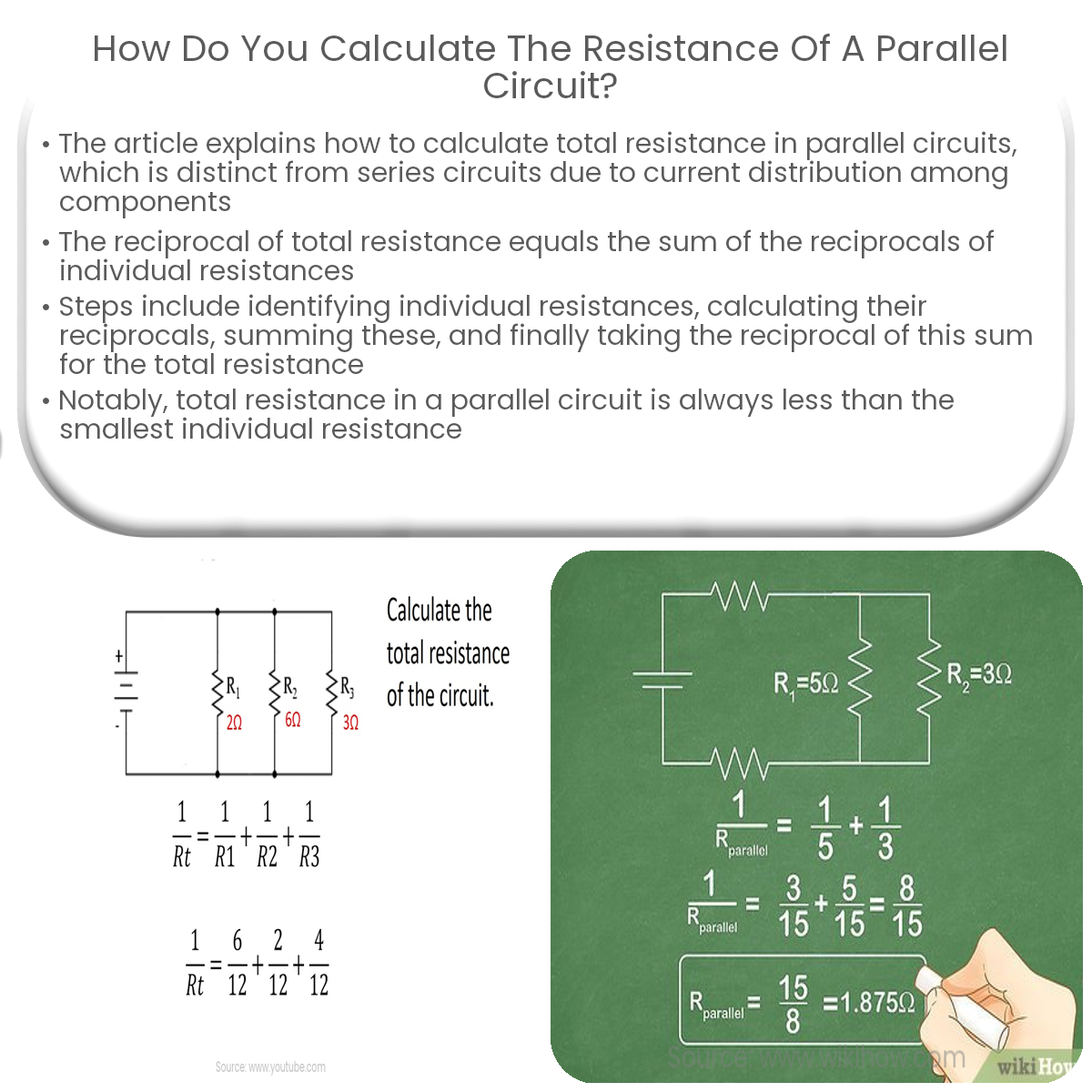
In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is calculated using the formula: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn. RT is the total resistance, and R1, R2, etc. are individual resistances.
Calculating Resistance in Parallel Circuits
In a parallel circuit, multiple components are connected in parallel, meaning that their terminals are connected to the same points in the circuit. This allows current to flow through multiple paths, distributing the current among the components. The total resistance in a parallel circuit is unique and differs from that of a series circuit. In this article, we’ll explore the method for calculating the total resistance of a parallel circuit.
Formula for Resistance in Parallel Circuits
For a parallel circuit, the reciprocal of the total resistance (1/RT) is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances (1/R1, 1/R2, …, 1/Rn). This relationship can be expressed by the following formula:
1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn
Steps to Calculate Resistance in a Parallel Circuit
- First, identify the individual resistances (R1, R2, …, Rn) of each component in the parallel circuit.
- Next, calculate the reciprocal of each resistance (1/R1, 1/R2, …, 1/Rn).
- Sum the reciprocals to obtain the reciprocal of the total resistance (1/RT). Use the formula mentioned above:
- Finally, find the reciprocal of the sum to obtain the total resistance (RT):
1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn
RT = 1 / (1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn)
Following these steps will provide the total resistance for a parallel circuit. It is important to remember that the total resistance in a parallel circuit is always less than the smallest individual resistance, as the current has multiple paths to flow through.