Explore the world of DC-DC converters, their types, working principles, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and future trends in this comprehensive guide.
Understanding DC-DC Converters
A DC-DC converter is an essential component in the world of electronics, playing a crucial role in managing the power supply of various devices. As its name suggests, a DC-DC converter’s fundamental function is to convert Direct Current (DC) from one voltage level to another.
These converters are integral to numerous applications, from charging your mobile phone to powering large machinery. Understanding their inner workings can offer valuable insights into the broad realm of power electronics.
Types of DC-DC Converters
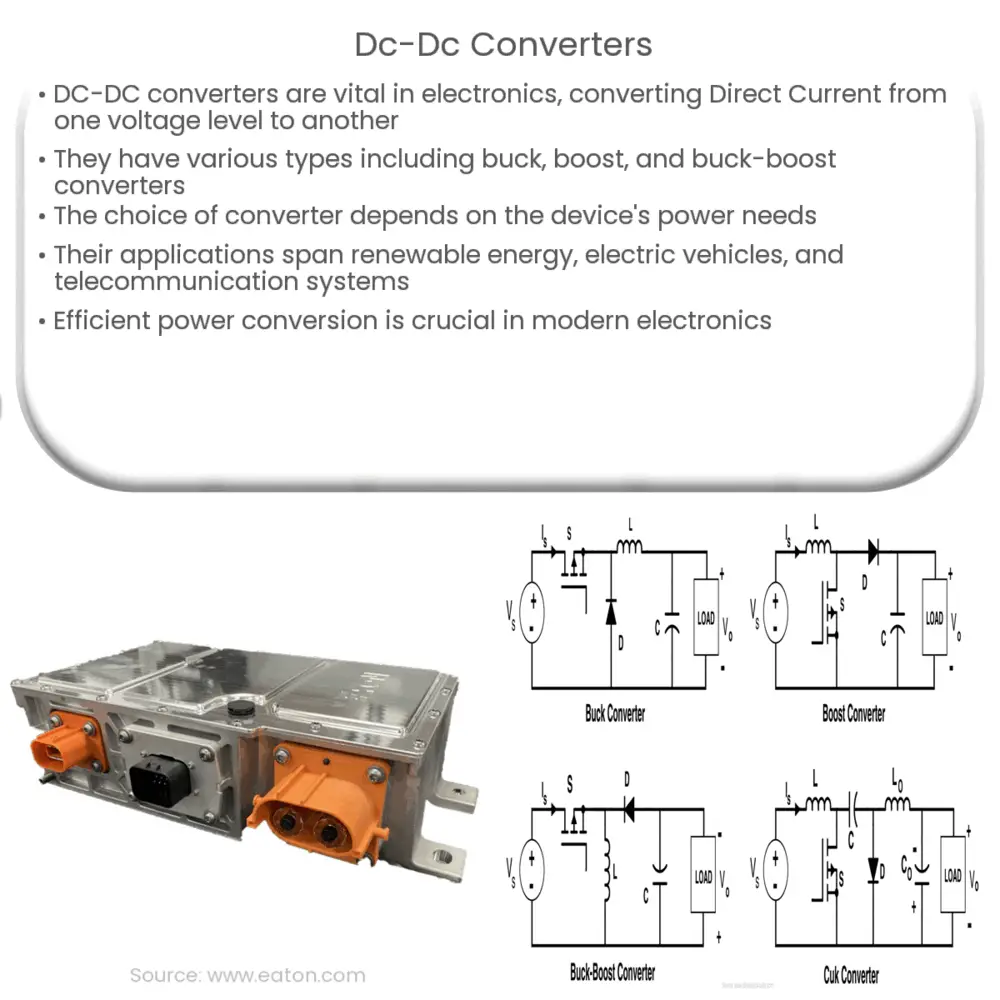
- Buck Converter: Also known as a step-down converter, a buck converter reduces the input voltage while increasing the output current.
- Boost Converter: Opposite to the buck converter, a boost converter, or step-up converter, increases the input voltage and decreases the output current.
- Buck-Boost Converter: This type of converter can either increase or decrease the input voltage, depending on the duty cycle of the switch.
Choosing the right type of DC-DC converter depends on the specific application and the power requirements of the device in question.
The Working Principle of DC-DC Converters
The working principle of DC-DC converters involves an intricate process of energy storage and release. The basic principle can be understood by considering a simple switch mode power supply (SMPS) converter. It contains an inductor, capacitor, diode, and a switch.
When the switch is turned on, energy from the input source is stored in the inductor. Conversely, when the switch is turned off, the stored energy in the inductor is transferred to the load through the diode. The capacitor is used to reduce the ripple in the output voltage. This switching action between on and off states results in a stable output voltage.
Applications of DC-DC Converters
- Renewable Energy Systems: DC-DC converters play a significant role in renewable energy systems, like solar power and wind energy. They are used to optimize the power output and adjust the voltage levels according to the grid requirements.
- Electric Vehicles: The battery management system in electric vehicles extensively uses DC-DC converters to manage power distribution, and optimize battery performance and life.
- Telecommunication Systems: In telecommunications, DC-DC converters help to maintain stable voltage levels, which is crucial for the smooth functioning of communication equipment.
Considering their diverse applications, DC-DC converters are indispensable in modern electronics, making it essential for electronic engineers and hobbyists to understand their operation and implementation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DC-DC Converters
Like any other technology, DC-DC converters come with their own set of pros and cons. On the upside, they offer high efficiency, especially in applications that require power to be transferred over long distances. They also provide a consistent and stable output, even in the face of fluctuating input voltage. This is a significant advantage in applications where power stability is crucial.
On the downside, DC-DC converters can be relatively complex to design and manufacture due to their intricate circuitry. This can potentially lead to higher costs. They also produce noise due to the switching operation, which can interfere with the operation of sensitive electronic devices. Moreover, due to their switching nature, they tend to generate heat, which must be effectively managed to prevent overheating and subsequent damage to the converter.
Future of DC-DC Converters
As technology advances, the demand for efficient and reliable power conversion continues to grow. DC-DC converters are continuously being refined to enhance their efficiency, minimize their size, and reduce their cost. With the advent of technologies like Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC), the power electronics industry is witnessing a transformation that could make DC-DC converters even more compact and efficient.
Moreover, the ongoing trend towards green energy and the rise of electric vehicles present new challenges and opportunities for DC-DC converters. Their role in energy harvesting from renewable sources and electric vehicle charging infrastructure cannot be understated. As such, the future of DC-DC converters seems promising and exciting.
Conclusion
DC-DC converters are the unsung heroes of the electronics world. They silently and efficiently perform the critical task of power conversion, ensuring that our gadgets and appliances operate seamlessly. Understanding their operation, types, advantages, and disadvantages is essential not only for electronic engineers but also for anyone who wishes to understand the fundamental principles that underpin our technology-dependent lives. As we forge ahead into the future, DC-DC converters will continue to evolve, offering solutions to new challenges and facilitating the next generation of electronic innovation.

