Explore the role, types, and applications of fiber optic couplers in telecommunications and data networks in our in-depth article.
Fiber Optic Couplers: An Insight
Fiber optic couplers are a critical element in the landscape of modern telecommunications and data networks. They serve an essential role in managing the flow of light, which is the fundamental unit of data in fiber optic systems. This article explores the function, types, and applications of fiber optic couplers in depth.
Understanding Fiber Optic Couplers
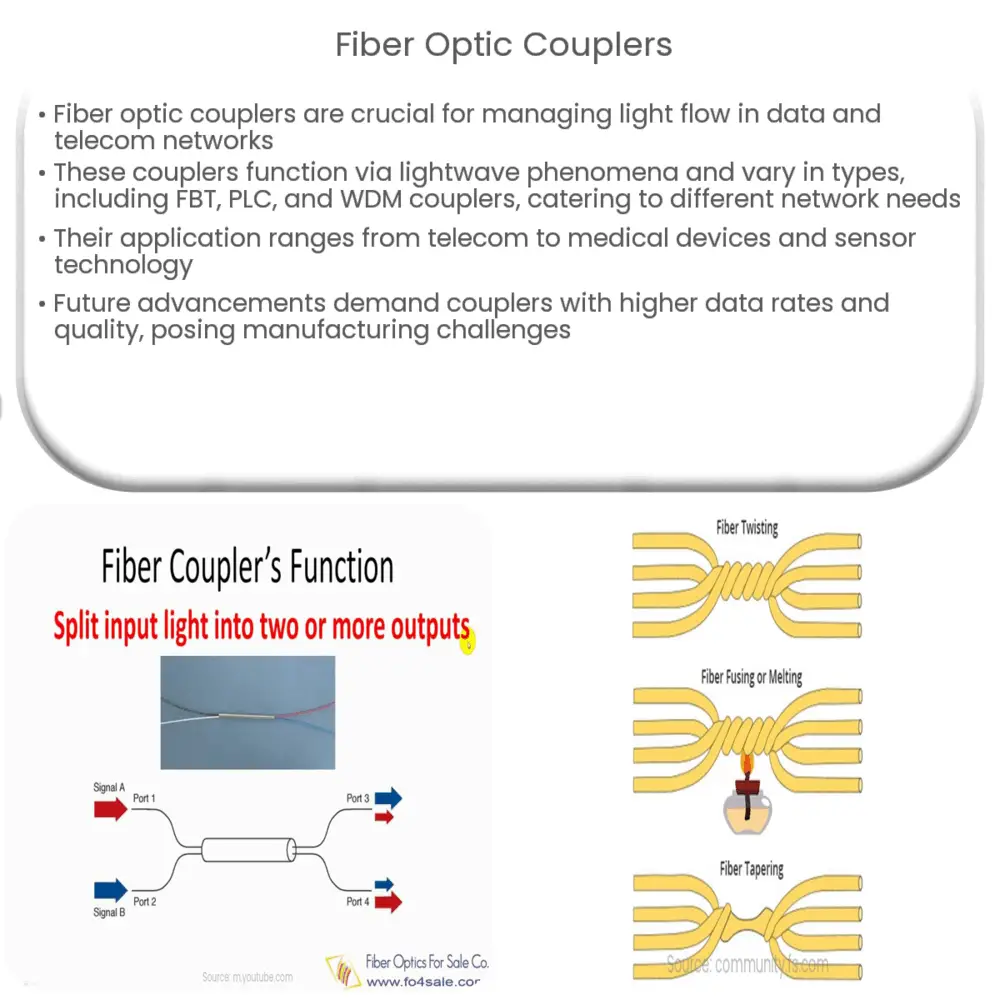
At a fundamental level, a fiber optic coupler is a device that distributes or combines optical signals (light) between two or more optical fibers. In simple terms, they serve as the ‘traffic managers’ of the light that carries information within the fiber optic network. The working principle of these couplers is based on the phenomena of lightwave technology, including refraction, reflection, and interference.
Types of Fiber Optic Couplers
- Fused Biconical Taper (FBT) Coupler: This type of coupler is one of the earliest and most common types. The process involves heating and elongating two or more fibers, causing them to fuse together and allowing the optical signal to split between the fibers.
- Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) Coupler: PLC couplers use an optical splitter chip to divide light between output fibers. They are known for their compact size and ability to split signals evenly across multiple outputs.
- Wavelength Division Multiplexers (WDM): WDM couplers operate by combining or separating light of different wavelengths. They’re pivotal in systems that require multiplexing and demultiplexing signals for effective data transmission.
Role of Fiber Optic Couplers in Network Architecture
Fiber optic couplers hold a pivotal role in shaping network architecture. They are integral in directing the flow of light, essentially controlling the distribution of data within the system. Depending on the nature of the network and the requirements of the system, different types of couplers may be employed. For instance, in a star network topology, multiport couplers are used to distribute the signals evenly across all connected nodes.
Similarly, for Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) systems, WDM couplers are used to combine or split different wavelength signals, thereby maximizing the data carrying capacity of the fiber. It’s also important to mention that couplers can be designed to work in either a single direction (splitter) or both directions (splitter/combiner), providing the flexibility necessary for diverse network architectures.
Applications of Fiber Optic Couplers
Given their central role in managing the flow of light within fiber optic networks, couplers find applications in a diverse array of fields. Some of the primary applications are detailed below:
- Telecommunications: With the increasing demand for high-speed data transmission, fiber optic couplers play an essential role in telecommunications, enabling efficient and high-volume data flow.
- Medical Devices: Fiber optic couplers are a crucial part of many medical devices, including endoscopes and laser surgery tools, where they guide light to the required areas.
- Sensor Technology: Couplers are integral to the operation of fiber optic sensors, which are employed in various industries for measuring parameters like temperature, pressure, and strain.
- Data Centers: The high-speed, high-volume data demands of modern data centers are met with the help of fiber optic couplers, which ensure efficient routing of light signals.
Future Prospects and Challenges
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the demands on fiber optic couplers. The future promises even faster data rates, increased need for signal quality, and further miniaturization of devices. However, these advancements also present challenges. Designing and manufacturing couplers that can meet these demands while maintaining cost-effectiveness and reliability will be a key hurdle to overcome.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fiber optic couplers are indispensable in today’s high-speed, data-driven world. From telecommunications to medical devices, their capacity to manage and direct the flow of light signals plays a crucial role in various fields. Despite the challenges that lie ahead, ongoing advancements in fiber optic technology promise to address these hurdles and further enhance the performance of these essential devices. As we move towards an increasingly connected world, the importance and impact of fiber optic couplers will continue to grow.




