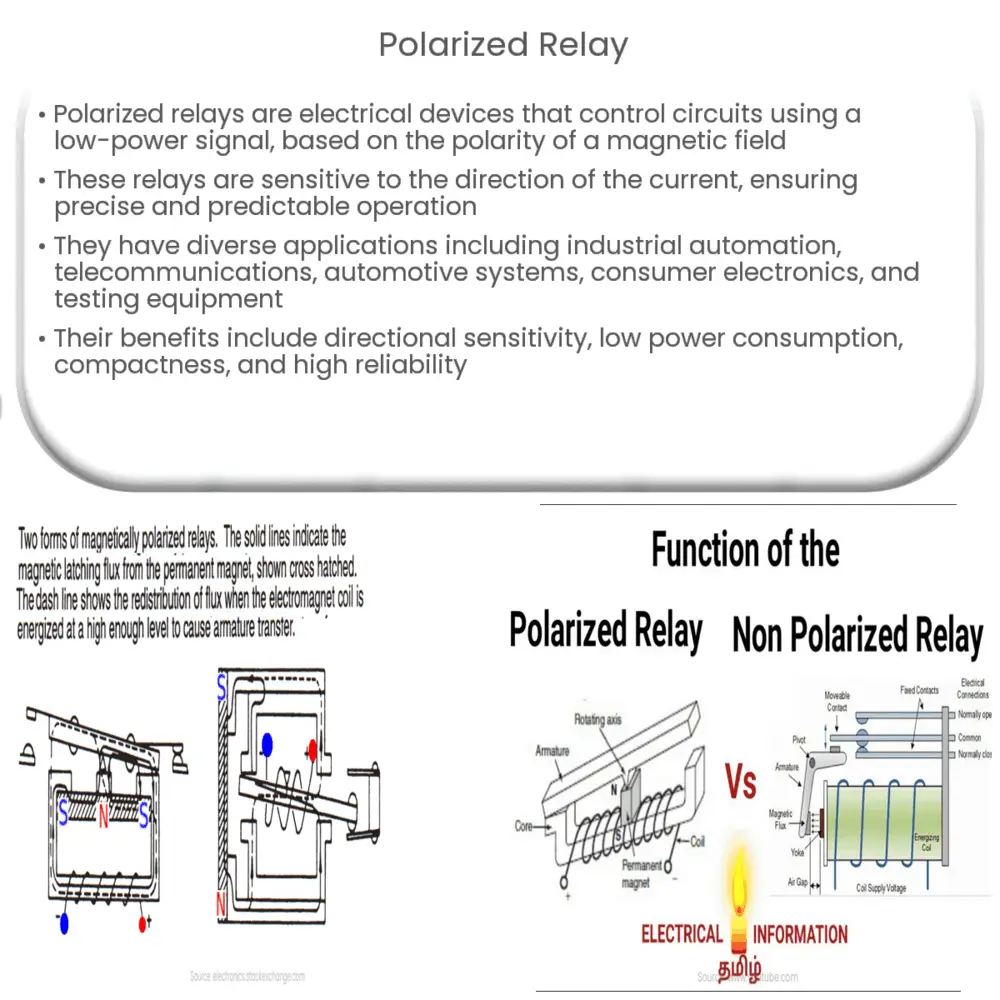
A polarized relay is a type of electromagnetic relay that utilizes the polarity of a magnetic field to control the movement of a movable armature. It consists of a coil, a set of stationary contacts, and a movable contact. When an electric current is passed through the coil, it generates a magnetic field, which attracts the movable contact to the stationary contacts. This action either completes or interrupts the high-power circuit, depending on the intended function of the relay.
One key aspect of polarized relays is their sensitivity to the direction of the current. This means that the relay will only operate when the current flows in a specific direction, ensuring that the relay functions as intended in the circuit. This feature makes polarized relays ideal for applications where precise control and predictable behavior are necessary.
Working Principle of a Polarized Relay
The working principle of a polarized relay is based on the interaction between the magnetic field generated by the coil and the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet. The current flowing through the coil creates an electromagnet with a specific polarity. The movable armature is then attracted or repelled by the combined magnetic field, depending on the direction of the current in the coil.
When the current flows in the intended direction, the magnetic field created by the coil reinforces the field of the permanent magnet, causing the armature to be attracted towards the stationary contacts. Conversely, if the current flows in the opposite direction, the magnetic field generated by the coil opposes the permanent magnet’s field, preventing the armature from moving. This ensures that the relay operates only when the current flows in the correct direction, providing precise control over the high-power circuit.
Applications of Polarized Relays
Polarized relays have a wide range of applications across various industries, thanks to their unique characteristics and reliable performance. Some of the most common uses for polarized relays include:
- Industrial Automation: Polarized relays are commonly used in automation systems for controlling motors, solenoids, and other high-power devices. Their predictable behavior and directional sensitivity make them ideal for maintaining process efficiency and safety.
- Telecommunication: In the telecommunications industry, polarized relays are used for switching and signal routing. They provide reliable performance and low signal distortion, making them suitable for high-frequency applications.
- Automotive: Polarized relays are often found in automotive systems, where they control various components such as power windows, starter motors, and fuel pumps. Their ability to handle high currents and their compact size make them ideal for automotive applications.
- Consumer Electronics: In consumer electronics, polarized relays are used for controlling power supply circuits, protecting sensitive components from overloads or short circuits. They offer precise control and predictable behavior, ensuring the safety and reliability of electronic devices.
- Test and Measurement Equipment: Polarized relays are used in test and measurement equipment to switch between different inputs or outputs. They offer low contact resistance and high isolation between contacts, making them suitable for accurate signal measurements.
Advantages of Polarized Relays
There are several advantages of using polarized relays in various applications, some of which are:
- Directional Sensitivity: As mentioned earlier, polarized relays are sensitive to the direction of the current, ensuring that they operate only when the current flows in the intended direction. This feature provides a higher level of control and predictability in their operation.
- Low Power Consumption: Polarized relays typically require a lower amount of power to operate, making them energy-efficient and ideal for battery-operated devices or systems with limited power resources.
- Compact Size: Due to their simple design and construction, polarized relays are often smaller than other types of relays, making them suitable for applications with limited space availability.
- High Reliability: Polarized relays are known for their reliable performance, with a low failure rate and long service life. This makes them an attractive choice for applications where dependability is critical.
Conclusion
Polarized relays have emerged as an essential component in various industries, thanks to their unique features, reliable performance, and wide range of applications. Their sensitivity to the direction of the current and the ability to handle high currents make them a suitable choice for many applications, including industrial automation, telecommunications, automotive, consumer electronics, and test and measurement equipment. As technology continues to advance, polarized relays will likely play an even more significant role in the development of innovative and efficient solutions across various sectors.

