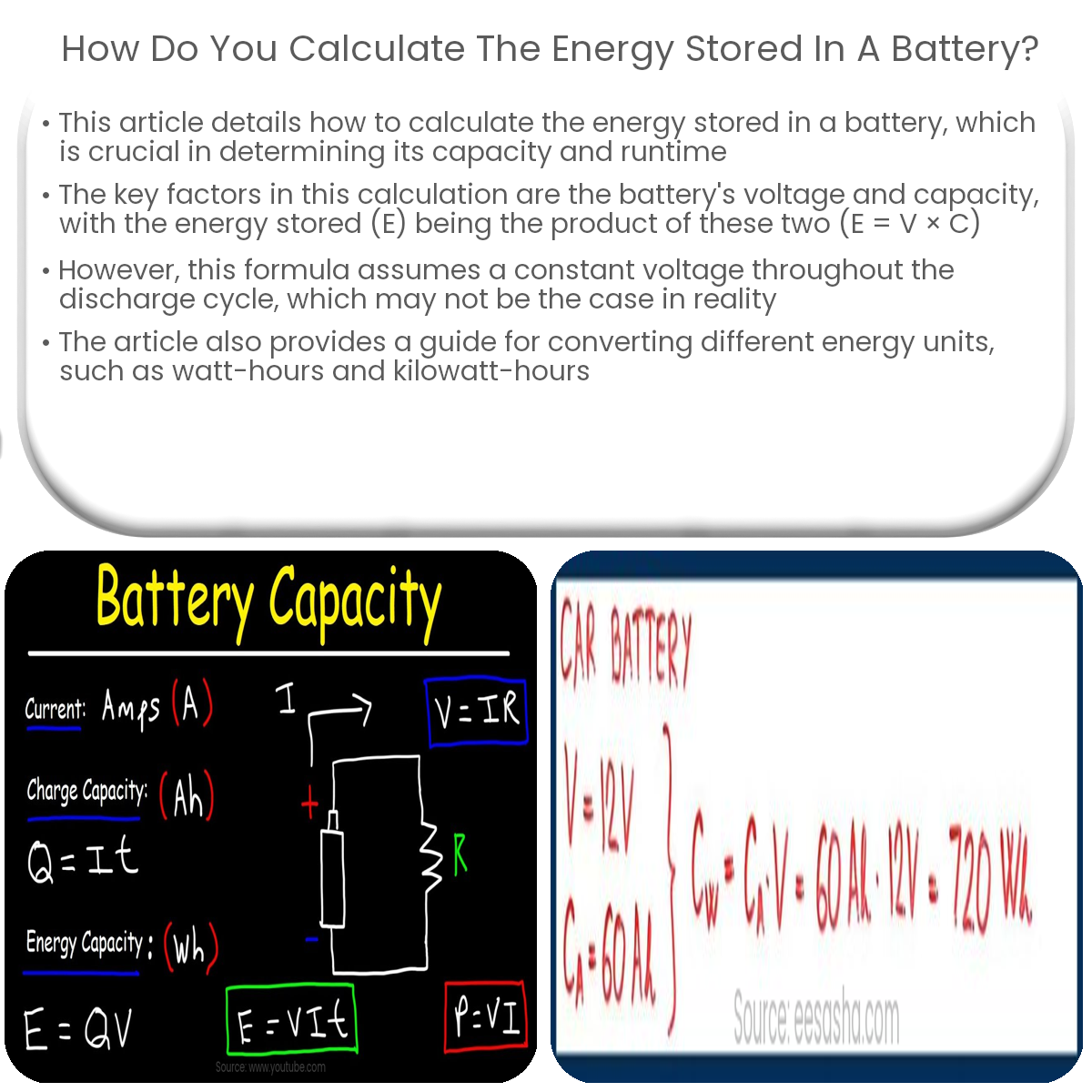
To calculate the energy stored in a battery, multiply the battery’s voltage (V) by its capacity (Ah): Energy (Wh) = Voltage (V) × Capacity (Ah).
Calculating the Energy Stored in a Battery
Understanding the energy stored in a battery is crucial for determining its capacity and runtime for various applications. This article will guide you through the process of calculating the energy stored in a battery.
Key Concepts
There are three primary factors to consider when calculating the energy stored in a battery:
- Voltage (V): The electric potential difference between the battery’s positive and negative terminals, typically measured in volts (V).
- Capacity (C): The total charge the battery can hold, typically measured in ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh).
- Energy (E): The total amount of energy stored in the battery, typically measured in watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Calculating Energy Stored
To calculate the energy stored in a battery, use the following formula:
E = V × C
Where E is the energy stored, V is the battery’s voltage, and C is the battery’s capacity.
Keep in mind that this formula assumes a constant voltage throughout the battery’s discharge cycle. In reality, the voltage may vary as the battery discharges, leading to a slightly different energy calculation. However, this formula provides a good approximation for most applications.
Example Calculation
Let’s calculate the energy stored in a 12V battery with a capacity of 50Ah:
- Identify the battery’s voltage (V) and capacity (C): V = 12V and C = 50Ah.
- Use the formula E = V × C to calculate the energy stored: E = 12V × 50Ah = 600Wh.
In this example, the energy stored in the 12V, 50Ah battery is 600 watt-hours (Wh).
Converting Units
If you need to convert energy values to different units, use the following conversions:
- 1 watt-hour (Wh) = 1,000 milliwatt-hours (mWh)
- 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) = 1,000 watt-hours (Wh)
- 1 ampere-hour (Ah) = 1,000 milliampere-hours (mAh)
Conclusion
Calculating the energy stored in a battery is a straightforward process that involves multiplying the battery’s voltage and capacity. This information is valuable for determining the battery’s runtime and suitability for different applications. Keep in mind that the actual energy stored may vary slightly due to changes in voltage throughout the discharge cycle.