Explore the world of D-Sub connectors, their design, types, applications, and future in the evolving landscape of electronics.
D-Sub Connectors: An Integral Component in Electronics
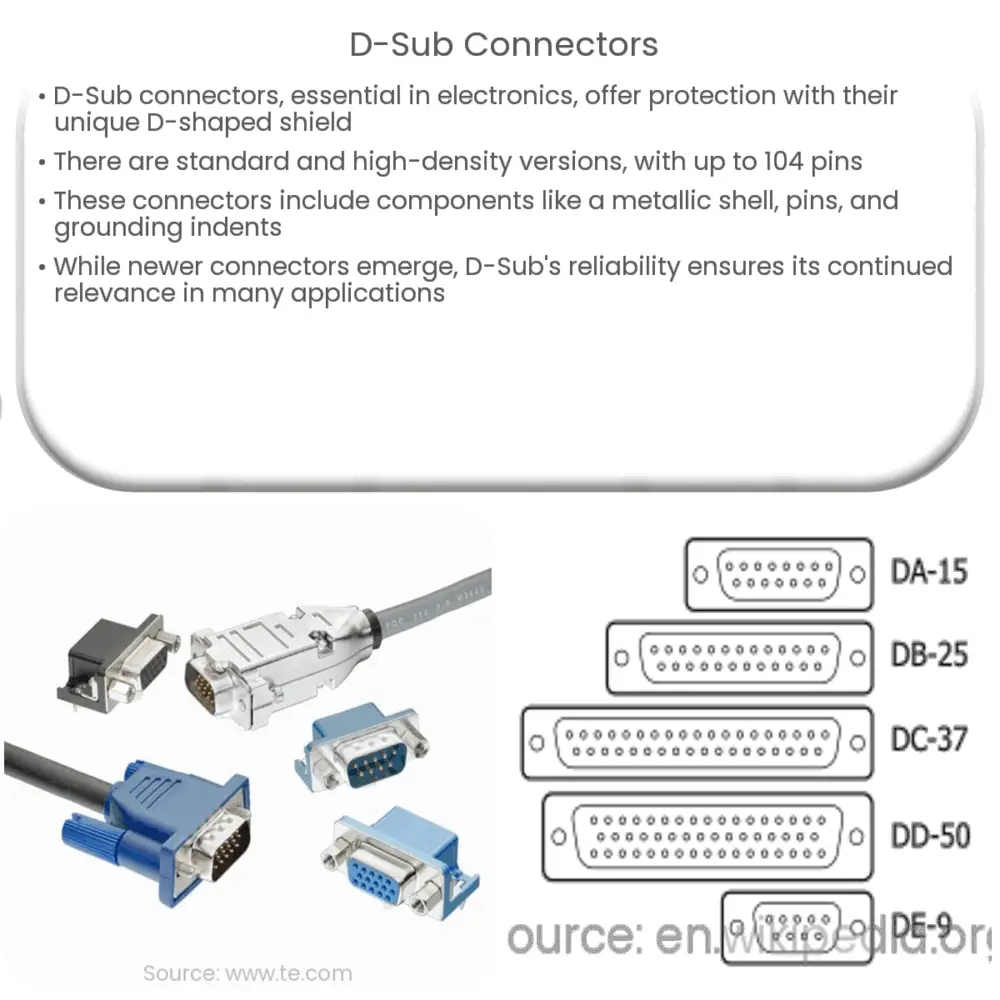
D-Sub connectors, also known as D-Subminiature connectors or simply D-Subs, have been an essential part of electronics and data communication systems for decades. Originating from their unique D-shaped metal shield, these connectors offer a sturdy interface and a high degree of protection for various connection types.
There are several types of D-Sub connectors, each serving distinct functionalities. The two most common varieties include standard density and high-density D-Sub connectors. Standard density D-Subs typically consist of two to three rows and up to 50 pins. On the other hand, high-density D-Subs, such as HD15 and HD26, feature three rows and can contain up to 104 pins.
The Anatomy of a D-Sub Connector
Every D-Sub connector comprises a few fundamental components. They are designed with a metallic shell to ensure robustness and reduce electrical interference. The shell design also ensures a solid mechanical mating with the corresponding socket. Within the shield, we find the pins or sockets – the signal carriers. These pins come in various formats and carry out different tasks, including signal, power, and grounding functions.
- Shell: It is the robust outer cover, typically made from zinc-plated steel, ensuring durability and shielding from interference.
- Insulator: A piece of non-conductive material usually made from thermoplastic or thermoset materials, creating a barrier between the metallic shell and the internal pins or sockets.
- Pins/Sockets: They are the conducting parts of the connector, facilitating data or power transmission. The number of pins or sockets determines the connector type, such as 9-pin or 25-pin D-Sub.
- Grounding Indents: Small indents are formed into the shell during manufacturing to ensure proper grounding when the connector is mated.
D-Sub connectors come in either a male (plug) or female (socket) variant. The pin layout in these connectors is standardized, ensuring compatibility and interoperability with devices. Their durable and reliable design, alongside the variety of pin layouts, makes D-Sub connectors suitable for a wide range of applications.
The benefits and applications of D-Sub connectors extend beyond just hardware interfacing. Their relevance in modern electronics, despite the advent of newer connector types, is a testament to their reliability and versatility. The second part of this article will delve deeper into these applications and the future of D-Sub connectors in the ever-evolving landscape of electronics.
Applications of D-Sub Connectors
D-Sub connectors have found widespread application in diverse areas of technology. Historically, they were the go-to choice for serial and parallel port connections in computers, particularly for RS-232 serial communications. Here are some typical applications:
- Computer Systems: From connecting monitors via VGA (Video Graphics Array) to enabling data transfer through serial and parallel ports, D-Sub connectors were integral in older computer systems. Despite newer connectors, some applications still prefer them due to their robustness and reliability.
- Industrial Machinery: Industrial applications often require durable and reliable connections. Here, D-Sub connectors shine because of their rugged design and ability to withstand harsh conditions.
- Telecommunications: In telecommunications equipment, D-Sub connectors help in data transmission and interface networking hardware.
- Aerospace and Defense: Owing to their reliability and high-pin density options, these connectors are widely used in aerospace and defense applications.
The Future of D-Sub Connectors
While we see an increase in the use of more compact and higher-speed connectors in the realm of consumer electronics, the D-Sub connectors continue to maintain their position in various sectors. Their durability, versatility, and high-pin count make them an ideal choice for applications requiring reliable and robust connections. However, with the advent of advanced technologies like USB-C, the usage of D-Sub connectors in consumer devices may continue to decrease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, D-Sub connectors have played a pivotal role in the evolution of electronics and data communication systems. Their unique design, characterized by their D-shaped metal shield and varying pin layouts, caters to a wide range of connection types. Despite the emergence of newer, smaller, and faster connectors, D-Sub connectors’ durability, reliability, and versatility keep them relevant in numerous applications.
As technology continues to evolve, we may see a decrease in their usage in certain sectors. Nevertheless, their significance in areas requiring robust and high-pin density connections is likely to remain unchallenged in the foreseeable future. Therefore, D-Sub connectors will continue to be an important component in the ever-changing landscape of electronics.

