Explore the basics of induction AC motors, their types, design, applications, and control methods in this comprehensive guide.
Introduction to Induction AC Motors
An Induction AC Motor, or simply an induction motor, plays an integral role in modern industries and technology. Recognized for its versatility and efficiency, it’s one of the most commonly utilized types of electric motors worldwide. This article explores the fundamental aspects of these ingenious devices.
Principle of Operation
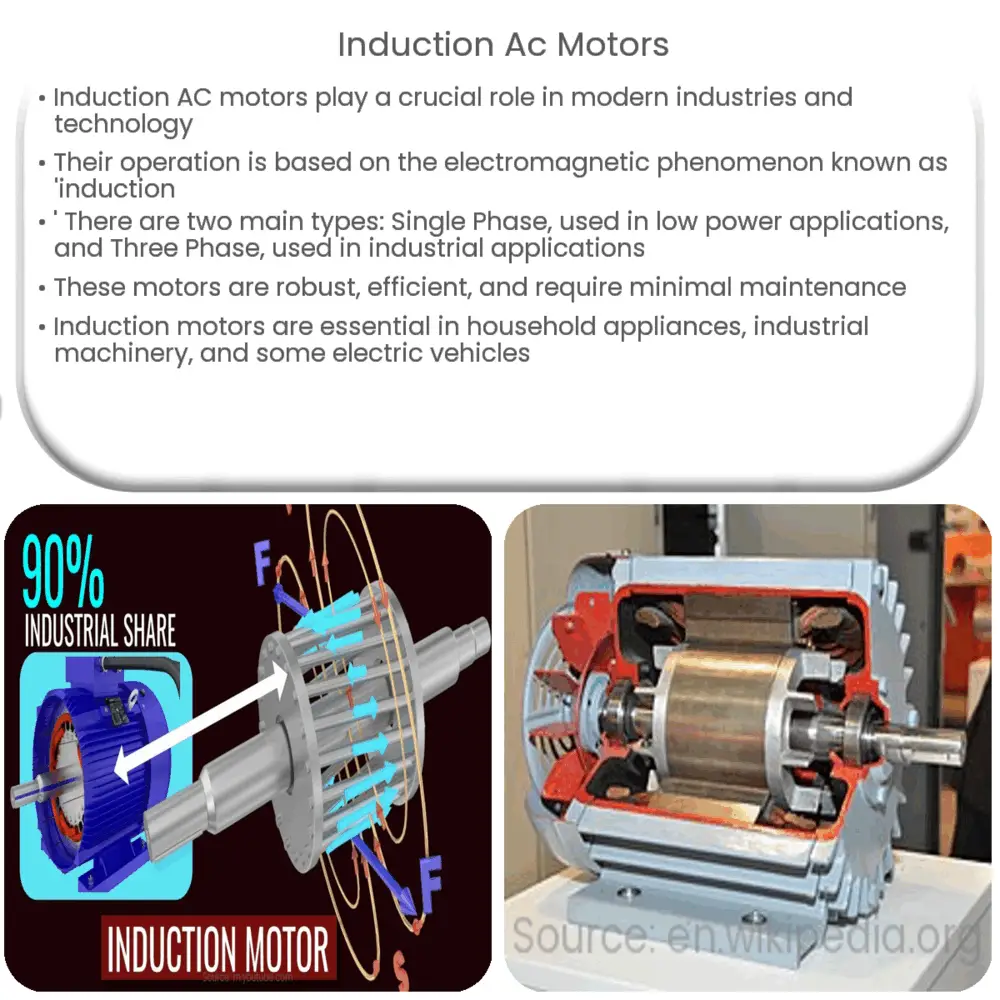
The operating principle of induction motors relies on the electromagnetic phenomenon known as ‘induction.’ A typical induction motor consists of two main parts: the stator and the rotor. The stator houses windings connected to an alternating current power source, while the rotor, located inside the stator, is typically composed of conductive bars arranged in a cage-like fashion.
When alternating current flows through the stator windings, it generates a rotating magnetic field. This dynamic field cuts across the rotor conductors, inducing an electromotive force (EMF) and resulting in current flow within the rotor. The interaction between the rotating magnetic field and the current in the rotor bars produces torque, causing the rotor to spin and thus driving the motor.
Types of Induction Motors
- Single Phase Induction Motors: These motors are primarily used in low power applications, like domestic appliances and small machines. They operate on single-phase AC power.
- Three Phase Induction Motors: These are the most common type of induction motors, used in various industrial and commercial applications. They operate on three-phase AC power, ensuring a more uniform and efficient magnetic field rotation.
Characteristics of Induction Motors
Induction motors stand out due to a few notable characteristics:
- Robustness: These motors are known for their rugged construction and durability, ensuring they can withstand demanding industrial environments.
- Efficiency: With their ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy effectively, induction motors are highly efficient.
- Low Maintenance: Because the stator and rotor are separated by an air gap, and there are no brushes or commutators involved, maintenance needs are minimal.
Induction motors are not without their limitations, however. One key constraint is their dependence on a constant frequency power supply for constant speed operation, which may limit their usefulness in certain applications.
This overview provides an insight into the basics of induction AC motors. In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into their design, operation, and applications.
Design and Construction of Induction Motors
Induction motors are designed with simplicity and efficiency in mind. As mentioned earlier, the two main components of an induction motor are the stator and the rotor. The stator is the stationary part of the motor, consisting of a cylindrical frame and stator windings. The rotor, on the other hand, is the rotating part, typically constructed either as a squirrel cage or a wound rotor.
The squirrel cage rotor is the most common type due to its robust and maintenance-free nature. It gets its name from its structure, which looks like a running wheel for small rodents. On the other hand, the wound rotor is used in motors designed for speed control or high starting torque, and its windings are connected to external resistors through slip rings.
Applications of Induction Motors
Induction motors have a wide range of applications due to their versatility and robustness:
- Home appliances: Smaller, single-phase induction motors are used in appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and fans.
- Industrial machines: Larger, three-phase induction motors drive many types of industrial machinery, such as pumps, compressors, and conveyor belts.
- Electric vehicles: Some modern electric cars use three-phase induction motors for their propulsion systems.
Controlling Induction Motors
Induction motors, particularly three-phase types, can be controlled using a method known as Variable Frequency Drive (VFD). A VFD can vary the motor’s speed and torque by changing the input frequency and voltage, thereby offering precise control and improved efficiency in a range of applications.
Conclusion
In summary, induction AC motors are a core component in modern technology and industry. Their reliability, efficiency, and wide range of applications make them a versatile and indispensable tool. From powering everyday household appliances to driving complex industrial machinery, induction motors continue to underpin the progress of our technological world. Despite the inherent limitations regarding speed control, solutions like the Variable Frequency Drive have been developed to mitigate these issues and enhance the functionality of these motors. It is without a doubt that the induction AC motor, with its humble origins and unassuming nature, holds a pivotal role in our increasingly electrified society.



