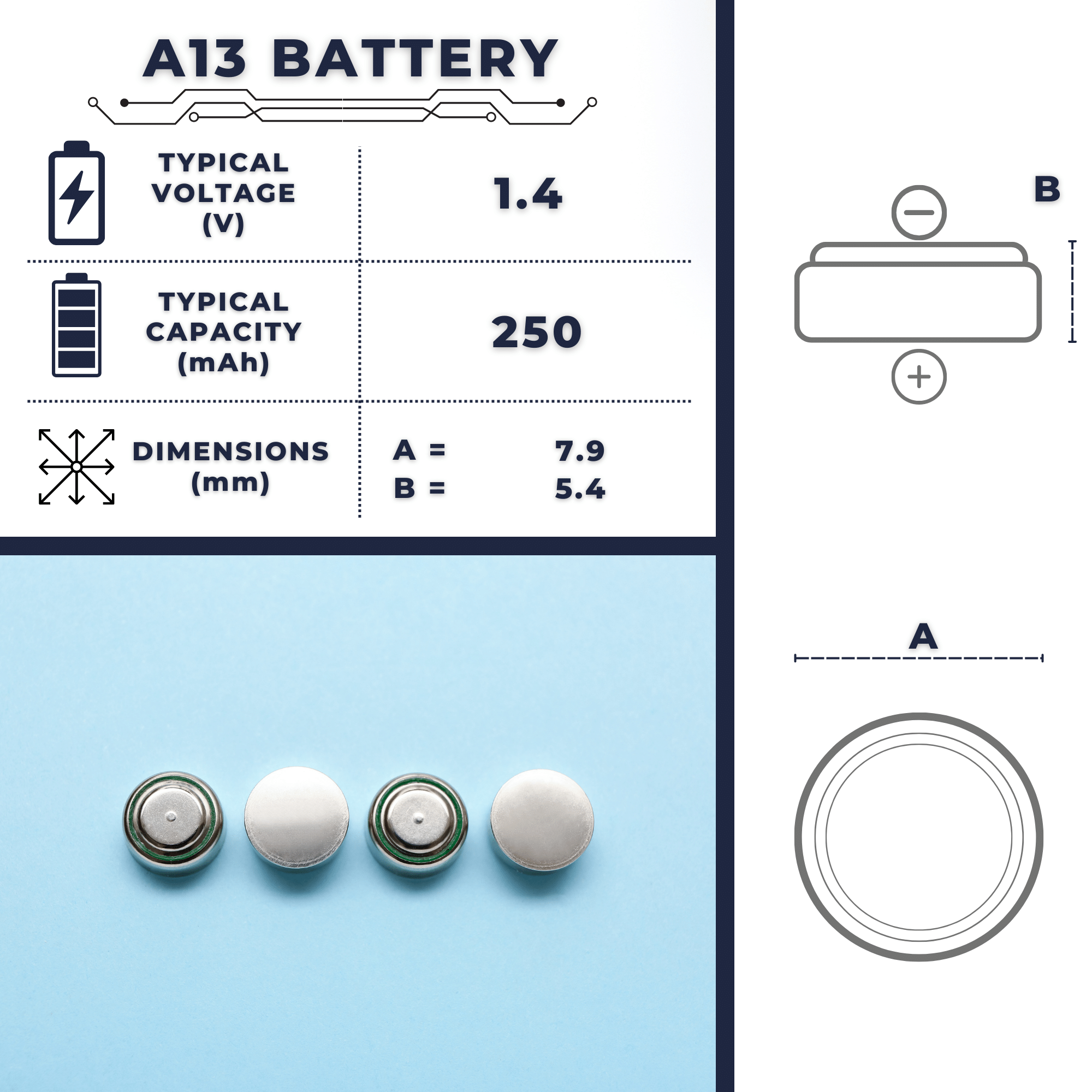
Introduction to the A13 Battery
The A13 batteries, part of the zinc-air battery group, are a notable type of metal-air fuel cells. They are characterized by their ability to oxidize zinc with the air’s oxygen. These batteries have high energy densities and their production is relatively inexpensive.
Features and Operation
The zinc-air battery, like the A13, offers specific and volumetric energy densities of approximately 500 Wh.kg-1 and 1000 Wh.L-1, respectively, figures that are among the highest for a battery system. The overall reaction in these batteries can be represented as Zn(s) + O2(g) ⇌ 2ZnO(s), with a standard potential e° of +1.59 V.
In terms of its design, the A13 batteries have a nominal diameter of 7.9 millimeters and a height of 5.4 millimeters, with an approximate weight of 0.8 grams and a typical capacity of 280 mAh.
Electrochemical Principles
The foundation of electric batteries, including the A13, lies in the conversion of stored chemical energy into electrical energy through an electrochemical process. This provides an electromotive force necessary for the flow of currents in electrical and electronic circuits. Each battery consists of one or more voltaic cells, where spontaneous redox reactions in two electrodes separated by an electrolyte (an ionic and electrically insulating conductive substance) facilitate this process.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Zinc-air batteries like the A13 are known for their high energy density and low cost. However, they have limitations in terms of power output, mainly due to the insufficient performance of the air electrodes. Additionally, their performance and operational period depend on environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature.
A distinctive feature of the A13 battery is that it comes with an adhesive over the air access holes, which is removed before use. Continuous use is recommended once the adhesive is removed to avoid electrolyte contamination.
Applications and Future
Zinc-air batteries are used in a range of sizes, from small button cells for hearing aids to larger batteries for large-scale energy storage and electric vehicle propulsion. Although these batteries are primarily non-rechargeable, options for their electrical recharge are being developed, which could revolutionize their use in the future.
Comparison with Other Types of Batteries
Compared to other batteries such as alkaline, lithium, or nickel-cadmium, zinc-air batteries offer advantages in terms of energy density and cost but have limitations in terms of power and dependence on environmental conditions. The wide range of batteries available in the market, from AA to 21700, demonstrates the diversity of options for different applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the A13 zinc-air battery is an impressive example of innovation in battery technology, offering high energy density at a low cost. Despite its disadvantages, its development and improvement continue, promising an even brighter future in the field of energy storage.