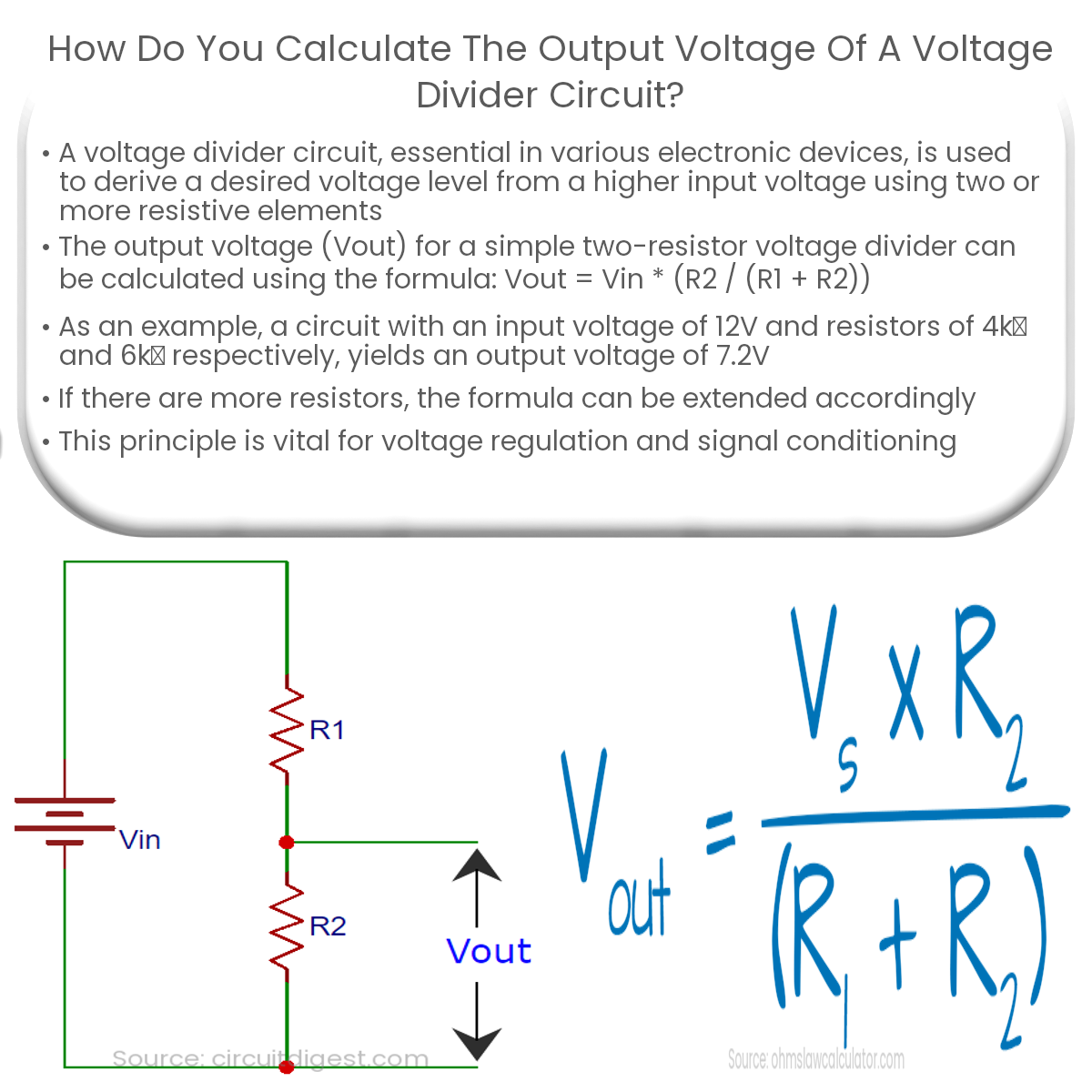
To calculate the output voltage of a voltage divider, use the formula: Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2)), where Vin is input voltage, and R1 and R2 are resistances.
Calculating the Output Voltage of a Voltage Divider Circuit
A voltage divider circuit is a simple yet essential component in various electronic devices, used to create a desired voltage level from a higher input voltage. It consists of two or more resistive elements connected in series. To calculate the output voltage of a voltage divider circuit, you must understand the relationship between the input voltage, the resistances involved, and the output voltage.
Basic Voltage Divider Formula
The most common voltage divider circuit consists of two resistors connected in series. The output voltage is taken across the second resistor, and the input voltage is applied across both resistors. The formula to calculate the output voltage (Vout) for a simple two-resistor voltage divider is as follows:
Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
Where:
- Vin is the input voltage.
- R1 is the resistance of the first resistor.
- R2 is the resistance of the second resistor.
Example
Let’s consider a voltage divider circuit with an input voltage of 12V, a first resistor (R1) of 4kΩ, and a second resistor (R2) of 6kΩ. To find the output voltage, plug the values into the voltage divider formula:
Vout = 12V * (6kΩ / (4kΩ + 6kΩ))
Vout = 12V * (6kΩ / 10kΩ)
Vout = 12V * 0.6
Vout = 7.2V
In this example, the output voltage is 7.2V.
Multiple Resistors in Series
If there are more than two resistors in the voltage divider circuit, the output voltage can be calculated by extending the basic formula. For a voltage divider with ‘n’ resistors, the output voltage across the nth resistor is given by:
Vout,n = Vin * (Rn / (R1 + R2 + … + Rn))
In conclusion, calculating the output voltage of a voltage divider circuit is a straightforward process using the voltage divider formula. This fundamental principle is widely employed in electronic devices for voltage regulation and signal conditioning applications.