Explore the intriguing world of electret materials: their discovery, characteristics, wide-ranging applications, and potential for future innovation.
Understanding Electret Materials
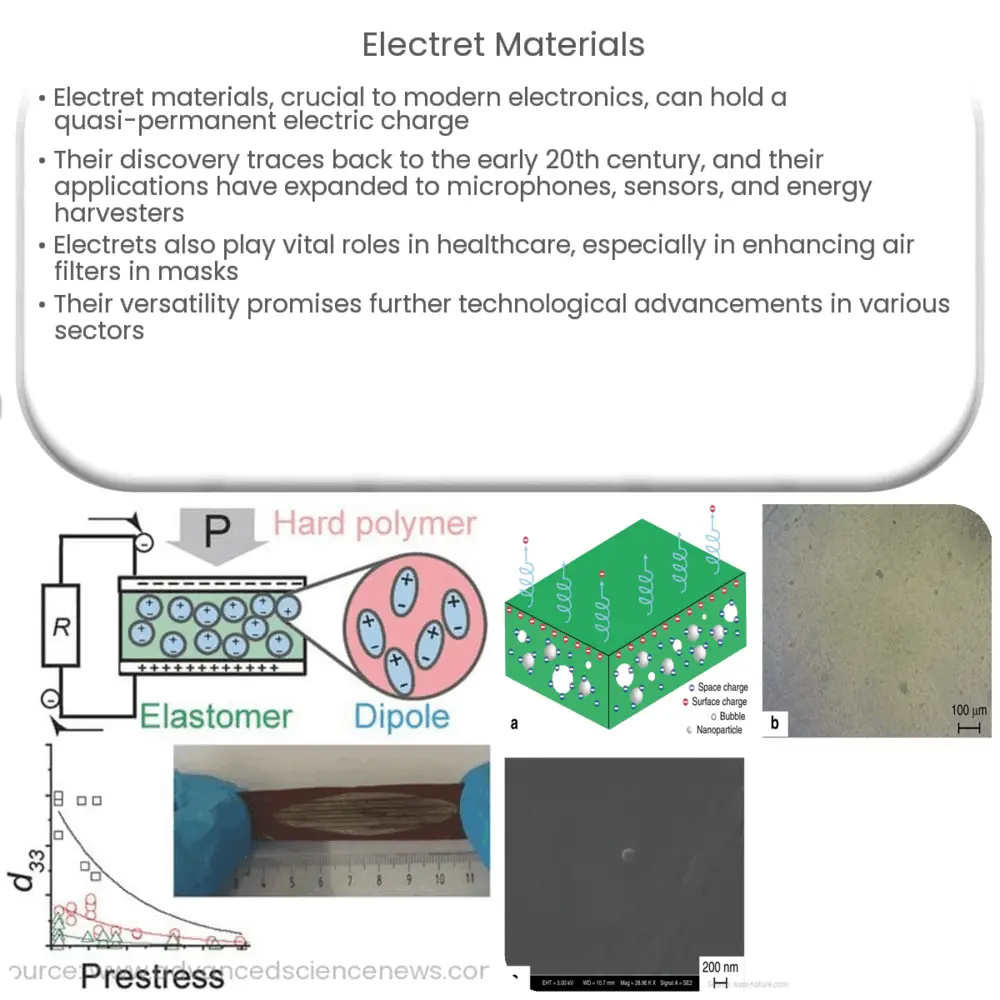
Electret materials, a portmanteau of ‘electric’ and ‘magnet’, form a critical part of modern electronics. They are essentially dielectric materials, insulators that can hold a quasi-permanent electric charge or polarization. After the material undergoes a polarization process, it exhibits a persistent electric field, similar to the magnetic field in a permanent magnet.
Discovery and Composition of Electrets
The discovery of electrets dates back to the early 20th century. The Japanese physicist Mototaro Eguchi first observed this phenomenon in 1922. However, it wasn’t until the 1960s that the real potential of electrets was recognized, thanks to the invention of electret microphones.
Electret materials can be made from a wide range of substances. Early electrets were created from natural materials like beeswax or resin, but today, synthetic polymers like polypropylene or fluoropolymers are commonly used due to their superior ability to retain a charge and their physical properties. Other materials, like silicon dioxide and certain ceramics, can also form electrets under specific conditions.
Characteristics of Electrets
- Permanent Polarization: Electrets are characterized by their ability to maintain an electric charge over a long period. This is due to the alignment of electric dipoles within the material.
- Stability: Once formed, an electret’s charge is remarkably stable. It can persist for many years or even decades. This stability makes electrets useful in a variety of applications.
- Variability: The properties of electrets can be modified by adjusting the type of material used, the process of polarization, and the conditions under which the electret is stored. This makes them highly adaptable for various uses.
Applications of Electret Materials
Electret materials have a vast array of applications in the electronics industry. One of the most well-known applications is in the electret microphone, where an electret material is used to convert sound into an electrical signal. Other uses include electrostatic filters, sensors, and generators. Even the humble laser printer relies on an electret material to function properly.
Further Developments and Research
In the realm of scientific research, electret materials continue to be a subject of intense study. One area of interest is the development of more efficient electret materials that can retain their charge for longer periods, even under adverse conditions. Scientists are also exploring the use of electrets in energy harvesting applications, such as capturing energy from mechanical vibrations or thermal fluctuations.
Electrets in Sustainable Energy
In the realm of sustainable energy, electrets hold significant promise. Their potential for energy harvesting is being thoroughly investigated. For instance, scientists are exploring the feasibility of electret-based energy harvesters that can convert ambient energy into usable electricity. These harvesters could tap into the vibrations caused by industrial machinery, the movement of cars, or even human activity to generate power. This has substantial implications for the future of renewable energy and sustainability.
Healthcare and Biomedical Applications
Another field where electrets are gaining traction is healthcare. In biomedical applications, electrets are used in air filters, an essential component in surgical masks and respirators. The electret material in these filters enhances their ability to trap tiny particles, including bacteria and viruses, providing superior protection compared to regular filters.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electrets are an intriguing class of materials that combine the properties of insulators with the ability to retain an electric charge. From the electronics industry to healthcare, they serve vital roles in various applications. With ongoing research and development, the utility of these materials is set to expand even further. As we continue to explore their potential, we can expect to see new innovations and applications that leverage the unique characteristics of electret materials, underlining their relevance in our technologically advanced world.

