Explore the revolutionary world of near-field imaging touchscreens: their components, working principle, benefits, and future prospects.
Introduction to Near-Field Imaging Touchscreens
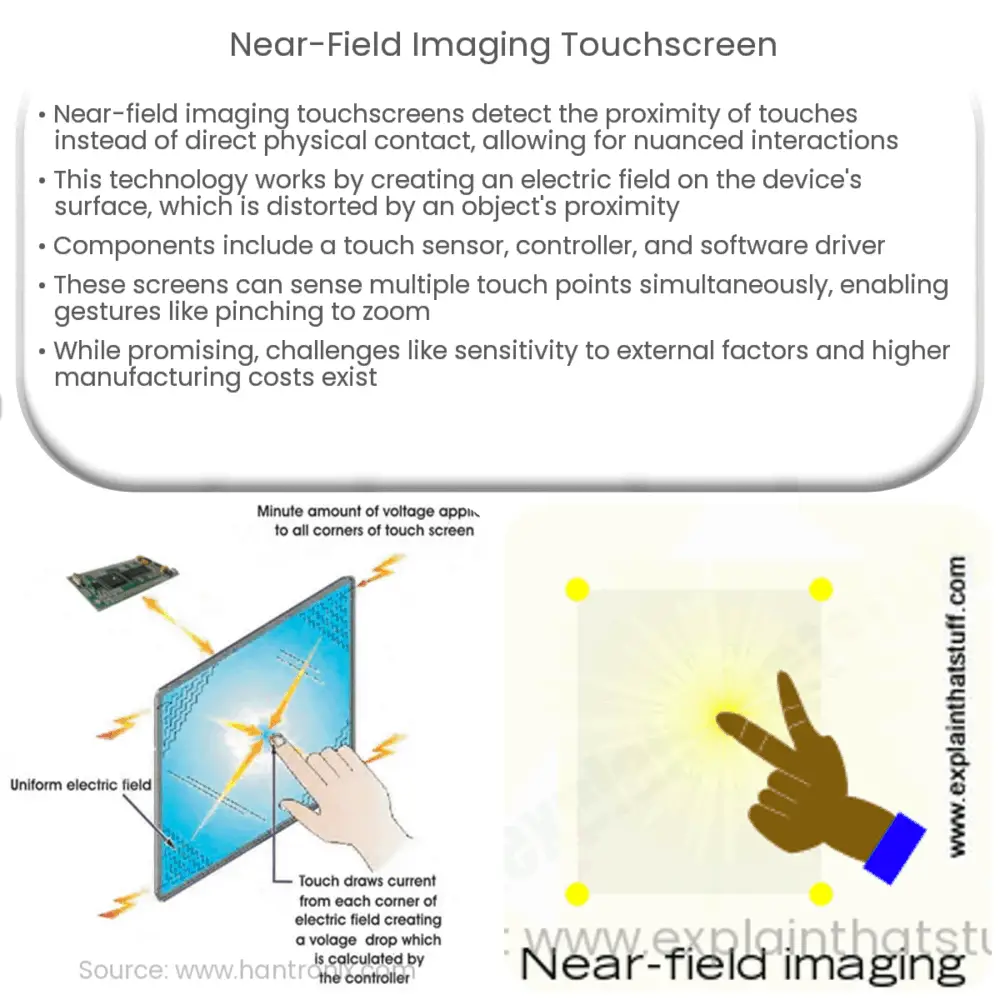
The world of human-computer interaction has been revolutionized by touch-based interfaces, with near-field imaging touchscreens pushing the boundaries of this technology. This innovative technology captures the proximity of a touch rather than relying on direct physical contact, enabling more complex and nuanced interactions.
What is Near-Field Imaging?
Near-field imaging is a type of touch sensing technology that captures the proximity of an object, such as a finger or stylus, to the surface of a device. This is achieved by creating an electric field over the device’s surface, which is then distorted by the object’s presence. This distortion is measured and used to determine the object’s position and proximity to the surface.
Components of Near-Field Imaging Touchscreens
- Touch Sensor: The touch sensor is a panel coated with a capacitive material that reacts to the proximity of an object. It creates the electric field necessary for near-field imaging.
- Controller: The controller is a piece of hardware that processes the signal from the touch sensor. It measures the distortion in the electric field caused by the object’s proximity.
- Software Driver: The software driver translates the controller’s data into information that the device’s operating system can understand and respond to.
Working Principle of Near-Field Imaging Touchscreens
Near-field imaging touchscreens work on the principle of capacitance. When an object approaches the screen, it interacts with the device’s electric field, creating a distortion. This distortion is detected by the controller, which calculates the object’s position and proximity to the surface. The controller then passes this information to the software driver, which translates it into a format that the device’s operating system can understand. This process happens almost instantaneously, allowing for real-time interaction with the device.
Advantages of Near-Field Imaging Touchscreens
One of the major benefits of near-field imaging touchscreens is their ability to detect multiple touch points simultaneously. This multi-touch capability enables more complex and nuanced interactions, such as pinching to zoom or using multiple fingers to manipulate an image. Additionally, these screens can detect a touch before it physically contacts the screen, allowing for hover or proximity-based interactions.
Applications of Near-Field Imaging Touchscreens
Near-field imaging touchscreens have found widespread application in various fields. In the consumer electronics industry, these screens are used in smartphones, tablets, and other touch-enabled devices. They enable more intuitive user interfaces and allow for more complex gestures. These touchscreens also find use in industrial settings, where they can be used in control panels and other devices that require precise and reliable touch inputs.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their numerous advantages, near-field imaging touchscreens have some limitations. The accuracy of the touch detection can be affected by external factors such as temperature and humidity, which can alter the electric field. Additionally, these touchscreens can be more expensive to manufacture than traditional resistive or capacitive touchscreens. Overcoming these limitations is a key area of ongoing research and development in this field.
Future of Near-Field Imaging Touchscreens
The future of near-field imaging touchscreens looks promising. As the technology matures and manufacturing processes improve, these screens are expected to become more common and affordable. Advances in the technology, such as improved sensitivity and resolution, could open up new possibilities for touch-based interaction. For example, future touchscreens could detect the presence of a finger or stylus before it touches the screen, enabling hover or proximity-based interactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, near-field imaging touchscreens represent a significant leap forward in touch-based interaction technology. By detecting the proximity of an object rather than relying on physical contact, these screens enable more complex and nuanced interactions. While the technology still faces some challenges, ongoing research and development are expected to overcome these hurdles, leading to wider adoption and new possibilities for human-computer interaction. As we continue to embrace the digital age, the role of touchscreens, and specifically near-field imaging touchscreens, will undeniably become increasingly important in shaping our interactions with technology.