The Holtz Machine, a 19th-century invention by Wilhelm Holtz, generates high-voltage static electricity for research and inspired modern electrostatic devices.
The Revolutionary Holtz Machine: A Glimpse Into the Past
The Holtz Machine, a groundbreaking piece of technology from the 19th century, remains an essential part of the history of electromechanical devices. In this article, we will explore its origin, mechanism, and significance in the advancement of electrical engineering.
Origin and Inventor
Wilhelm Holtz, a German physicist born in 1836, is the mastermind behind the invention of the Holtz Machine. As an esteemed professor and researcher, Holtz dedicated his career to the study of electricity and magnetism. He first introduced the concept of the Holtz Machine in 1865, with the aim of generating high-voltage static electricity for various scientific experiments.
Design and Mechanism
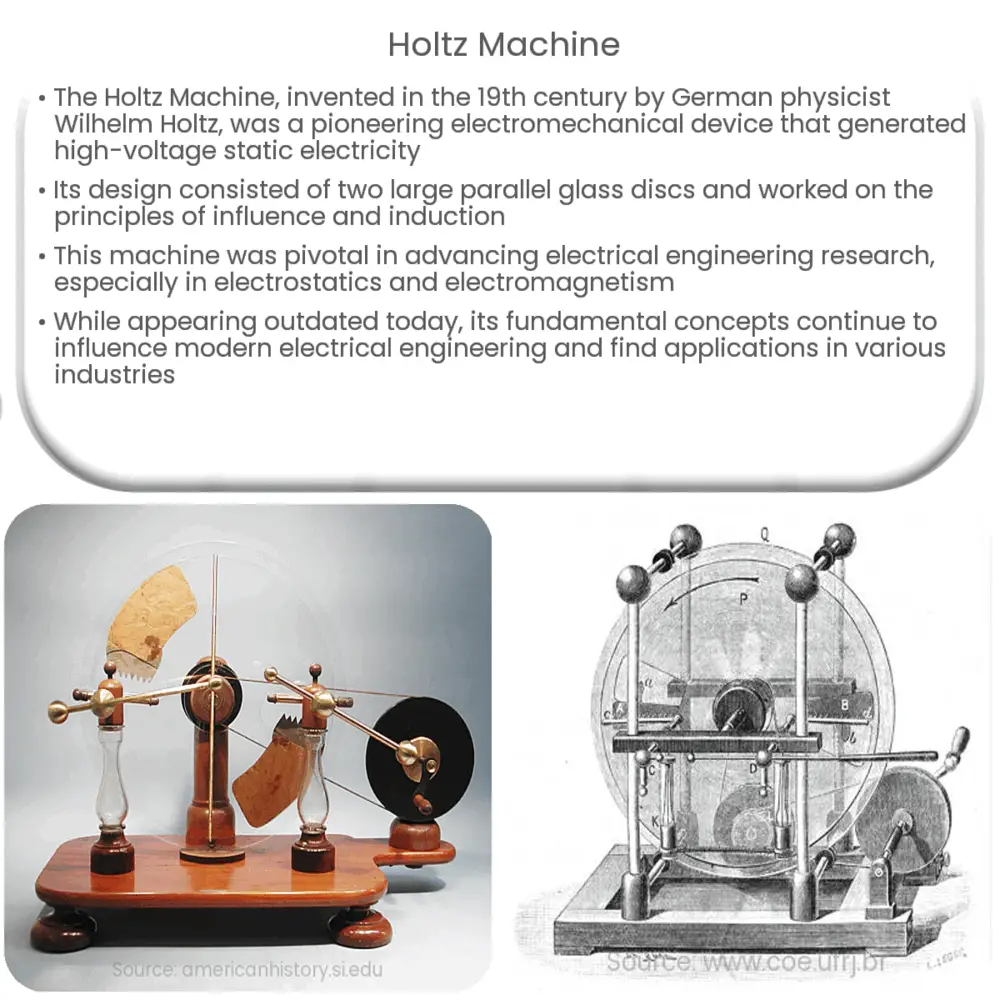
The Holtz Machine operates on the principle of influence and induction, enabling it to produce high-voltage static electricity. Its design consists of two large, parallel glass discs mounted on a common axis. One disc, the fixed disc, is mounted on an insulating stand, while the other, the rotating disc, is mounted on a spindle driven by a hand crank or an external motor. The fixed disc features two metal sectors, while the rotating disc has a number of equally spaced metal brushes.
As the rotating disc spins, the metal brushes come into close proximity with the metal sectors on the fixed disc. This causes an imbalance in the charge distribution, which, in turn, generates an electrostatic charge. A Leyden jar, an early form of capacitor, collects and stores the accumulated charge for later use or experimentation.
Applications and Significance
The Holtz Machine played a vital role in the advancement of electrical engineering during the 19th century. Its ability to generate high-voltage static electricity made it an essential tool for scientific research and experimentation, particularly in the fields of electrostatics, electromagnetism, and the study of atmospheric electricity.
Furthermore, the Holtz Machine paved the way for the development of more sophisticated electrostatic generators, such as the Wimshurst Machine and the Van de Graaff generator. These later inventions built upon the principles of the Holtz Machine, refining and enhancing its capabilities to produce even greater voltage potentials.
Though it may appear antiquated by today’s standards, the Holtz Machine remains an important milestone in the evolution of electrical engineering. Its ingenious design and functionality continue to inspire researchers and engineers, who draw upon its principles to develop new and innovative electromechanical devices for modern applications.
Legacy of the Holtz Machine
The Holtz Machine’s enduring legacy is evident in the study of electrostatics and its applications, even in contemporary times. Despite the emergence of newer and more advanced technologies, the machine’s fundamental principles and underlying concepts continue to influence modern research in electrical engineering.
For instance, the static electricity generated by the Holtz Machine and its successors has found practical applications in various industries. From air purifiers utilizing electrostatic precipitation to remove pollutants to the electrostatic coating processes used in manufacturing and painting, the principles behind the Holtz Machine remain relevant and valuable.
Preservation and Demonstration
Given its historical significance, several examples of the Holtz Machine are preserved in museums and scientific institutions worldwide. These artifacts serve as testaments to the ingenuity of 19th-century inventors and offer valuable insights into the development of electromechanical devices.
Many institutions also conduct demonstrations of the Holtz Machine to showcase its operation and educate the public about its importance in the history of electrical engineering. These interactive displays help people appreciate the marvels of early electromechanical technology and understand the foundational principles that underpin modern electrical devices.
Conclusion
The Holtz Machine, an impressive feat of 19th-century engineering, has left an indelible mark on the field of electrical engineering. Its innovative design, based on the principles of influence and induction, enabled it to generate high-voltage static electricity, which was crucial for scientific research and experimentation during its time.
Though the machine may be considered archaic in comparison to today’s advanced electromechanical devices, its core principles continue to hold relevance in modern applications. From inspiring the development of new electrostatic generators to finding practical uses in various industries, the Holtz Machine remains a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
In preserving and showcasing this remarkable invention, we not only pay homage to Wilhelm Holtz and his groundbreaking work, but we also inspire future generations of engineers and researchers to continue pushing the boundaries of electrical engineering and uncovering new technological wonders.

