Explore the crucial role of heatsinks in electronics, their types, selection process, and future prospects in our in-depth guide.
Understanding Heatsinks: An Integral Component of Modern Technology
Within the realm of electronics, one component stands out as essential for the longevity and reliability of a myriad of devices – the heatsink. This often-overlooked part plays an instrumental role in managing the heat produced by electronic components, ensuring that devices operate within their optimum temperature range. Without heatsinks, our beloved laptops, game consoles, and even sophisticated server machines would face significant performance degradation and potential failure.
What is a Heatsink?
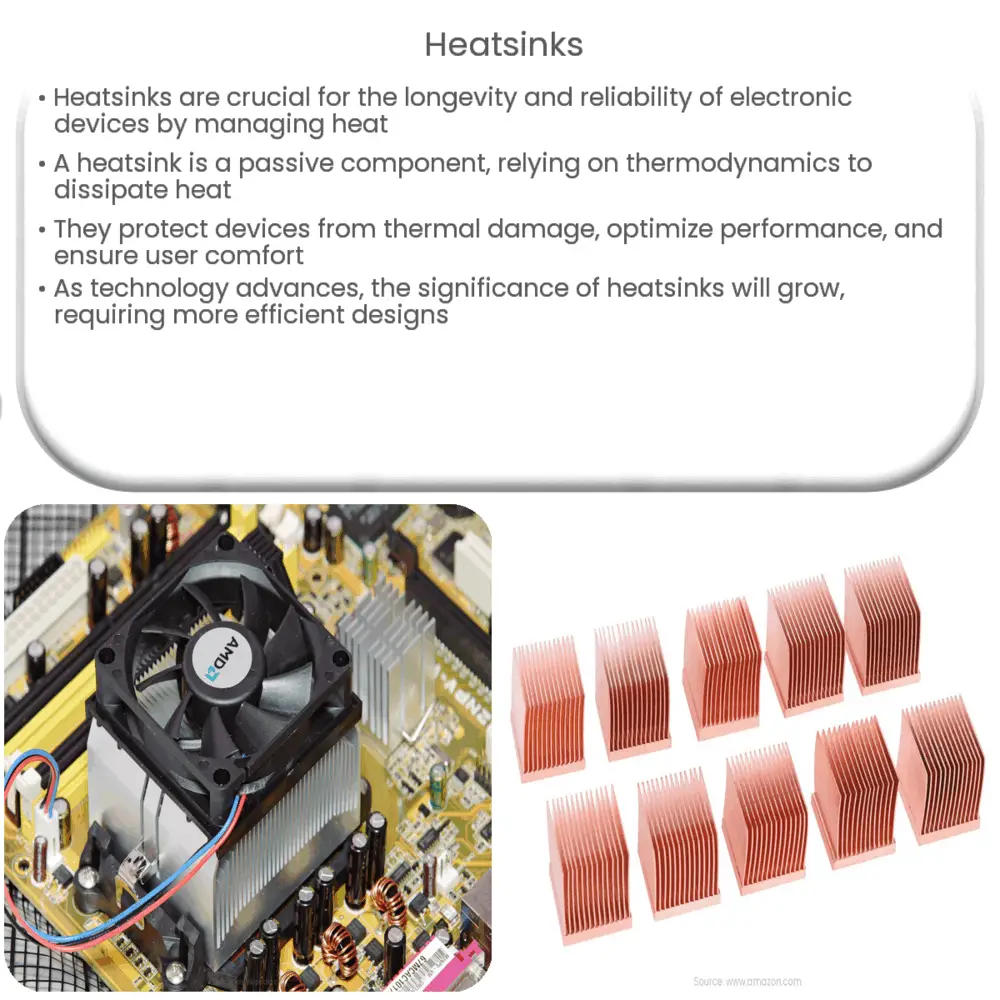
A heatsink is a passive heat exchanger that cools a device by dissipating heat into the surrounding air. It functions as a conduit, guiding heat away from a device’s crucial components. The term ‘passive’ here indicates that heatsinks do not have any mechanical components. They rely solely on the laws of thermodynamics to perform their function.
Why are Heatsinks Important?
-
Device Protection: Heatsinks shield sensitive components from thermal damage. Excess heat can lead to malfunctioning, decreased lifespan, and even the total failure of a device.
-
Performance Optimization: Many devices throttle their performance when they get too hot to prevent damage. By controlling the temperature, heatsinks help maintain peak performance.
-
Comfort: Electronic devices like laptops can become uncomfortably hot to touch without a heatsink’s cooling capabilities.
The Anatomy of a Heatsink
A typical heatsink consists of a base and an array of ‘fins.’ The base, usually a flat piece of metal, makes direct contact with the heat source (e.g., a computer’s CPU1 or GPU2). The fins, extending from the base, increase the surface area of the heatsink, allowing for efficient heat dissipation. The configuration and number of fins play a critical role in determining a heatsink’s cooling performance.
The material used to construct a heatsink also significantly impacts its efficiency. Metals like aluminum and copper are popular choices due to their excellent thermal conductivity. In some instances, a combination of both is used—copper for the base for its superior heat absorption and aluminum for the fins due to its lighter weight.
Heatsinks may seem simple, but the science behind them is a fascinating blend of physics, engineering, and materials science. In the next part of this article, we will delve deeper into the types of heatsinks, their design philosophies, and how to choose the right heatsink for your device.
1 CPU: Central Processing Unit
2 GPU: Graphics Processing Unit
Types of Heatsinks
Heatsinks come in several forms, each designed to cater to a particular need. Some common types include:
-
Active Heatsinks: Contrary to the ‘passive’ heatsinks described earlier, active heatsinks use a mechanical component, such as a fan, to enhance the cooling process by actively pushing hot air away.
-
Passive Heatsinks: These are typically made of an aluminum or copper block with fins. They dissipate heat solely through natural convection.
-
Liquid Coolers: Technically not a heatsink in the traditional sense, liquid coolers use water or another liquid to draw heat away from a device. This system includes a water block (which replaces a traditional heatsink), a radiator, and a fan.
Selecting the Right Heatsink
Choosing the right heatsink depends on various factors, such as the device you’re using, the environment it operates in, and the device’s thermal design power (TDP). A larger heatsink with more fins can generally dissipate more heat, but it might not fit inside a compact device. Similarly, active heatsinks may provide better cooling, but they also consume additional power and can produce noise. In contrast, passive heatsinks operate silently and require no power, making them ideal for low-power devices or quiet environments.
Heatsinks and Future Technology
As technology continues to evolve and more powerful devices emerge, the role of heatsinks will become increasingly significant. With power-dense components like quantum processors on the horizon, traditional heatsinks may need to evolve, becoming more efficient or perhaps transitioning towards advanced cooling systems, such as liquid or phase-change cooling. Understanding heatsinks is not just about appreciating current technology; it’s also about anticipating the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heatsinks serve as an unsung hero in our increasingly tech-dependent world. They protect our devices from the damaging effects of heat, ensuring that they can operate safely and effectively. As the demand for more powerful, smaller, and more efficient devices grows, so does the importance of these essential components. Next time you’re using your computer or gaming console, spare a thought for the humble heatsink, working tirelessly to keep your device cool and performing at its best.

