Explore the significance of ESD safe swabs, their structure, application, and proper handling. Learn why they’re pivotal in electronic-based industries.
Understanding ESD Safe Swabs
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) safe swabs, also known as antistatic swabs, are unique tools utilized extensively in various industries, particularly in areas requiring high precision and cleanliness. As a crucial part of maintenance and cleaning processes, understanding the importance and application of ESD safe swabs is key.
What are ESD Safe Swabs?
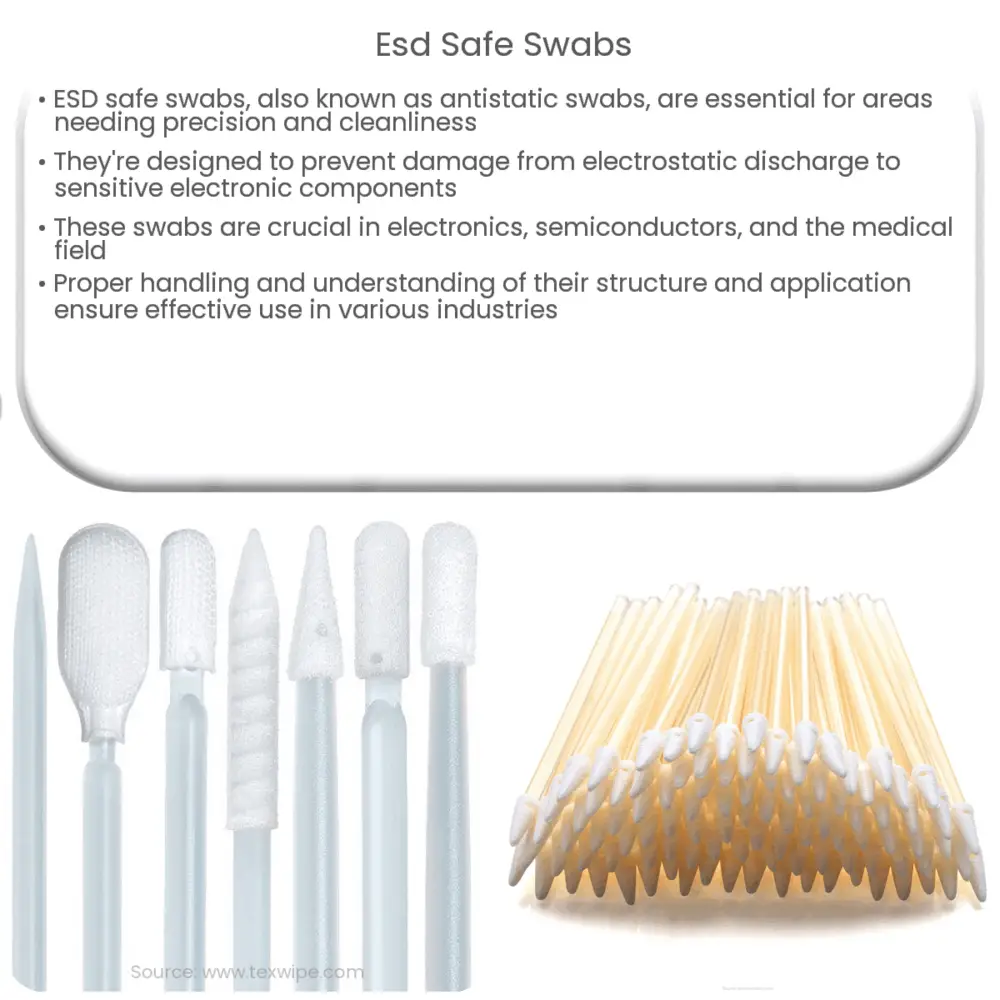
ESD safe swabs are specialized cleaning tools designed to mitigate the harmful effects of electrostatic discharge. These swabs are often constructed from materials that dissipate static electricity, ensuring that they do not generate or hold an electrostatic charge that could potentially damage sensitive electronic components.
Significance of ESD Safe Swabs
Handling electronic components poses a risk of ESD, which is a sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects. This can lead to irreversible damage to the electronic components, thereby causing significant losses. ESD safe swabs come in handy in minimizing such risks by providing a safe and efficient cleaning solution.
- Protection of Sensitive Components: ESD safe swabs are specifically designed to clean delicate and static-sensitive components without the risk of damage. They are used in an array of industries like semiconductors, biotech, medical, and more.
- Prevention of Contamination: These swabs help maintain the cleanliness required in controlled environments. They are often lint-free and non-abrasive, ensuring they don’t leave residues or cause any micro-scratches.
- Enhanced Precision: With their tightly wound tips and flexible handles, these swabs allow for precise cleaning, especially in hard-to-reach areas.
The Structure of ESD Safe Swabs
ESD safe swabs typically consist of a handle and a tip. The handle is usually made from a material that can efficiently dissipate static charges, such as polypropylene. The tip, on the other hand, is generally constructed from long-fiber polyester or foam, materials known for their ability not to generate static electricity. These carefully chosen materials, combined with the meticulous design, contribute to the overall safety and efficiency of ESD safe swabs.
Applications of ESD Safe Swabs
The use of ESD safe swabs is extensive in industries requiring high precision and cleanliness. The most common applications are in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing, data centers, laboratory settings, and the medical field. These swabs are ideal for cleaning sensitive equipment, removing contaminants, and applying or removing specific chemicals or solutions without the fear of ESD-related damage.
Choosing the Right ESD Safe Swabs
There are several factors to consider when selecting the appropriate ESD safe swabs for a specific task. This includes the size and shape of the swab tip, the length and flexibility of the handle, and the overall design of the swab. In addition, the swab’s material is crucial as it needs to have the necessary anti-static properties.
Maintenance and Handling of ESD Safe Swabs
Proper handling and storage of ESD safe swabs are essential to maintain their functionality and prolong their lifespan. It’s recommended to store these swabs in their original packaging to avoid dust and other contaminants. Furthermore, users should handle these swabs with clean, ESD-safe gloves to prevent potential damage from oils or debris from their hands.
ESD Safe Swabs in the Future
With the continuous advancement in technology, the need for ESD safe swabs is likely to grow. This is due to the ever-shrinking size of electronic components and the increasing complexity of the devices. Therefore, the development of more sophisticated and efficient ESD safe swabs is expected in the future to meet the evolving needs of various industries.
Conclusion
ESD safe swabs play a pivotal role in maintaining the functionality and longevity of sensitive electronic components. Their unique design and materials help minimize the risk of electrostatic discharge, making them indispensable tools in many industries. As technology continues to advance and the need for precision and cleanliness increases, the demand for EDS safe swabs is likely to grow. Understanding the structure, applications, and proper handling of these swabs will ensure their effective use, ultimately contributing to the overall success and efficiency of electronic-based industries.

