Infrared line sensors use IR light to detect lines, offering ambient light immunity, material compatibility, and high precision for robotics, automation, and industrial applications.
Infrared Line Sensors: An Introduction to the Technology
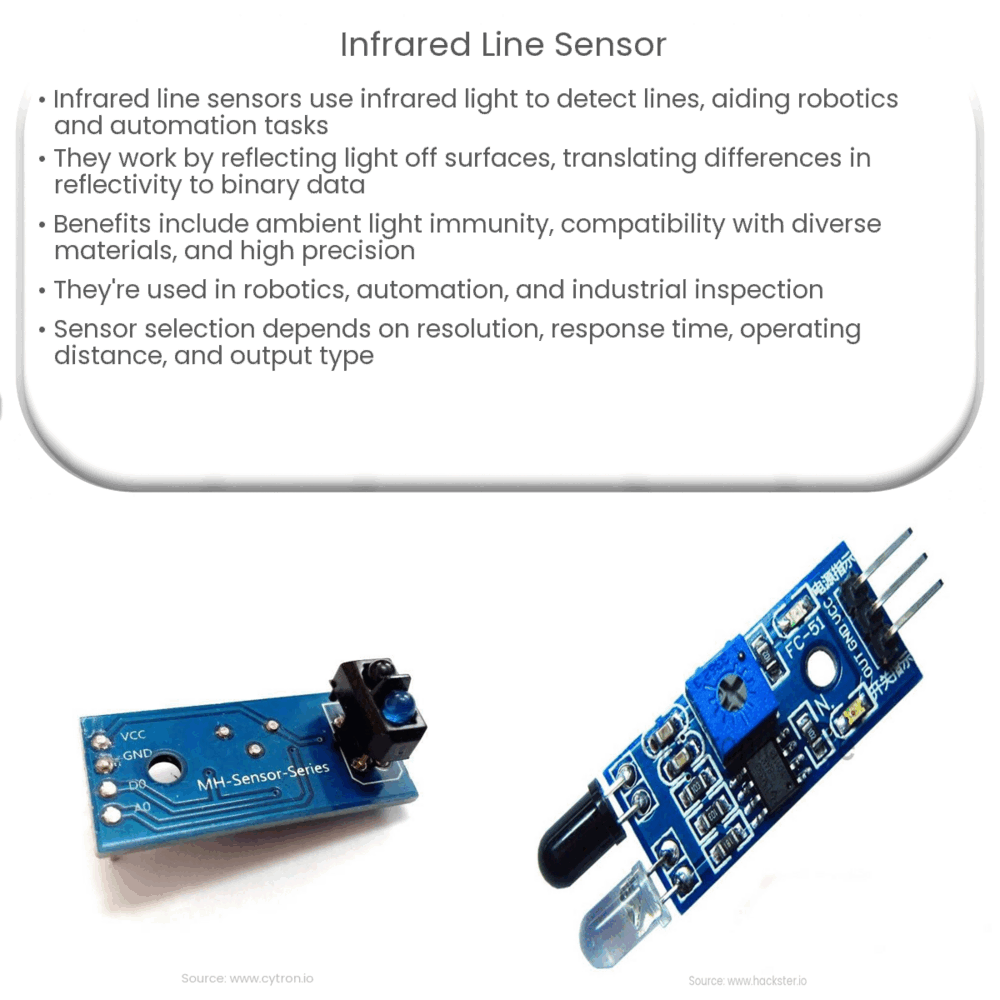
Overview of Infrared Line Sensors
Infrared line sensors are a type of optical sensor that utilize infrared light to detect and measure the presence or absence of a line. These sensors are typically used in robotics, automation, and various industrial applications to provide guidance, control, and positioning information. In this article, we will explore the fundamental principles of infrared line sensors, their advantages, and their applications.
How Infrared Line Sensors Work
Infrared line sensors operate by emitting infrared light from an LED (Light Emitting Diode) and measuring the amount of light that is reflected back. The sensor contains a photodetector, which is sensitive to infrared light, and is responsible for converting the light into an electrical signal. The strength of this signal depends on the amount of light reflected, which in turn depends on the surface properties of the object being sensed.
When the sensor is placed above a line, the infrared light will reflect differently off the line compared to the background surface. This difference in reflectivity allows the sensor to distinguish between the line and the background. By processing the electrical signal, the sensor can output a binary value, indicating the presence or absence of the line beneath it.
Advantages of Infrared Line Sensors
There are several advantages to using infrared line sensors in various applications. These include:
- Ambient Light Immunity: Infrared line sensors are less sensitive to ambient light compared to visible light sensors. This means that they can perform reliably even in environments with variable or harsh lighting conditions.
- Material Compatibility: Infrared light can be reflected off a wide range of materials, making infrared line sensors suitable for use with various line and background materials. This flexibility is particularly useful in industrial applications where the sensor may need to adapt to different materials and surfaces.
- High Precision: Infrared line sensors can detect lines with high accuracy, enabling precise control and positioning. This level of precision is essential in applications such as robotics and automation, where even small errors can have significant consequences.
Applications of Infrared Line Sensors
Infrared line sensors are commonly used in a variety of applications, such as:
- Robotics: Infrared line sensors are often used in robots for line-following tasks. They enable robots to follow a predefined path, navigate complex environments, and avoid obstacles.
- Automation: In manufacturing and assembly lines, infrared line sensors help guide and position components accurately. This ensures that parts are correctly aligned and assembled, improving overall product quality and reducing waste.
- Industrial Inspection: Infrared line sensors can be used to inspect materials and products for defects, such as cracks or misalignments, by detecting variations in line patterns or reflectivity.
Integration with Other Sensor Technologies
Infrared line sensors can be combined with other sensor technologies to improve performance and adapt to specific application requirements. For example, ultrasonic sensors can provide additional distance measurement data, while cameras and vision systems can offer more detailed visual information. Combining these technologies enables more advanced and versatile sensing capabilities, increasing the accuracy and reliability of the system.
Selecting the Right Infrared Line Sensor
When choosing an infrared line sensor for a particular application, there are several factors to consider:
- Resolution: The resolution of an infrared line sensor determines its ability to detect fine details and accurately differentiate between the line and background. Higher resolutions offer better precision but may come at a higher cost.
- Response Time: The response time of a sensor is the time it takes for the sensor to detect a change in the line position and output an updated signal. Faster response times enable quicker adjustments and higher-speed operation.
- Operating Distance: The operating distance is the range within which the sensor can reliably detect a line. It is important to choose a sensor with an appropriate operating distance for your specific application to ensure reliable performance.
- Output Type: Infrared line sensors can have different output types, such as digital or analog signals. The choice of output type depends on the requirements of your system and how the sensor data will be processed.
Conclusion
Infrared line sensors are a versatile and reliable technology for detecting and measuring lines in a variety of applications. Their immunity to ambient light, compatibility with various materials, and high precision make them an ideal choice for robotics, automation, and industrial inspection tasks. By carefully considering factors such as resolution, response time, operating distance, and output type, you can select the right infrared line sensor for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and results.

