Explore the role of Integrated Circuit (IC) Voltage Regulators in modern electronics, their types, working principles, key components, and applications.
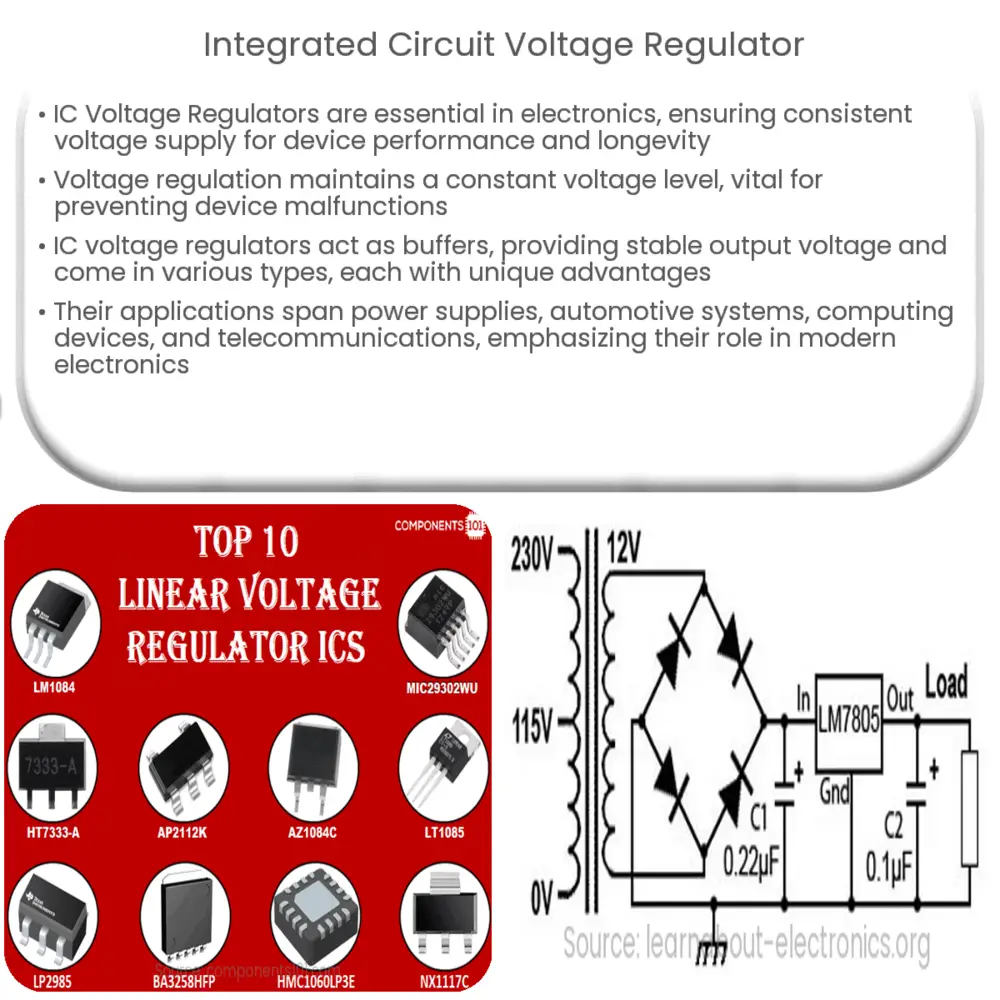
Introduction to Integrated Circuit Voltage Regulators
An Integrated Circuit (IC) Voltage Regulator is a pivotal component in the realm of electronics, acting as a vital intermediary between power sources and electronic devices. It plays a vital role in ensuring a consistent voltage supply, thereby optimizing device performance and longevity.
Understanding Voltage Regulation
In simple terms, voltage regulation is the process of maintaining a constant level of voltage in an electrical circuit. This is crucial as electronic devices typically require a steady and specific voltage to function optimally. Fluctuations or deviations can lead to malfunction or even irreversible damage.
The Role of IC Voltage Regulators
IC voltage regulators are primarily designed to tackle the issue of voltage instability. They function as a buffer, absorbing voltage fluctuations from the power source, thereby delivering a stable output voltage to the device. The output voltage of these regulators is fixed or adjustable based on the type of IC voltage regulator used.
Types of IC Voltage Regulators
- Linear Voltage Regulators: These are the most commonly used type of voltage regulators. Linear voltage regulators operate by dropping the input voltage to the desired level using a transistor in active mode.
- Switching Voltage Regulators: Unlike linear regulators, switching regulators use a switch to control the flow of energy from the input to the output. These are more efficient than linear regulators but can cause more electrical noise.
- Series Voltage Regulators: In these regulators, the regulating device is in series with the load. They have the advantage of a very steady output.
- Shunt Voltage Regulators: Here, the regulating device is parallel to the load. They offer better control but can waste more energy.
It’s essential to note that each type of IC voltage regulator has its own unique advantages and trade-offs. The choice of regulator depends on the specific requirements of the electrical system in question.
The Working Principle of an IC Voltage Regulator
An IC voltage regulator works on the principle of voltage division and regulation. The regulator controls the current passing through a network of resistors to maintain the desired output voltage. This is achieved by adjusting the resistance in the network based on the input voltage.
Key Components of an IC Voltage Regulator
An IC voltage regulator is composed of three key components:
- Voltage Reference: This is a stable voltage source against which the output voltage is compared to. It serves as the benchmark for the desired output voltage.
- Error Amplifier: This component compares the output voltage with the reference voltage. If there is a deviation, it amplifies the error signal and feeds it to the control block.
- Control Block: This is where the actual voltage regulation happens. The control block takes the error signal and adjusts the resistance in the network, thereby controlling the output voltage.
Applications of IC Voltage Regulators
IC voltage regulators find a wide array of applications in electronic devices and systems where stable voltage is a necessity. Some of these include:
- Power Supplies: They ensure a stable voltage supply to electronic devices, regardless of changes in input voltage or load conditions.
- Automotive Systems: They are used in car electronics to manage power supply to different components, ensuring optimal operation.
- Computers and Mobile Devices: They are integral to managing power in computing systems and handheld devices, helping to optimize performance and battery life.
- Telecommunication Systems: They are used to regulate power in communication devices and infrastructure, ensuring reliable operation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the IC voltage regulator is a fundamental component in modern electronics, ensuring devices operate efficiently and reliably by maintaining a stable voltage supply. From linear to switching regulators, each type has its own specific characteristics and applications, with their choice depending on the specific requirements of the electronic system.
As technology continues to advance, the demand for reliable and efficient power supply solutions will continue to rise. IC voltage regulators will undoubtedly remain a key player in this arena, contributing to the smooth operation of an ever-growing range of electronic devices and systems.