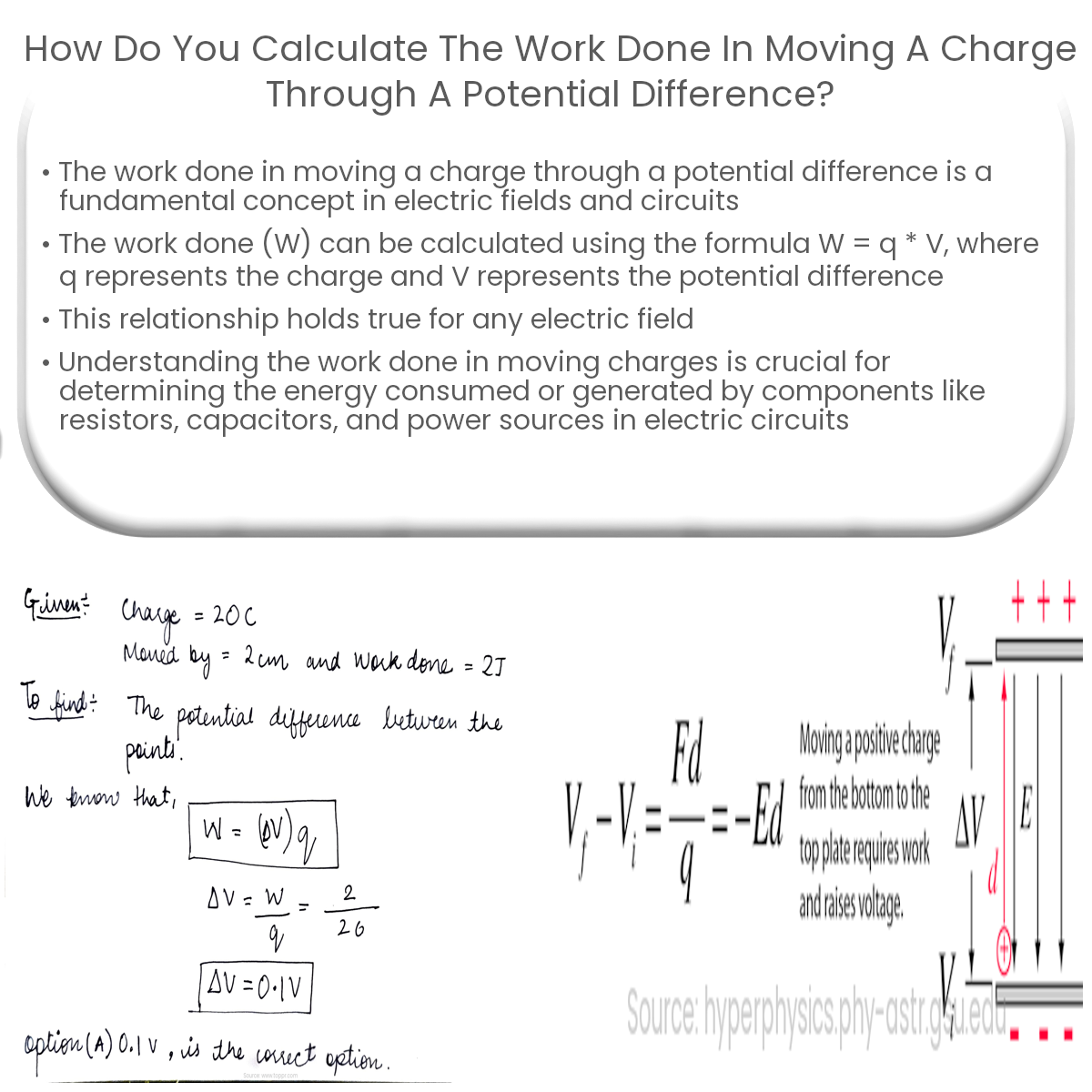
To calculate the work done in moving a charge through a potential difference, use the formula W = q * V, where W is work, q is charge, and V is voltage.
Calculating Work Done in Moving a Charge Through a Potential Difference
The work done in moving a charge through a potential difference (or voltage) is a fundamental concept in the study of electric fields and circuits. In this article, we’ll explore how to calculate the work done when a charge moves through a potential difference.
Electric Work and Potential Difference
In an electric field, the work done on a charged particle is the product of the electric force acting on the particle and the distance it moves. When a charge moves in an electric field, the potential difference (or voltage) between two points is the amount of work per unit charge required to move the charge from one point to another.
Mathematically, the work done (W) in moving a charge (q) through a potential difference (V) can be expressed as:
W = q * V
Example Calculation
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the calculation of work done in moving a charge through a potential difference. Suppose we have a charge of 3 x 10-6 C (3 microcoulombs) and it moves through a potential difference of 12 V. To calculate the work done, we can use the formula mentioned above:
W = q * V
W = (3 x 10-6 C) * (12 V)
Upon calculating the result, we find that:
W = 3.6 x 10-5 J (36 microjoules)
Thus, the work done in moving the 3-microcoulomb charge through a 12-volt potential difference is 36 microjoules.
Key Points to Remember
- The work done in moving a charge through a potential difference is the product of the charge and the potential difference.
- This relationship holds true for any electric field, whether it is a uniform field or a complex field with varying potential differences.
- In practical applications, such as electric circuits, understanding the work done in moving charges helps in determining the energy consumed or generated by components like resistors, capacitors, and power sources.
In summary, calculating the work done in moving a charge through a potential difference is a crucial aspect of understanding and analyzing electric fields and circuits. By using the formula W = q * V, we can easily determine the work done for any given charge and potential difference.