Explore the fundamentals of metal film resistors, their construction, properties, applications, advantages, limitations, and future trends.
Introduction to Metal Film Resistors
Resistors are one of the fundamental components in electronic devices. They play a crucial role in controlling the flow of electrical current and voltage levels in circuits. Among the various types of resistors, metal film resistors have gained significant recognition due to their advantageous properties. In this article, we delve into the basics of metal film resistors and explore their applications and benefits.
What are Metal Film Resistors?
Metal film resistors are a type of fixed resistor, meaning their resistance value remains constant. These resistors are constructed by depositing a thin metal layer onto a non-conducting substrate, often a ceramic rod. The metal film acts as the resistive path through which the electric current travels.
The Construction of Metal Film Resistors
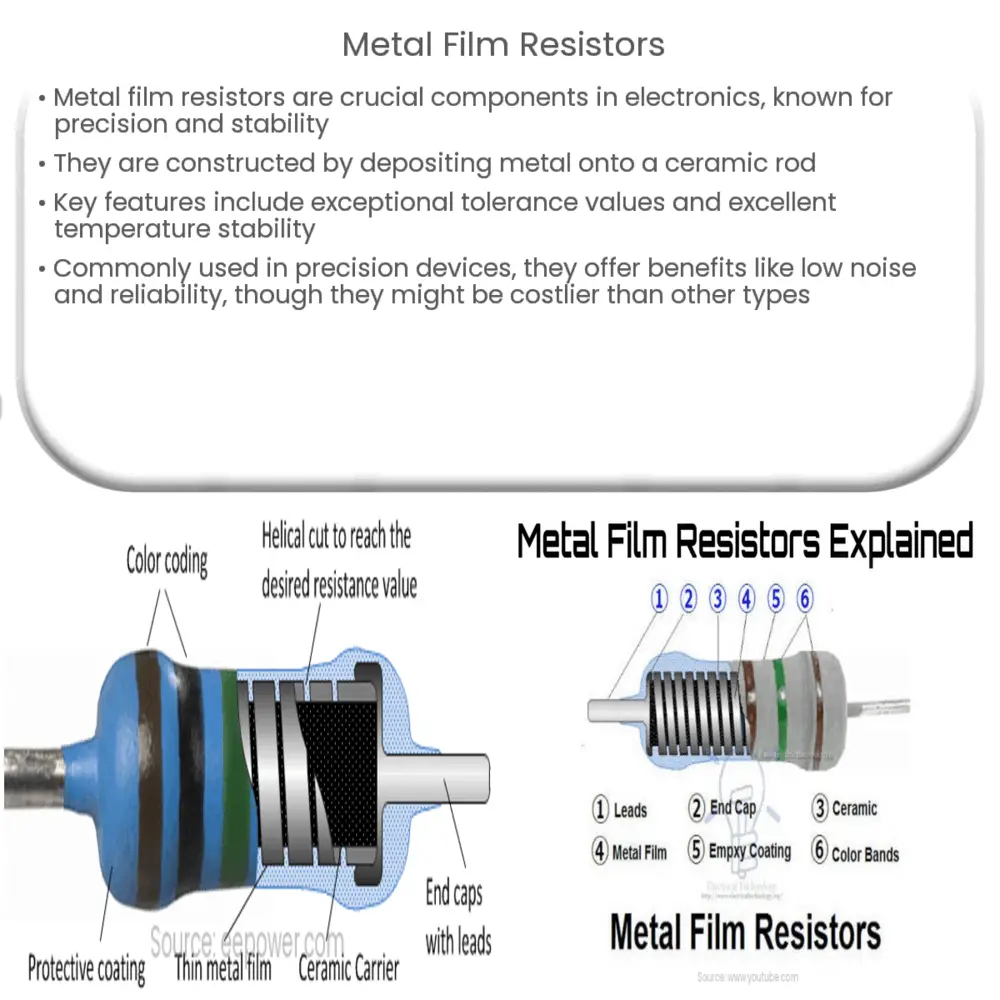
The construction of metal film resistors starts with a high-grade ceramic rod. A thin layer of pure metal, typically nickel-chromium (NiCr) or a similar metal alloy, is deposited onto this rod. The film’s thickness and the ceramic rod’s length and diameter control the resistor’s overall resistance value.
- Sub: The ceramic rod, which serves as the substrate.
- Film: A thin metal layer (the resistive material) deposited onto the ceramic rod.
- Leads: Metal wires connected at both ends of the ceramic rod, used to integrate the resistor into a circuit.
- Protective Coating: An outer layer that protects the resistor from physical damage and environmental factors.
Key Properties of Metal Film Resistors
One of the key features of metal film resistors is their exceptional tolerance values. Typically, these resistors offer tolerance levels as low as 0.1%, which means the actual resistance value deviates very minimally from the specified value. This makes them an excellent choice for precision circuits where accurate resistance is critical.
Moreover, these resistors have excellent temperature stability. In other words, their resistance value does not significantly change with temperature variations. This is due to the metallic nature of the resistive film, which exhibits lower temperature coefficients compared to other materials.
Applications of Metal Film Resistors
Metal film resistors find applications in a variety of areas. They are especially common in precision applications due to their low tolerance levels. Examples include medical equipment, test equipment, audio systems, and high-end electronics where precise resistance values are necessary.
Advantages and Limitations of Metal Film Resistors
Several advantages make metal film resistors a preferred choice in many applications. These include:
- High precision: With low tolerance values, metal film resistors offer high accuracy, making them suitable for precision applications.
- Excellent temperature stability: The resistance value changes minimally with temperature fluctuations, leading to consistent performance.
- Low noise: These resistors produce less electrical noise compared to other types, which is beneficial in sensitive audio or signal processing circuits.
- High reliability: Their robust design and construction enhance their longevity and reliability in various operating conditions.
Despite their many advantages, metal film resistors have certain limitations:
- They are usually not suitable for high power applications due to their lower power ratings compared to other resistor types like wirewound resistors.
- The cost of metal film resistors is typically higher than that of carbon film resistors, although the improved performance often justifies the additional cost.
The Future of Metal Film Resistors
As technology continues to evolve, the demand for highly precise and reliable components is expected to increase. Therefore, the future of metal film resistors looks promising. Innovations are continually being made to enhance their performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. There is also an increasing trend towards miniaturization, with smaller, more efficient resistors being developed to meet the needs of compact electronic devices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, metal film resistors are an essential component in the electronics industry due to their high precision, excellent temperature stability, low noise, and high reliability. Despite certain limitations such as power handling and cost, their benefits often outweigh these factors. As technology advances, we can expect to see continued improvements in metal film resistors, enhancing their performance and making them even more valuable in the electronics landscape.

