Piezomagnetic actuators use magnetostrictive materials to create precise, high-force motion, with applications in robotics, energy harvesting, and active vibration control.
Piezomagnetic Actuator: An Overview
Introduction
Piezomagnetic actuators have emerged as a cutting-edge technology in the field of micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS), offering several advantages over conventional piezoelectric and electromagnetic actuators. This article aims to provide an overview of piezomagnetic actuators, discussing their operating principles, advantages, applications, and future prospects.
Operating Principle
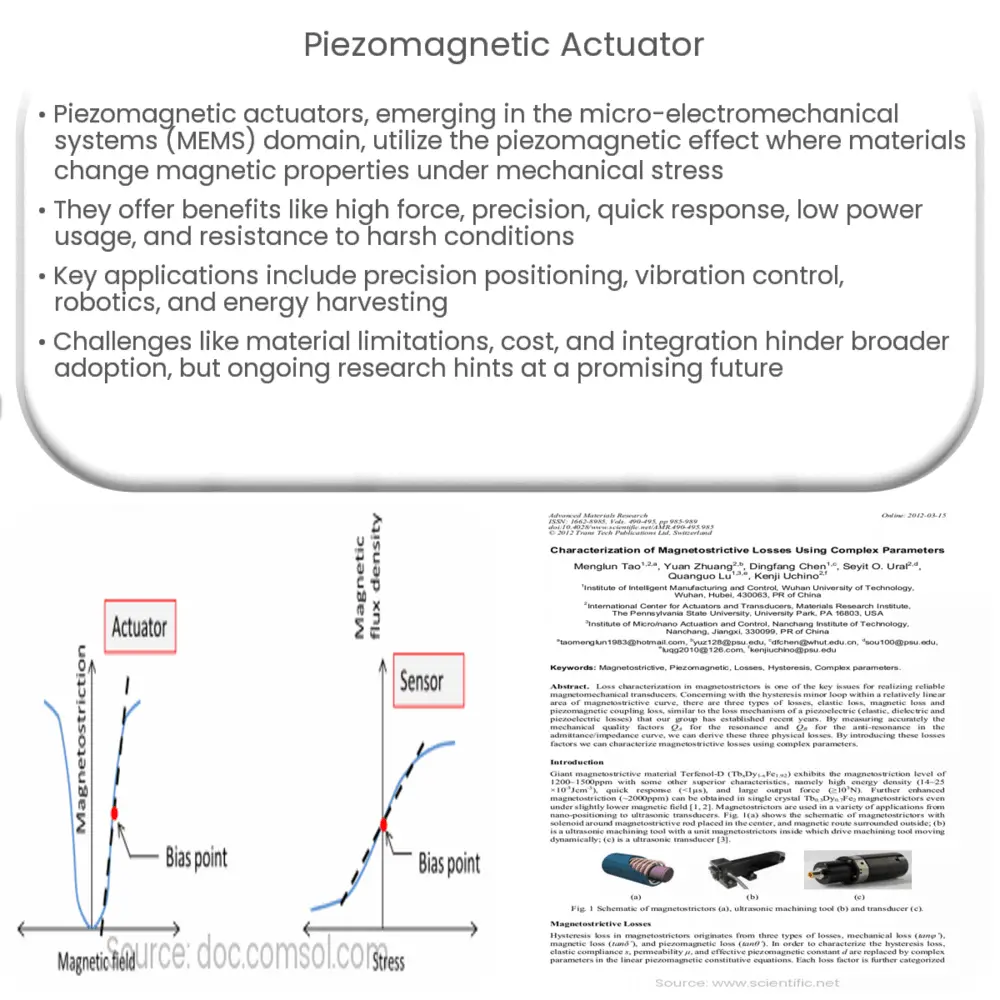
Piezomagnetic actuators are based on the piezomagnetic effect, a phenomenon wherein certain materials exhibit a change in their magnetic properties when subjected to mechanical stress. These materials, known as magnetostrictive materials, undergo a reversible dimensional change in response to an applied magnetic field. This deformation can then be harnessed to produce linear or rotary motion in a variety of applications.
The most common magnetostrictive materials used in piezomagnetic actuators are Terfenol-D and Galfenol. Terfenol-D, an alloy of terbium, dysprosium, and iron, is characterized by its high magnetostriction and strong magnetic coupling. Galfenol, an iron-gallium alloy, offers a more moderate magnetostriction but boasts excellent mechanical and thermal properties, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Advantages of Piezomagnetic Actuators
Compared to traditional actuators, piezomagnetic actuators offer several key advantages:
- High force and precision: Piezomagnetic actuators can generate high force and precision motion in a compact form factor. This makes them suitable for applications requiring both high power and accuracy, such as precision positioning or active vibration control.
- Fast response time: The response time of piezomagnetic actuators is typically on the order of microseconds, much faster than that of electromagnetic actuators. This rapid response time enables applications in high-speed positioning and control systems.
- Low power consumption: Due to their inherent efficiency, piezomagnetic actuators consume less power than traditional actuators, reducing the overall energy requirements of a system.
- Resistance to harsh environments: Piezomagnetic materials are less sensitive to temperature variations and other environmental factors compared to piezoelectric materials, making them suitable for use in harsh conditions.
Applications
Piezomagnetic actuators are increasingly being employed in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Precision positioning: The high force and accuracy of piezomagnetic actuators make them ideal for use in precision positioning systems, such as those used in semiconductor manufacturing, microscopy, and optics.
- Active vibration control: Piezomagnetic actuators can be used to generate counteracting forces in real-time, mitigating vibrations in machinery or structures, and improving overall performance and stability.
- Robotics: The compact size and low power consumption of piezomagnetic actuators enable their use in robotics, particularly in applications where weight and energy efficiency are critical.
- Energy harvesting: By converting ambient mechanical vibrations into electrical energy, piezomagnetic actuators can serve as energy harvesters in self-powered systems, such as wireless sensors and IoT devices.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their numerous advantages, piezomagnetic actuators also face certain challenges that need to be addressed for further development and wider adoption:
- Material limitations: The performance of piezomagnetic actuators largely depends on the properties of magnetostrictive materials. The development of new materials with higher magnetostriction, better thermal stability, and improved mechanical properties is essential for enhancing the performance of these actuators.
- Cost: The high cost of certain magnetostrictive materials, such as Terfenol-D, can be a barrier to widespread adoption. Research into more cost-effective materials and fabrication techniques is necessary to make piezomagnetic actuators more accessible for various industries.
- Integration challenges: The integration of piezomagnetic actuators into existing systems may require specialized expertise and customized solutions. Developing standardized integration methods and guidelines will help facilitate the adoption of these actuators in a broader range of applications.
As researchers continue to explore and improve upon piezomagnetic actuator technology, new applications and possibilities are expected to emerge. The development of novel materials and fabrication techniques, as well as advancements in control systems and sensor technology, will contribute to the growth and adoption of piezomagnetic actuators across various industries.
Conclusion
Piezomagnetic actuators offer numerous advantages over conventional actuators, including high force and precision, fast response time, low power consumption, and resistance to harsh environments. These features make them well-suited for applications in precision positioning, active vibration control, robotics, and energy harvesting. However, challenges related to material limitations, cost, and integration must be addressed to facilitate broader adoption.
As research in this field continues to advance, piezomagnetic actuators hold great potential for revolutionizing various industries and contributing to a more efficient and sustainable future. By overcoming the current challenges and further developing the technology, piezomagnetic actuators are poised to make a significant impact on the way we design and build systems in the coming years.

