Electromagnetic waves, such as light, radio waves, and microwaves, are an essential aspect of our daily lives. These waves propagate through various media, including vacuum, air, and solid materials.
How Electromagnetic Waves Propagate Through Different Media
Electromagnetic waves, such as light, radio waves, and microwaves, are an essential aspect of our daily lives. These waves propagate through various media, including vacuum, air, and solid materials. In this article, we will explore how electromagnetic waves travel through different media and how their speed and behavior change as they pass through these materials.
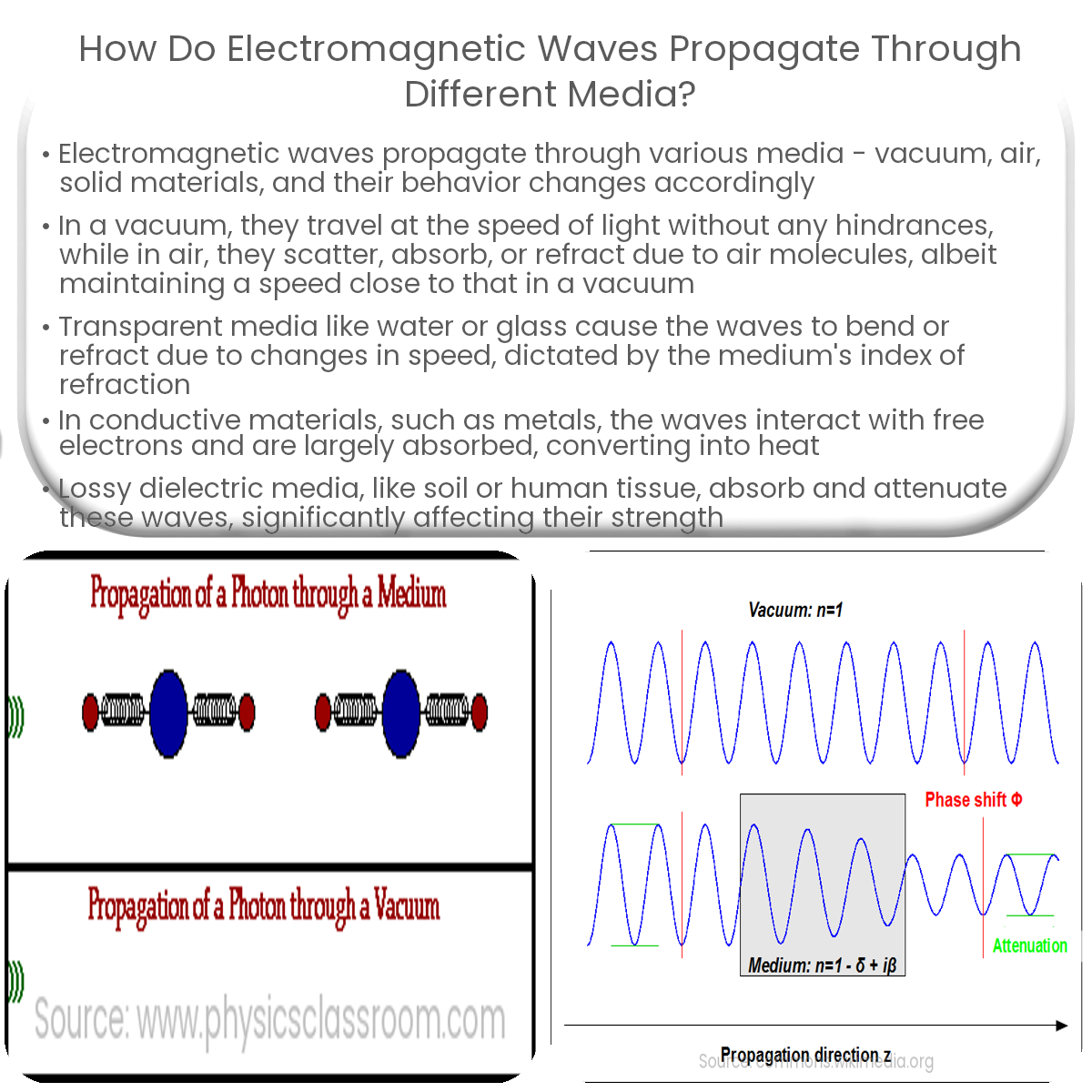
Propagation in Vacuum
Electromagnetic waves propagate most efficiently through a vacuum, traveling at the speed of light, approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (km/s). In a vacuum, there are no particles or obstacles to impede their path, allowing them to maintain their original speed and direction.
Propagation in Air
As electromagnetic waves pass through the Earth’s atmosphere, they encounter air molecules, which can cause them to scatter, absorb, or refract. Despite these interactions, their propagation speed remains close to that in a vacuum. The index of refraction for air is about 1.0003, which means the speed of light in air is roughly 299,702 km/s, just slightly slower than in a vacuum.
Propagation in Transparent Media
When electromagnetic waves enter a transparent medium, such as water or glass, their speed changes due to the medium’s index of refraction. This change in speed causes the waves to bend, a phenomenon known as refraction. The index of refraction for a given material is defined as the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the material.
- Water: Index of refraction ≈ 1.33, Speed ≈ 225,056 km/s
- Glass: Index of refraction ≈ 1.5, Speed ≈ 199,861 km/s
As the index of refraction increases, the speed of light within the material decreases, leading to more significant refraction.
Propagation in Conductive Media
Electromagnetic waves propagating through conductive materials, such as metals, interact with the free electrons in the material. This interaction causes the waves to be absorbed and converted into heat, significantly reducing their propagation speed and depth. Radio waves, for example, can penetrate only a few millimeters into a conductive material before being absorbed.
Propagation in Lossy Dielectric Media
Some materials, like soil or human tissue, are considered lossy dielectric media. These materials have a dielectric constant and a loss tangent that determines the degree to which electromagnetic waves are absorbed and attenuated. In these materials, the propagation of waves is significantly affected, with both attenuation and absorption playing a role in the decrease of wave strength as they travel through the medium.
In conclusion, electromagnetic waves’ propagation through different media is influenced by factors such as the medium’s index of refraction, dielectric constant, and loss tangent. Understanding how electromagnetic waves interact with various media is crucial in fields like telecommunications, optics, and medical imaging.