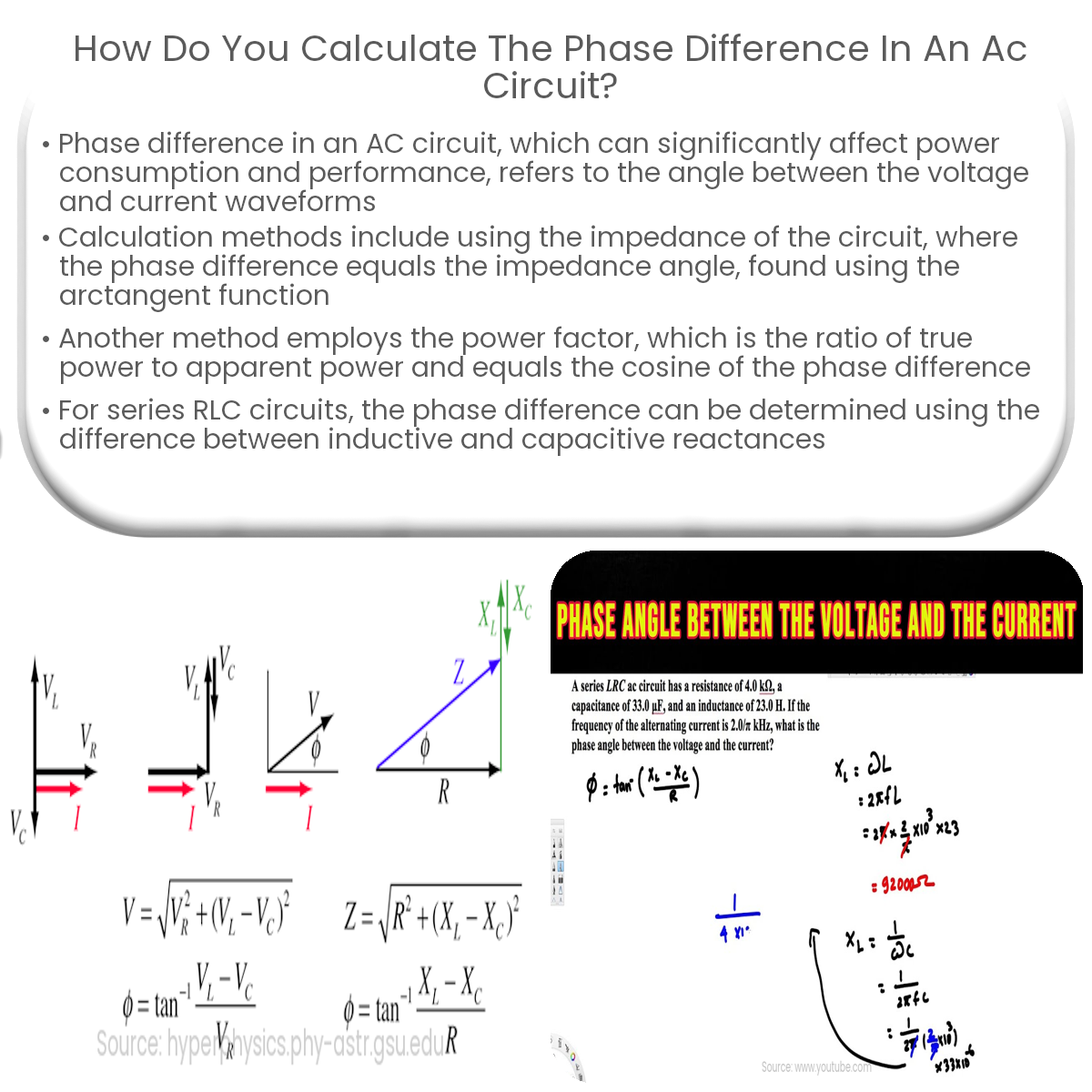
To calculate phase difference in an AC circuit, use the arctangent function with the net reactance and resistance: φ = arctan(Xnet/R).
Calculating Phase Difference in an AC Circuit
Phase difference in an alternating current (AC) circuit refers to the angle between the voltage and current waveforms. This angle has a crucial impact on power consumption and overall circuit performance. This article explains the methods used to calculate the phase difference in an AC circuit.
Understanding Phase Difference
In an AC circuit, voltage and current waveforms oscillate sinusoidally. When these waveforms are perfectly in sync, their peaks and troughs align, indicating no phase difference. However, when they are out of sync, the phase difference arises. The phase difference, usually represented by the Greek letter phi (φ), is measured in degrees or radians and can range from 0° to 360°, or 0 to 2π radians.
Calculating Phase Difference Using Impedance
In an AC circuit with resistive, inductive, and capacitive components, the phase difference between voltage and current can be found using the impedance (Z) of the circuit. Impedance is a complex quantity that combines resistance (R) and reactance (X), and it is represented as:
Z = R + jX
Here, j is the imaginary unit. The impedance angle (θ) can be found using the arctangent function:
θ = arctan(X/R)
The phase difference (φ) is equal to the impedance angle:
φ = θ
Using Power Factor
Another method to determine the phase difference is by using the power factor (PF). The power factor is the ratio of true power (P) to apparent power (S), and is also equal to the cosine of the phase difference:
PF = P/S = cos(φ)
To find the phase difference, the inverse cosine (arccos) function is used:
φ = arccos(PF)
Phase Difference in RLC Circuits
In a series RLC circuit, the phase difference can be found using the reactance values of the inductor (XL) and capacitor (XC). The net reactance (Xnet) is the difference between inductive and capacitive reactances:
Xnet = XL – XC
Then, the phase difference is calculated using the arctangent function:
φ = arctan(Xnet/R)
Understanding and calculating phase difference in AC circuits is essential for analyzing circuit behavior and optimizing power consumption. By using impedance, power factor, or reactance values, the phase difference can be easily determined.