30-second summary
Electrostatic Discharge
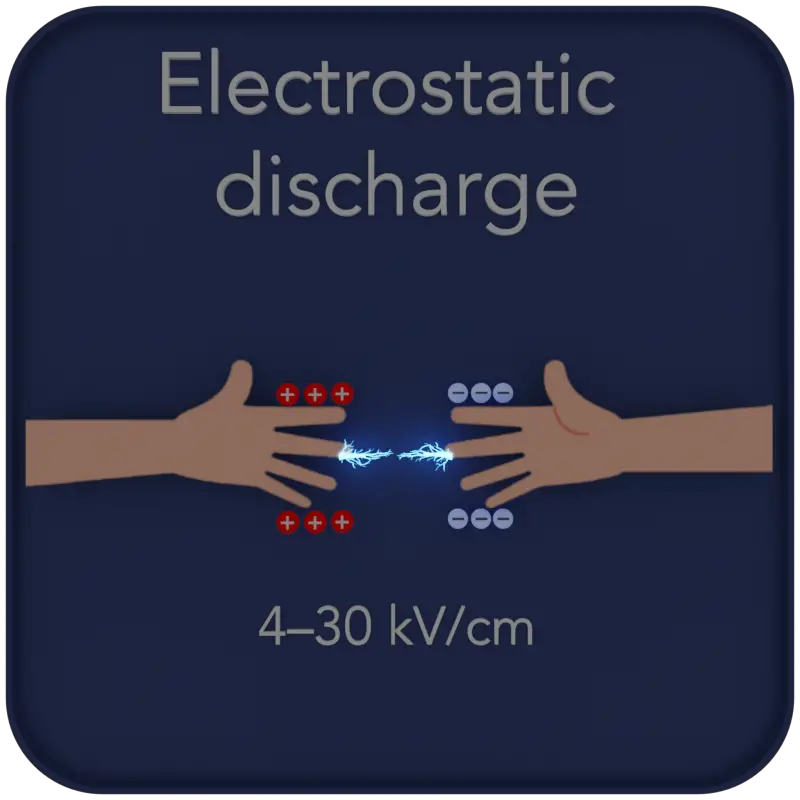
An electrostatic discharge, abbreviated as ESD, is a sudden and short-term electric current between two objects with different electric potentials.
A spark is triggered when the electric field strength exceeds approximately 4–30 kV/cm — the dielectric field strength of air.
Most of the static electricity we encounter every day is caused by the triboelectric effect.
Electrostatic discharge is a serious problem in technology, especially with electronic components, especially in integrated circuits.
On dry days, static electricity is much more noticeable since the air contains fewer water molecules to allow leakage.
Connection to the ground limits the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices.
About Electrostatic Discharge
An electrostatic discharge, abbreviated as ESD, is a sudden and short-term electric current between two objects with different electric potentials. A spark is triggered when the electric field strength exceeds approximately 4–30 kV/cm — the dielectric field strength of air.

An example of an electrostatic discharge in nature is lightning. Also, you have probably experienced static electricity when combing your hair or when taking a synthetic shirt from a clothes dryer. And you may have felt a shock when you touched a metal doorknob after sliding across a car seat or walking across a nylon carpet. Electrostatic discharge is a serious problem in technology, especially with electronic components, especially in integrated circuits. Even in an imperceptible moment, the circuit can be destroyed by its mere contact with another object with a different electrical potential.
On dry days, static electricity is much more noticeable since the air contains fewer water molecules to allow leakage. Usually, the charge leaks off onto water molecules in the air. This is because water molecules are polar — that is, even though they are neutral, their charge is not distributed uniformly. Thus the extra electrons can leak off from charged surface into the air because they are attracted to the positive end of water molecules. A positively charged object, on the other hand, can be neutralized by the transfer of loosely held electrons from water molecules in the air.
Connection to the ground also limits the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. Various antistatic devices are designed to ensure the safe grounding of the electrostatic charge. For domestic handling, for example, contact with metal gas pipes, water pipes or metal pipes and central heating radiators can be used for discharge; however, plastic wiring does not allow this.
An antistatic wrist strap, ESD wrist strap, or ground bracelet is an antistatic device used to safely ground a person working on very sensitive electronic equipment, to prevent the buildup of static electricity on their body, which can result in ESD.
Frequently asked questions
You have probably experienced static electricity when combing your hair or when taking a synthetic shirt from a clothes dryer. And you may have felt a shock when you touched a metal doorknob after sliding across a car seat or walking across a nylon carpet. This is caused by electrostatic discharge. Your body was probably charged via the triboelectric effect. On dry days, static electricity is much more noticeable since the air contains fewer water molecules to allow leakage.
Most of the static electricity we encounter every day is caused by the triboelectric effect. This can easily be produced by rubbing two dissimilar materials together, such as rubbing amber with fur or glass with silk. The friction of the two dissimilar materials greatly increases the effect due to the frequent contact and separation of these materials.
Connection to the ground limits the build-up of static electricity when handling flammable products or electrostatic-sensitive devices. Various antistatic devices are designed to ensure the safe grounding of the electrostatic charge. For domestic handling, for example, contact with metal gas pipes, water pipes or metal pipes and central heating radiators can be used for discharge; however, plastic wiring does not allow this.

