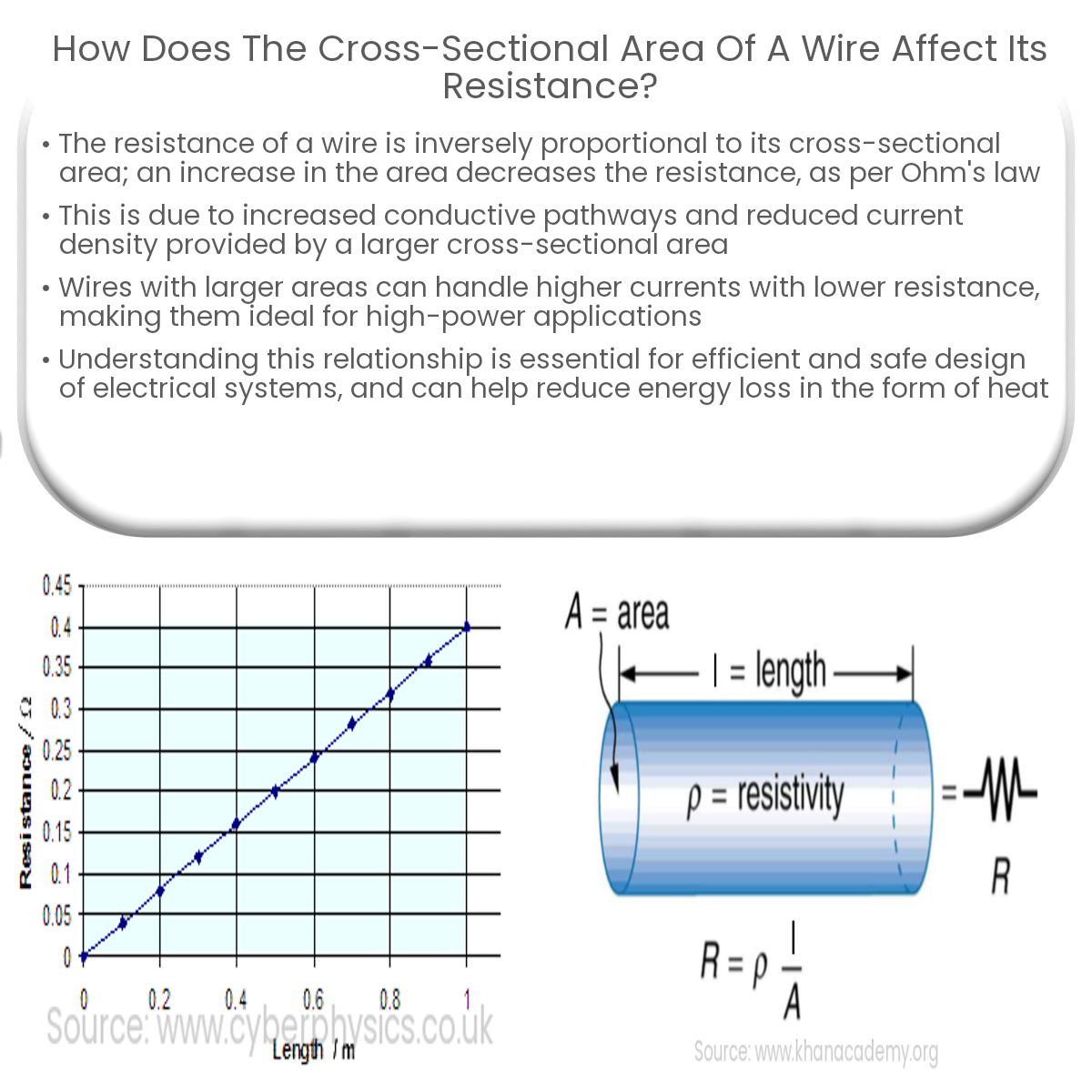
The resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area; as the area increases, resistance decreases due to more conductive paths.
How the Cross-Sectional Area of a Wire Affects Its Resistance
The resistance of a wire is influenced by several factors, one of which is its cross-sectional area. In this article, we will explore the relationship between the cross-sectional area of a wire and its resistance, explaining the underlying principles and implications for real-world applications.
Relationship between Cross-Sectional Area and Resistance
The resistance of a wire is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. As the cross-sectional area increases, the resistance decreases, and vice versa. This relationship can be expressed mathematically using Ohm’s law:
R = ρ (L / A)
Where:
- R is the resistance of the wire;
- ρ (rho) is the resistivity of the wire’s material;
- L is the length of the wire; and
- A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
This equation shows that the resistance is inversely related to the cross-sectional area of the wire, assuming the material’s resistivity and the wire’s length remain constant.
Why Cross-Sectional Area Affects Resistance
The relationship between the cross-sectional area of a wire and its resistance can be explained by two primary factors:
- Increased Conductive Pathways: A larger cross-sectional area provides more paths for electrons to flow through the wire, reducing the likelihood of collisions with atoms and resulting in a lower resistance.
- Reduced Current Density: A larger cross-sectional area distributes the flow of electric current over a wider area, reducing current density and lowering the resistance.
Practical Implications
Understanding the relationship between wire cross-sectional area and resistance has important practical implications:
- Energy Loss: Wires with larger cross-sectional areas have lower resistance, reducing energy loss in the form of heat and increasing the efficiency of electrical systems.
- Wire Sizing: Selecting the appropriate wire size for specific applications is essential to ensure efficient and safe operation. Wires with larger cross-sectional areas can handle higher currents with lower resistance, making them suitable for high-power applications.
In conclusion, the cross-sectional area of a wire plays a significant role in determining its resistance, with larger areas resulting in lower resistance. This relationship, governed by Ohm’s law, can be attributed to increased conductive pathways and reduced current density. A thorough understanding of the effects of wire cross-sectional area on resistance is crucial for designing efficient and safe electrical systems.