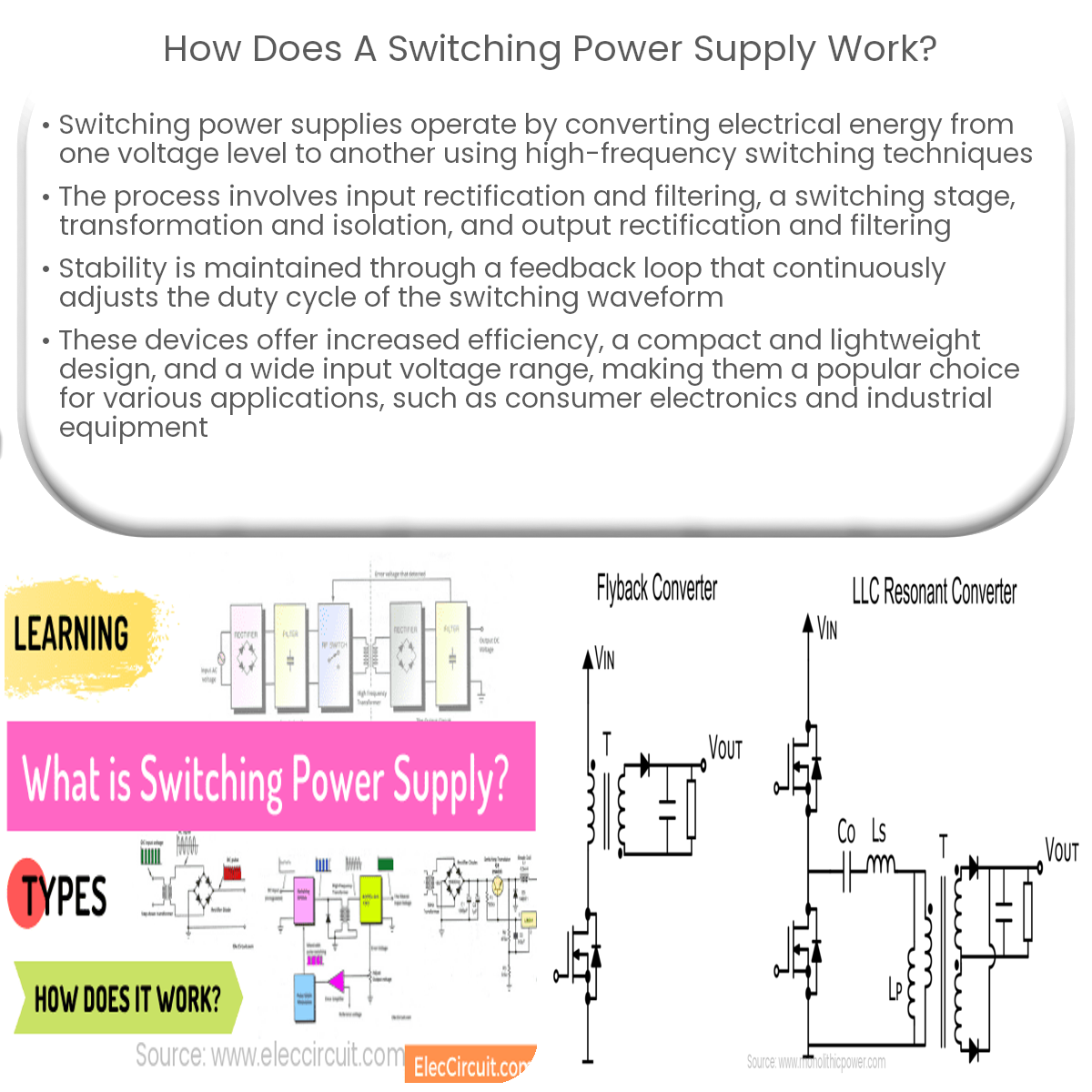
A switching power supply works by rapidly turning transistors on and off, transforming and filtering the high-frequency waveform to produce a stable output voltage.
Understanding Switching Power Supply Operation
A switching power supply is an efficient and compact device that converts electrical energy from one voltage level to another using high-frequency switching techniques. This article explores the operation of a switching power supply in detail.
Key Stages of Operation
The operation of a switching power supply can be broken down into several key stages:
- Input rectification and filtering: The input AC voltage is first converted into a DC voltage using a rectifier. A filter capacitor is used to smooth out any voltage fluctuations and remove noise.
- Switching stage: At this stage, high-frequency switching transistors rapidly turn on and off, controlling the flow of energy to the output. The duty cycle of the switching waveform determines the output voltage.
- Transformation and isolation: The high-frequency switching waveform is passed through a transformer, which steps up or steps down the voltage depending on the desired output level. The transformer also provides galvanic isolation between the input and output circuits for safety and noise reduction.
- Output rectification and filtering: The transformed high-frequency waveform is rectified and filtered to produce a stable DC output voltage. This stage often includes a regulator to maintain a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage and load current.
Feedback and Regulation
To ensure a stable output voltage, switching power supplies use a feedback mechanism that continuously monitors the output and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching waveform accordingly. This feedback loop is typically implemented using an error amplifier and a pulse-width modulation (PWM) controller, which compare the output voltage with a reference voltage and adjust the switching duty cycle to maintain a stable output.
Advantages of High-Frequency Switching
The high-frequency switching operation offers several benefits in a switching power supply:
- Increased efficiency: By minimizing energy dissipation as heat, switching power supplies can achieve efficiencies between 85% and 95%.
- Compact size and lightweight: The use of smaller transformers and filter components at high frequencies results in a more compact and lightweight design.
- Wide input voltage range: Switching power supplies can handle a broad range of input voltages, making them suitable for global applications.
Conclusion
Switching power supplies work by rapidly turning transistors on and off, creating a high-frequency switching waveform that is transformed, rectified, and filtered to produce a stable output voltage. The efficient and compact nature of switching power supplies makes them a popular choice for various applications, including consumer electronics, telecommunications, and industrial equipment.