Explore the importance of motor grounding equipment, its key components, methods, and the role it plays in ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems.
Understanding Motor Grounding Equipment
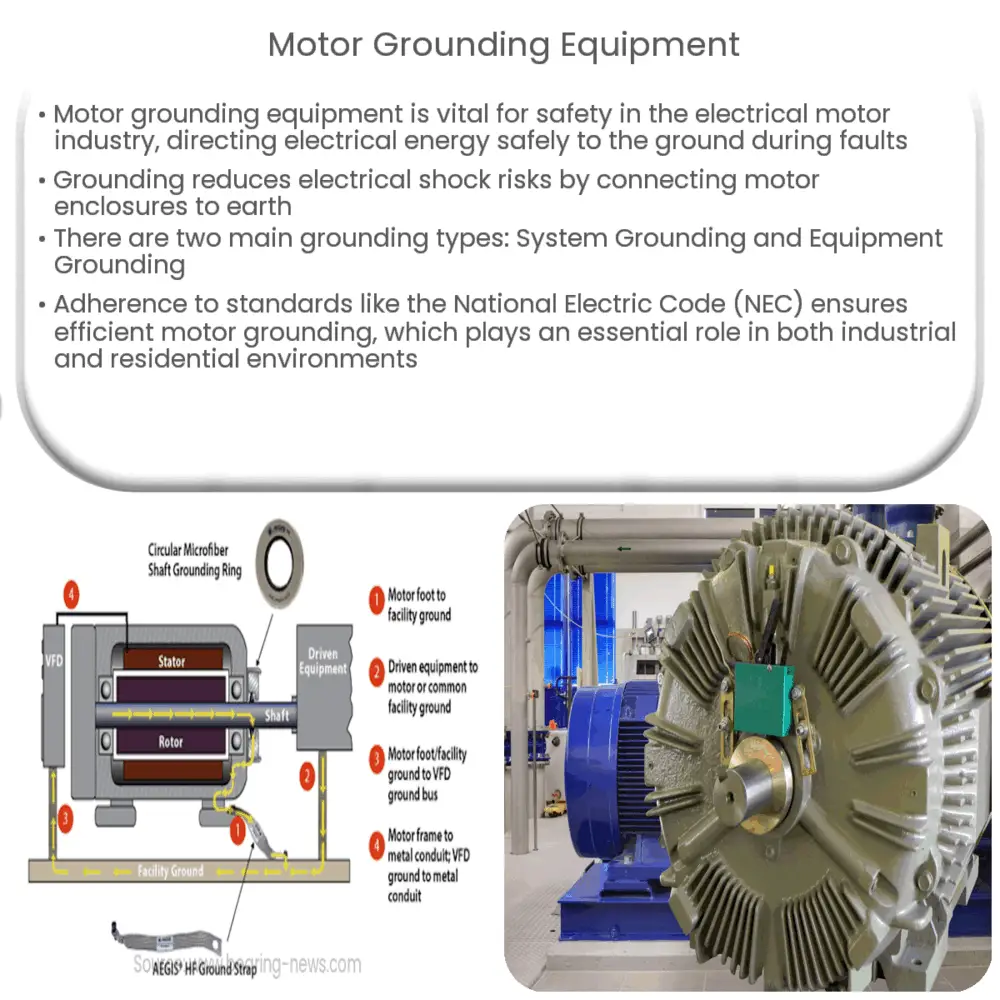
Motor grounding equipment is a critical safety mechanism used in the electrical motor industry. Its primary function is to offer a direct path for electrical energy to travel safely to the ground in the case of a fault. Without grounding, electrical faults can cause severe hazards, including electrocution and fires.
The grounding process involves connecting the motor’s metal enclosure to the earth, effectively reducing the risk of electrical shock by shunting unwanted energy to the ground. The direct path is often established using a grounding conductor, typically a wire that is connected to the ground at the electrical service panel.
Types of Grounding
- System Grounding: This type of grounding involves the connection of neutral points of a system to the earth. It assists in the stabilization of voltage during normal operations.
- Equipment Grounding: Here, the conductive material enclosing the electrical equipment is connected to the ground. This method provides protection against electrical shock by creating a safe pathway for fault current.
Motor grounding is governed by multiple standards to ensure safety and efficiency. The National Electric Code (NEC) in the United States, for instance, provides comprehensive rules and guidelines for motor grounding.
Significance of Motor Grounding
Motor grounding equipment plays an indispensable role in both industrial and residential settings. Beyond protecting against electrical shocks and potential fire hazards, it also:
- Promotes system longevity by preventing the accumulation of static electricity.
- Facilitates the proper operation of overcurrent devices like circuit breakers and fuses by creating an effective path for fault current, thereby preventing damage to the motor.
- Allows for the detection of insulation failure, mitigating the risk of larger faults and associated downtime.
Therefore, a well-grounded motor not only provides safety, but also enhances operational reliability and efficiency.
Key Components of Motor Grounding Equipment
Motor grounding equipment comprises several key components:
- Grounding Electrodes: These are conducting objects that establish a direct connection with the earth. Rods, plates, or wire mesh can serve as grounding electrodes.
- Grounding Conductors: These are typically wires that connect the grounding electrode to the equipment grounding conductor or the grounded conductor of the system.
- Equipment Grounding Conductors: They provide a pathway from a grounded non-current-carrying metal part of equipment, raceway, or enclosure to the grounding electrode.
Methods of Motor Grounding
The methods of motor grounding can vary according to the type of motor, its application, and prevailing regulatory requirements. However, the two most common methods are:
- Direct Grounding: Here, one terminal of the motor winding is directly connected to the earth. This method is typically used in DC motors and single-phase AC motors.
- Indirect Grounding: In this method, motor windings are not directly connected to the earth. Instead, a device such as a resistor or reactor is placed between the motor and the earth. Indirect grounding is often used in three-phase AC motors.
While the method of grounding is dictated by the type of motor and its application, it’s crucial to always comply with the relevant safety standards and guidelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, motor grounding equipment plays a critical role in ensuring safety and operational efficiency. By providing a safe path for electrical fault currents to the earth, it significantly reduces the risk of electrical shocks and fires. Furthermore, it enhances motor longevity and facilitates the smooth operation of protective devices. Understanding the types of grounding, their significant components, and appropriate grounding methods is essential to maximizing these benefits. As the industry continues to evolve, the principles of effective motor grounding remain a key focus, underpinning safer and more reliable electrical systems.

