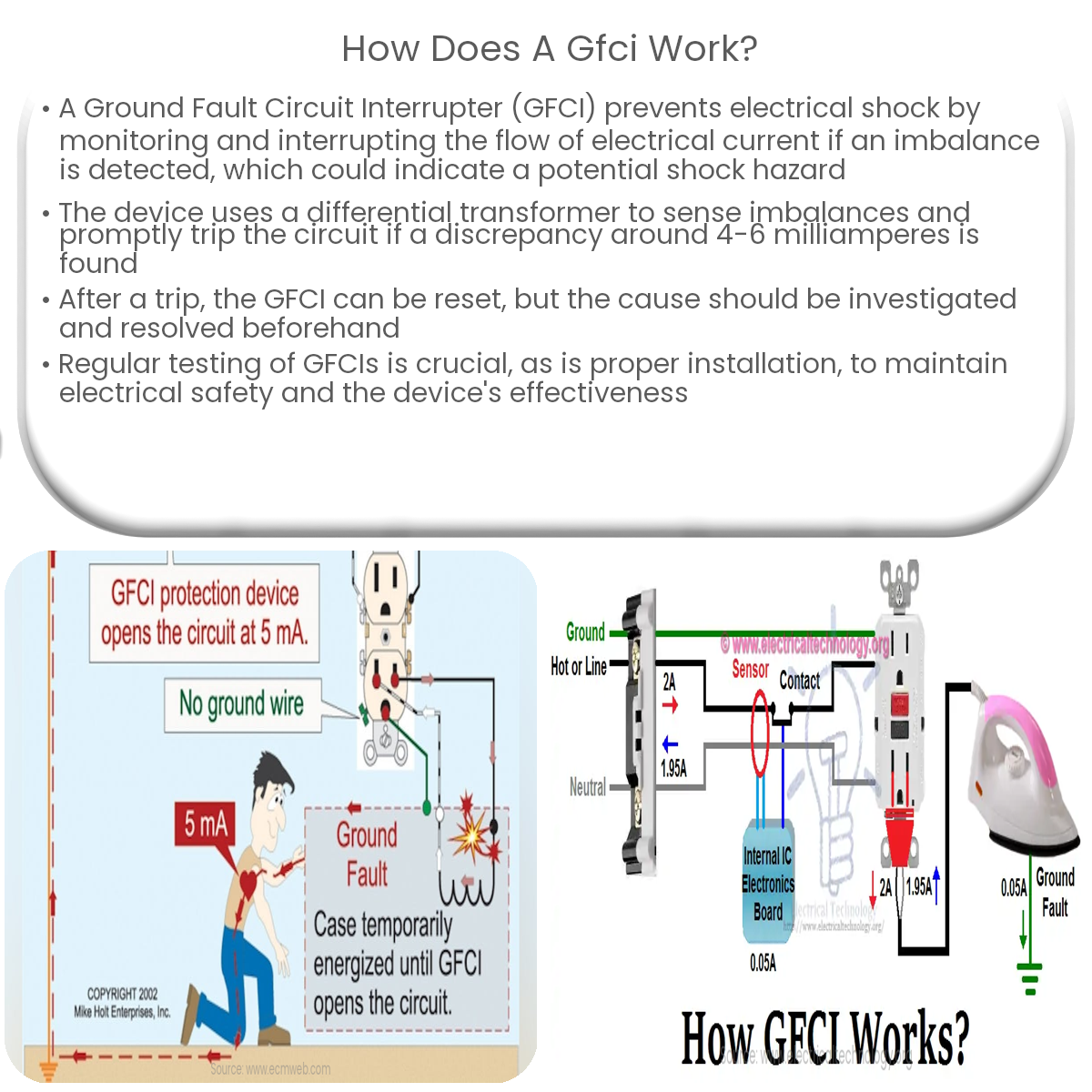
A GFCI works by monitoring current flow between hot and neutral wires, detecting imbalances, and quickly interrupting the circuit to prevent shock.
How Does a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Work?
A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) is an essential safety device designed to prevent electrical shock by quickly detecting ground faults and interrupting the flow of electrical current. In this article, we will explore the inner workings of a GFCI and explain how it provides protection against electrical hazards.
1. Principle of Operation
The primary function of a GFCI is to monitor the flow of electrical current between the hot (live) and neutral wires in a circuit. In a balanced circuit, the current flowing through the hot wire should equal the current returning through the neutral wire. If the GFCI detects an imbalance, it assumes that the current is leaking through an unintended path, such as a person’s body or a damaged appliance, which could lead to electrical shock.
2. Sensing Imbalance and Tripping Mechanism
A GFCI uses a differential transformer to continuously monitor the current flowing through the hot and neutral wires. If it detects an imbalance of typically around 4-6 milliamperes, the GFCI’s internal circuitry activates a tripping mechanism that interrupts the circuit within milliseconds, preventing electrical shock.
3. Resetting the GFCI
After tripping, the GFCI can be reset using the “reset” button located on the device. This restores the electrical connection and allows the GFCI to continue monitoring the circuit. It is important to investigate the cause of the GFCI trip and resolve any issues before resetting the device to ensure continued safety.
4. Testing Functionality
GFCIs should be tested regularly to ensure they are functioning correctly. Most GFCIs feature a “test” button that, when pressed, simulates a ground fault and causes the device to trip. If the GFCI trips as expected, it is functioning correctly. If it fails to trip, the device should be replaced immediately to maintain electrical safety.
5. GFCI Limitations
While GFCIs provide significant protection against electrical shock, they do have some limitations. For example, GFCIs may not protect against all types of electrical hazards, such as those caused by contact with both the hot and neutral wires simultaneously. Additionally, GFCIs may not function correctly if improperly installed or if the circuit’s grounding is inadequate. Therefore, proper installation and maintenance of electrical systems are essential to ensure comprehensive safety.
Conclusion
A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) works by continuously monitoring the flow of electrical current in a circuit and quickly interrupting it if an imbalance is detected. This rapid response helps prevent electrical shock and enhances the safety of electrical systems in homes, workplaces, and other environments. Regular testing and proper installation of GFCIs are crucial to maintaining their effectiveness and ensuring electrical safety.

.png)


