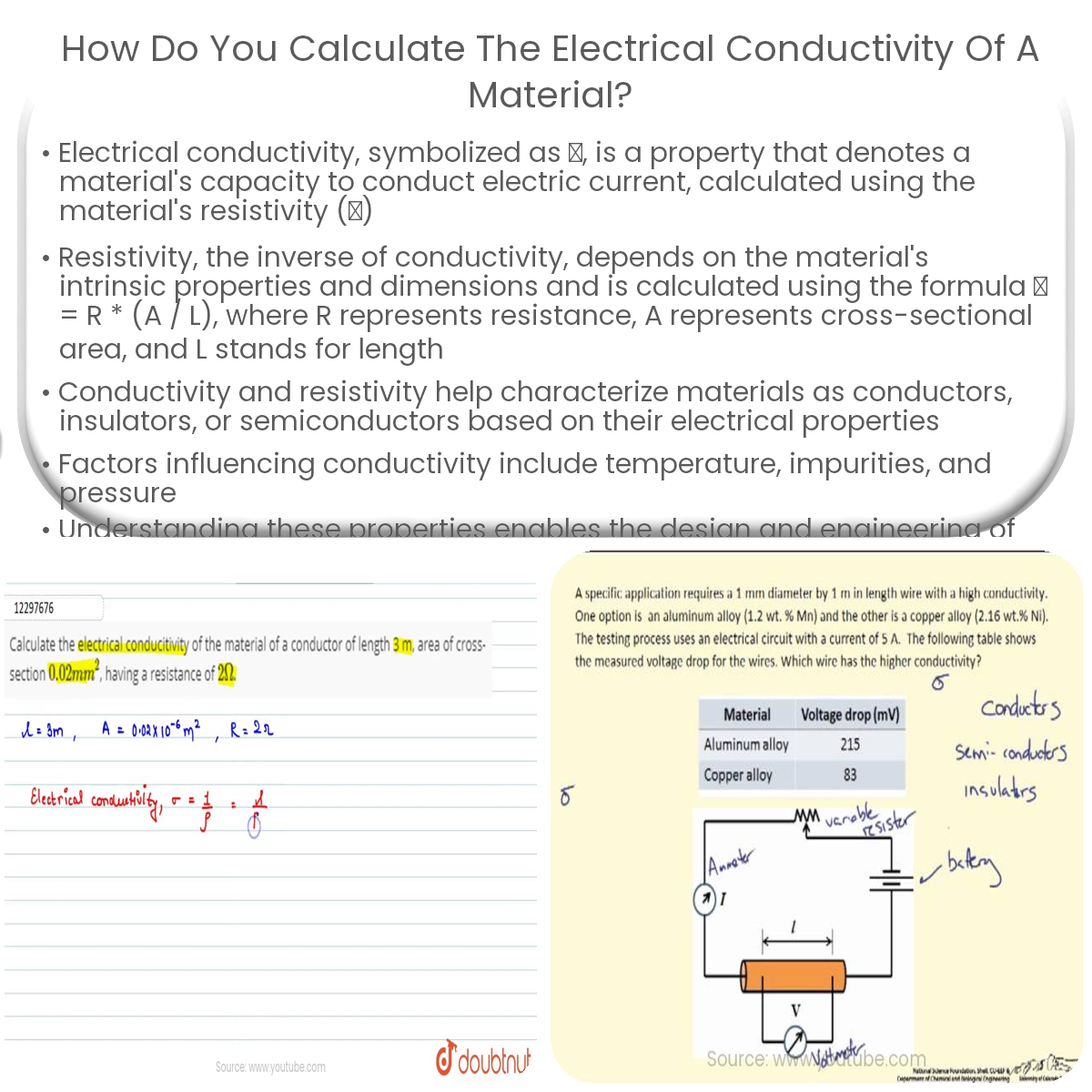
To calculate electrical conductivity, first determine the material’s resistivity (ρ) using ρ = R*(A/L), then find conductivity (σ) using σ = 1/ρ.
Calculating Electrical Conductivity of a Material
Electrical conductivity, represented by the symbol σ, is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct electric current. It is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity (ρ), which describes the opposition of a material to the flow of electric current. To calculate the electrical conductivity, we need to know the material’s resistivity and use the following formula:
σ = 1 / ρ
Determining Resistivity
Resistivity depends on both the material’s intrinsic properties and its dimensions. It can be calculated using the formula:
ρ = R * (A / L)
Where:
- R is the electrical resistance of the material (measured in ohms)
- A is the cross-sectional area of the material (measured in square meters)
- L is the length of the material (measured in meters)
By measuring resistance, area, and length, we can calculate the resistivity and subsequently the conductivity.
Using Resistivity and Conductivity to Characterize Materials
Resistivity and conductivity are useful for characterizing the electrical properties of various materials, including:
- Conductors: Materials with high electrical conductivity, such as metals like copper and silver, that readily allow the flow of electric current.
- Insulators: Materials with low electrical conductivity, such as rubber or glass, that resist the flow of electric current.
- Semiconductors: Materials with intermediate electrical conductivity, such as silicon or germanium, that can be manipulated to control the flow of electric current.
Factors Affecting Electrical Conductivity
Various factors can influence a material’s electrical conductivity, including:
- Temperature: Conductivity usually decreases with increasing temperature for conductors but increases for semiconductors and insulators.
- Impurities: The presence of impurities in a material can alter its conductivity, either by increasing or decreasing it, depending on the type of impurity.
- Pressure: Changes in pressure can affect the atomic structure of a material, which in turn can alter its conductivity.
Understanding how to calculate and analyze electrical conductivity allows us to design and engineer materials for various applications, such as electronics, power transmission, and energy storage.