Explore the workings, advantages, and disadvantages of Low Dropout Regulators (LDOs), their applications, and future trends.
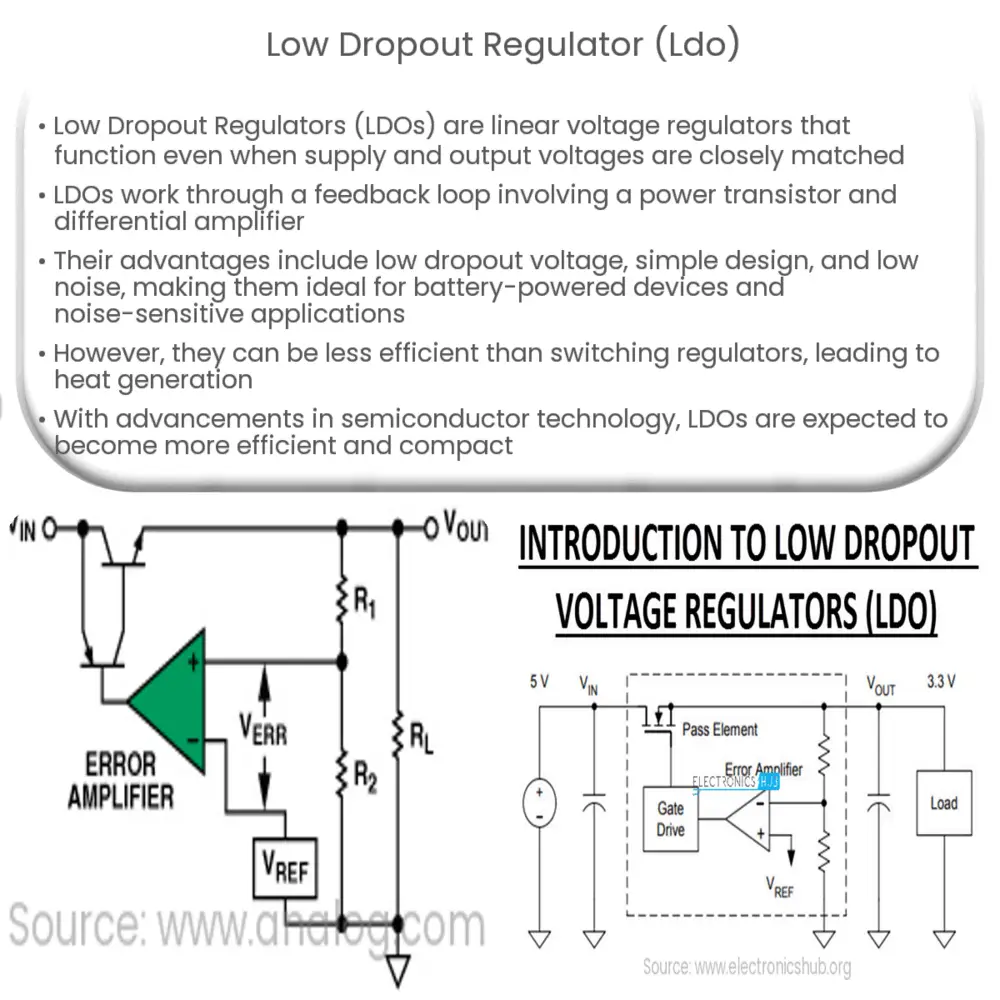
Introduction to Low Dropout Regulator (LDO)
A Low Dropout Regulator (LDO) is a type of linear voltage regulator often used in electronic devices. LDOs are designed to regulate an output voltage even when the supply voltage is very close to the output voltage. This characteristic ‘low dropout’ operation is what gives this type of regulator its name.
How Does an LDO Work?
At its core, an LDO consists of a power transistor and a differential amplifier. The amplifier continuously compares the regulated output voltage with a stable reference voltage. Any discrepancy in the comparison results in a change in the conductance of the power transistor, adjusting the output voltage accordingly. This feedback loop keeps the output voltage stable, regardless of variations in input voltage or load current.
Key Advantages of LDOs
Key Disadvantages of LDOs
Applications of LDOs
LDOs are used in a variety of applications. They are often found in battery-powered devices, like smartphones and portable media players, where the supply voltage drops over time. LDOs are also used in applications that require a clean and stable power supply, such as digital circuits, microcontrollers, and digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
Design Considerations for LDOs
While designing with LDOs, several factors need to be considered. These include the dropout voltage, the required output voltage, the maximum input voltage, and the load current. The power dissipation is also a crucial factor, especially in designs where space or thermal management are significant constraints. Adequate heat sinking or thermal vias may be necessary to maintain a reasonable operating temperature.
Selection of LDOs
Selecting the right LDO for a given application involves balancing several key parameters. These include:
Future of LDOs
With the ongoing trend of miniaturization and the increasing need for power-efficient devices, the future of LDOs looks promising. Innovations in semiconductor technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, resulting in LDOs with lower dropout voltages, higher efficiencies, and smaller form factors. Furthermore, the growing need for noise-free power supplies in sensitive electronics and the widespread use of battery-powered devices provide numerous opportunities for LDOs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Low Dropout Regulator (LDO) is a critical component in many electronic devices, providing a stable output voltage with a low dropout operation. While they may not be as efficient as switching regulators in some respects, their simplicity, low noise, and ability to work with low input-output voltage differentials make them a preferred choice for many applications. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see further improvements in LDO performance and efficiency, enhancing their value in the world of electronics.

