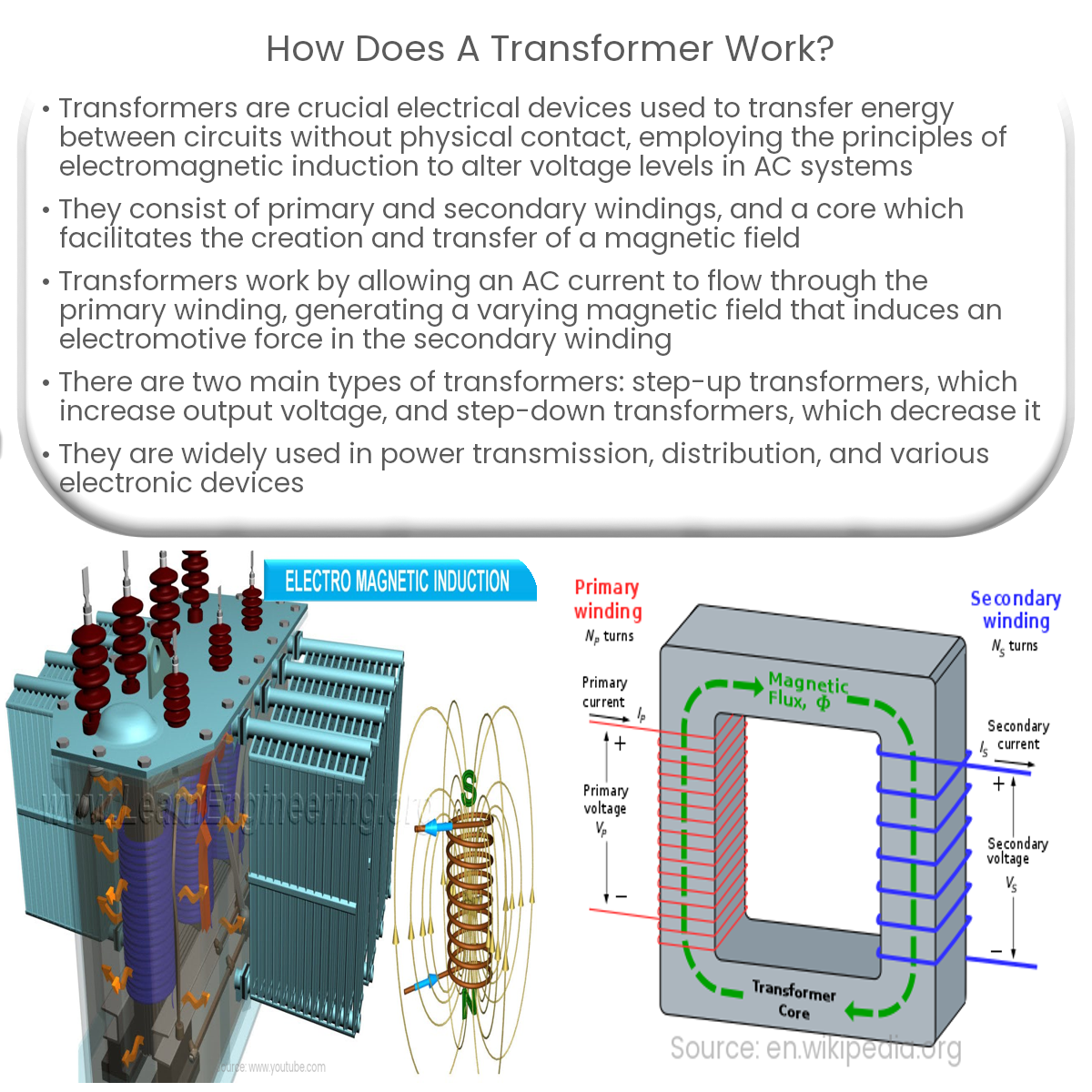
A transformer works by using electromagnetic induction to transfer energy between two coils, altering voltage levels in alternating current systems.
Introduction to Transformers
A transformer is an electrical device used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits without physical contact. It operates based on the principles of electromagnetic induction and is commonly used to change voltage levels in alternating current (AC) systems. In this article, we will discuss the working of a transformer and its essential components.
Components of a Transformer
A transformer consists of the following main components:
- Primary winding: This is a coil of wire connected to the input voltage source. The AC current flowing through the primary winding creates a varying magnetic field.
- Secondary winding: Another coil of wire, physically separated from the primary winding but wound around the same core, is connected to the load circuit.
- Core: A magnetic core made from laminated iron or steel provides a low reluctance path for the magnetic field generated by the primary winding.
Working Principle of a Transformer
A transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which states that a varying magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor. The working of a transformer can be summarized in the following steps:
- An AC current flows through the primary winding, creating a varying magnetic field around the core.
- The varying magnetic field links with the secondary winding through the core, inducing an EMF in the secondary winding.
- The induced EMF in the secondary winding is proportional to the turns ratio (N2/N1), where N1 and N2 are the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings, respectively.
- The secondary winding provides the transformed voltage to the load circuit.
Types of Transformers
Transformers can be classified into two main types based on their construction and application:
- Step-up transformer: Increases the output voltage by having more turns in the secondary winding than in the primary winding.
- Step-down transformer: Decreases the output voltage by having fewer turns in the secondary winding than in the primary winding.
Conclusion
Transformers are essential devices in electrical systems, allowing for the transfer of electrical energy between circuits without direct contact. They work on the principles of electromagnetic induction and are used to step-up or step-down voltage levels in AC systems. With their versatile applications, transformers play a crucial role in power transmission, distribution, and various electronic devices.