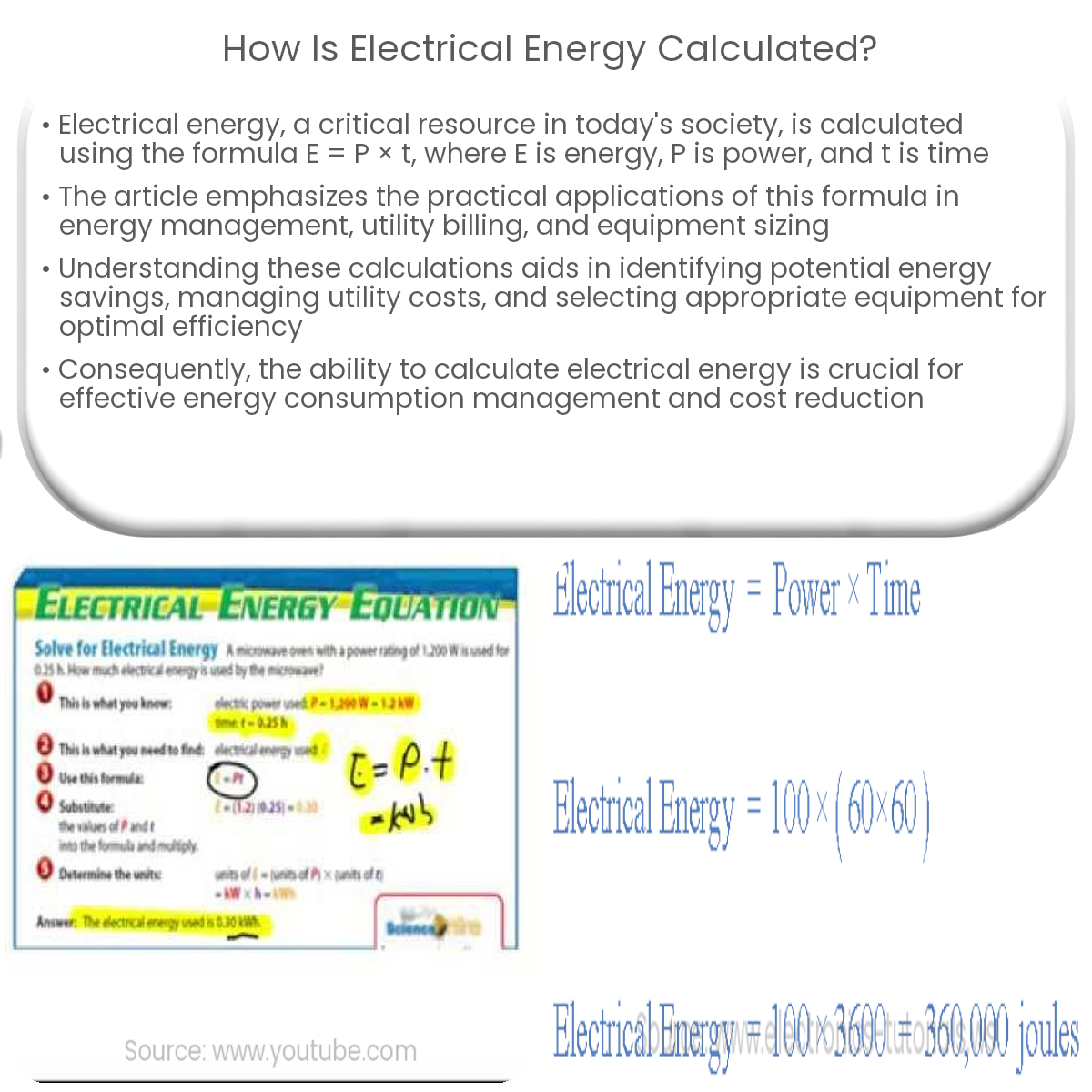
Electrical energy is calculated using the formula E = P × t, where E is energy, P is power, and t is time. E = V × I × t can also be used.
Calculating Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is a vital resource in modern society, powering homes, industries, and businesses. Understanding how to calculate electrical energy can help individuals and organizations manage their energy consumption and reduce costs. This article will explain the method for calculating electrical energy and provide examples of its applications.
Electrical Energy: A Definition
Electrical energy is a form of energy resulting from the movement of charged particles, such as electrons, through a conductor. It can be converted into other forms of energy, such as heat, light, or mechanical energy, depending on the application.
Formula for Calculating Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is calculated using the formula:
E = P × t
Where E is energy in watt-hours (Wh), P is power in watts (W), and t is time in hours (h). Power (P) represents the rate at which electrical energy is converted or utilized and is calculated as the product of voltage (V) and current (I):
P = V × I
By combining these two formulas, the electrical energy consumed by a device can be determined using the voltage, current, and time:
E = V × I × t
Example of Electrical Energy Calculation
Suppose you have a 60-watt light bulb that operates for 4 hours. To calculate the electrical energy consumed by this light bulb, use the formula E = P × t:
E = 60 W × 4 h = 240 Wh
This means that the light bulb consumed 240 watt-hours of electrical energy during the 4-hour period.
Applications of Electrical Energy Calculation
Calculating electrical energy has several practical applications, including:
- Energy management: By determining the energy consumption of various devices and appliances, individuals and organizations can identify areas for potential energy savings and implement strategies to reduce consumption.
- Utility billing: Electricity providers bill customers based on their energy consumption, typically in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Understanding how to calculate electrical energy can help customers manage their usage and costs.
- Equipment sizing and selection: Accurate electrical energy calculations can help engineers and technicians select the appropriate size and type of equipment for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
Conclusion
Calculating electrical energy is essential for managing energy consumption, reducing costs, and optimizing the performance of electrical systems. By using the formula E = P × t, individuals and organizations can determine the energy consumption of various devices and appliances, helping them make informed decisions about energy usage and efficiency.