Zinc-air Battery
Zinc-air batteries are non-rechargeable and also mechanically rechargeable metal-air batteries powered by oxidizing zinc with oxygen from the air. The zinc metal electrode forms the largest part of the cell and is the negative electrode. A solution of KOH or caustic soda works as an electrolyte and improves the standard potential. The separator isolates both electrodes mechanically in order to prevent electric conduction inside the cell. Oxygen from the air reacts at the cathode and forms hydroxyl ions which migrate into the zinc paste and form zincate, releasing electrons to travel to the cathode.
These batteries have high energy densities and are relatively inexpensive to produce. Zinc-air batteries offer specific and volumetric energy densities of around 500 Wh.kg−1 and 1000 Wh.L−1, respectively, which are among the highest for a battery system. The discharge profile is largely flat with a voltage of around 1.3 V. Size ranges from very small button cells for hearing aids, larger batteries used in film cameras that previously used mercury batteries, to very large batteries used for electric vehicle propulsion and grid-scale energy storage.
The major disadvantage is their limited power output, which is mainly due to the inadequate performance of air electrodes. The other major disadvantage is the dependence of both performance and operating period on ambient conditions such as humidity and temperature. The commercially available primary zinc-air battery has a sticker attached over the air access holes, which is removed just before use. Once the sticker has been removed, it is recommended that the battery be used continuously because the air access to the battery will inevitably result in water exchange and carbon dioxide contamination of the electrolyte, leading to the gradual deterioration of the battery. The storage characteristic of the zinc-air battery is satisfactory when the sticker is in place.
In general, metal-air batteries offer a high energy density because there is only one active mass inside the cell, and the cathodic reaction uses ambient air. Zinc is a very promising element because of its disposability, non-toxic behavior, and because it can be used as a secondary cell. Despite these advantages, this is a primary battery and cannot be recharged. For larger units, the batteries could be mechanically recharged by physically substituting the zinc electrode and electrolyte. Electrical recharge options are in development nowadays, but since this evolution is in its very prime stage, many years will be needed to achieve this technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Zinc-air Batteries
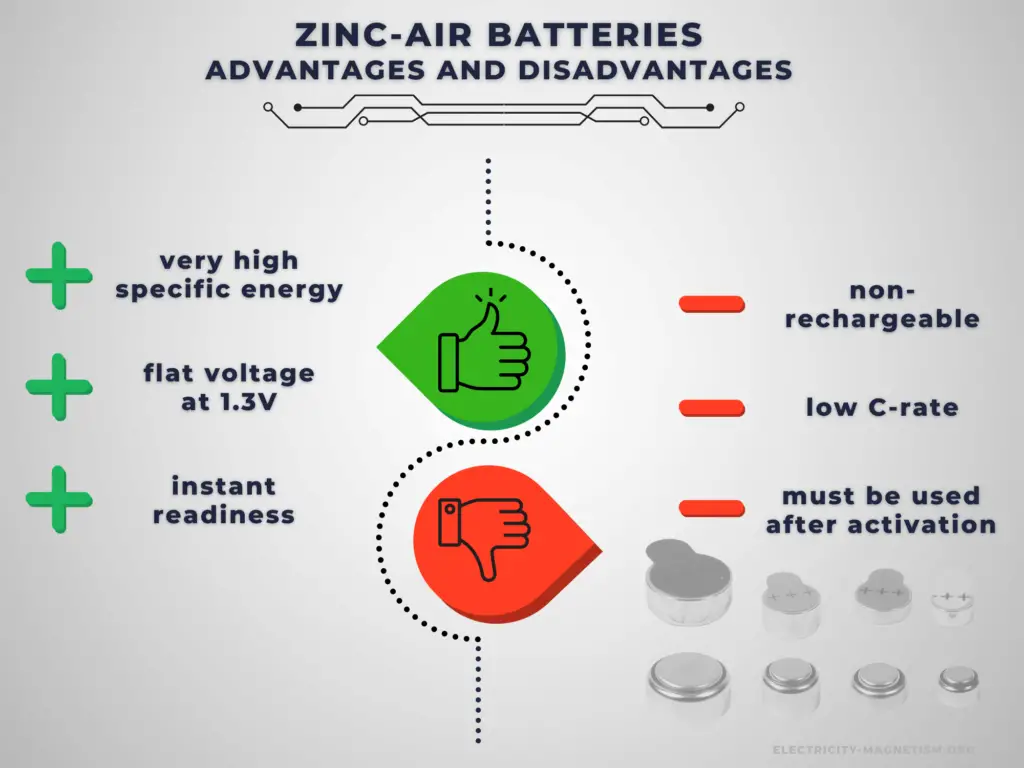
Advantages:
Primary batteries have higher energy density than rechargeable secondary cells. High specific energy, long storage times (low self-discharge), and instant readiness give primary batteries a unique advantage over other power sources. They are usually the best choice for low-drain applications. They can be carried to remote locations and used instantly, even after long storage; they are also readily available and environmentally friendly when disposed.
Zinc-air batteries offer specific and volumetric energy densities of around 500 Wh.kg−1 and 1000 Wh.L−1, respectively, which are among the highest for a battery system.
Disadvantages:
The main disadvantage of primary batteries is that they are non-rechargeable. Another disadvantage is their low C-rate. Even high current types are considered low in comparison to rechargeable batteries. They are also less environment friendly than rechargeable batteries. The application of primary batteries leads to a large amount of waste batteries to be recycled. For large batteries, primary batteries are usually not cost-effective.
The major disadvantage of zinc-air batteries is their limited power output, which is mainly due to the inadequate performance of air electrodes. The other major disadvantage is the dependence of both performance and operating period on ambient conditions such as humidity and temperature.

