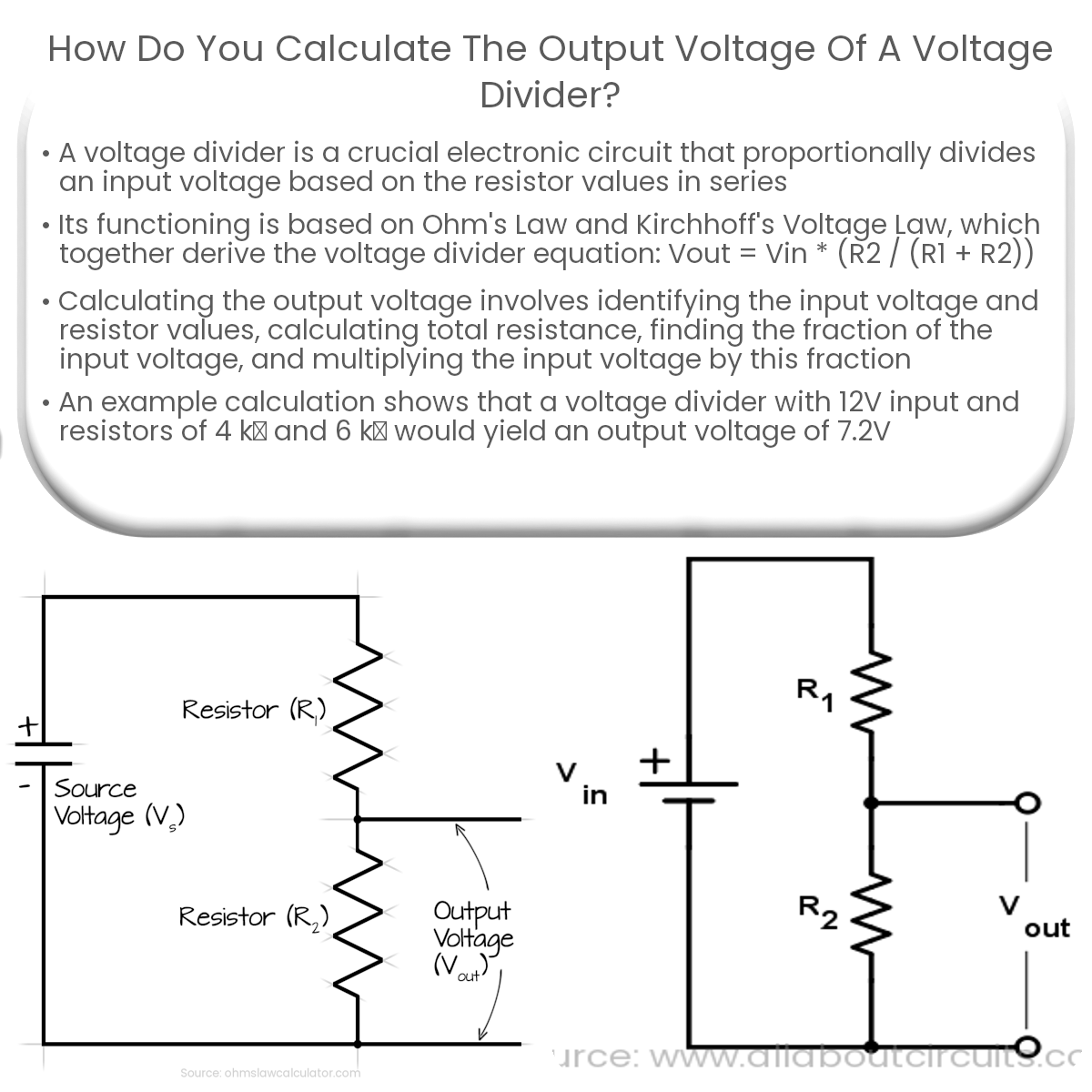
To calculate the output voltage of a voltage divider, use the equation Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2)), where Vin is the input voltage, and R1 and R2 are resistors.
Calculating the Output Voltage of a Voltage Divider
A voltage divider is an essential electronic circuit that proportionally divides an input voltage based on the values of resistors connected in series. To calculate the output voltage of a voltage divider, we need to understand the voltage divider equation and the principle behind it.
Voltage Divider Principle
The voltage divider circuit consists of two or more resistors connected in series between the input voltage (Vin) and ground. The output voltage (Vout) is measured across one of the resistors, typically the one connected to ground. The principle of the voltage divider is based on Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law.
Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a resistor is proportional to the current flowing through it and its resistance:
V = I * R
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law states that the sum of the voltages around a closed loop is equal to zero:
Vin – VR1 – VR2 = 0
Voltage Divider Equation
Using Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law, we can derive the voltage divider equation for a circuit with two resistors, R1 and R2:
Vout = Vin * (R2 / (R1 + R2))
Calculating the Output Voltage
With the voltage divider equation, we can calculate the output voltage by following these steps:
- Identify the input voltage (Vin) and the resistor values (R1 and R2).
- Calculate the total resistance of the series resistors (R1 + R2).
- Find the fraction of the input voltage by dividing R2 by the total resistance (R2 / (R1 + R2)).
- Multiply the input voltage (Vin) by the fraction obtained in the previous step to get the output voltage (Vout).
By following these steps, you can calculate the output voltage of any simple voltage divider circuit.
Example Calculation
Let’s consider a voltage divider circuit with an input voltage of 12V, R1 equal to 4 kΩ, and R2 equal to 6 kΩ. Applying the voltage divider equation:
Vout = 12V * (6 kΩ / (4 kΩ + 6 kΩ))
Vout = 12V * (6/10) = 7.2V
In this example, the output voltage of the voltage divider circuit is 7.2V.
In conclusion, calculating the output voltage of a voltage divider is a straightforward process that requires understanding the voltage divider equation and applying Ohm’s Law and Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law principles.