Explore the importance and design considerations of capacitor bleeder resistor circuits in ensuring safety in electronic applications.
Capacitor Bleeder Resistor Circuits
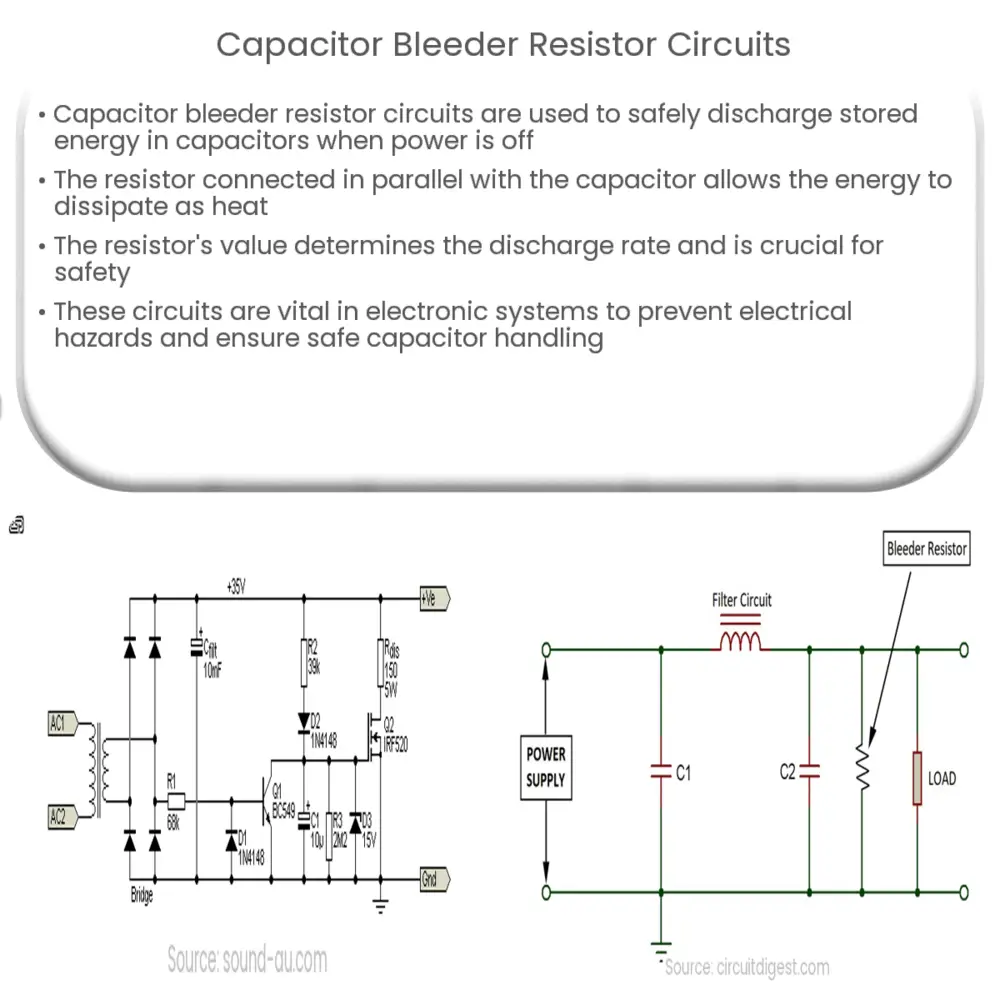
A capacitor bleeder resistor circuit is a commonly used configuration in electronic circuits to discharge the stored energy in a capacitor when the power is turned off. Capacitors have the ability to store electrical energy, and they can retain this energy even after the power source is disconnected. To safely handle or work with capacitors, it is important to discharge them to prevent any potential hazards.
When a capacitor is connected to a power source, it charges up and stores electrical energy in the form of an electric field. This stored energy can be potentially dangerous, especially if it is high-voltage capacitors or large capacitance values. If someone accidentally comes into contact with the terminals of a charged capacitor, they may receive an electric shock. To avoid such risks, a bleeder resistor circuit is employed to discharge the capacitor and make it safe to handle.
The basic principle behind a capacitor bleeder resistor circuit is to provide a discharge path for the stored energy in the capacitor. This is achieved by connecting a resistor in parallel with the capacitor. When the power is turned off, the resistor allows the energy stored in the capacitor to flow through it and dissipate as heat. As a result, the voltage across the capacitor decreases over time until it reaches a safe level.
The value of the bleeder resistor is crucial in determining the discharge time of the capacitor. A higher resistance value will result in a slower discharge rate, while a lower resistance value will discharge the capacitor more quickly. The selection of the resistor value depends on various factors such as the capacitance of the capacitor, the desired discharge time, and the power rating of the resistor.
Capacitor bleeder resistor circuits are widely used in various applications where capacitors are involved, such as power supplies, audio amplifiers, and electronic equipment. They provide a simple and effective solution to discharge capacitors safely and prevent potential electrical hazards.
In conclusion, a capacitor bleeder resistor circuit is an essential component in electronic circuits that involve capacitors. It ensures the safe discharge of stored energy in capacitors, reducing the risk of electric shock. By dissipating the stored energy through a resistor, the voltage across the capacitor gradually decreases to a safe level. Understanding and implementing capacitor bleeder resistor circuits are vital for maintaining safety in electronic systems.
Designing Capacitor Bleeder Resistor Circuits
Designing a capacitor bleeder resistor circuit involves the careful selection of a suitable resistor. The resistor’s value is calculated based on the desired discharge time and the voltage rating of the capacitor. Typically, the resistor should be able to discharge the capacitor to a safe voltage level within a reasonable time after power is removed.
To calculate the value of the bleeder resistor, the time constant (τ) of the circuit needs to be considered. The time constant is the product of the resistance (R) and the capacitance (C), i.e., τ = RC. The capacitor is considered discharged to a safe level after about five time constants.
Considerations and Precautions
While designing a bleeder circuit, a few important considerations must be kept in mind. The power rating of the resistor is one such crucial factor. During the discharge process, the resistor will dissipate the stored energy in the form of heat. Therefore, the resistor should have a sufficient power rating to handle this dissipated energy without overheating or damaging itself.
Additionally, safety is of utmost importance when working with capacitors and bleeder resistors. It’s essential to always ensure that the capacitor is fully discharged before handling. Even with a bleeder resistor in place, one should not assume that the capacitor is completely discharged immediately after the power is turned off. It’s good practice to manually discharge the capacitor using a suitable resistor before handling it.
Conclusion
Capacitor bleeder resistor circuits play an indispensable role in ensuring safety in various electronic applications. They allow the stored energy in capacitors to be discharged in a controlled manner, thereby reducing potential electrical hazards. The design of these circuits involves choosing an appropriate bleeder resistor, keeping in mind the capacitor’s voltage rating and the desired discharge time. Although bleeder circuits offer a simple and effective solution to capacitor discharging, care must be taken while handling capacitors to avoid any mishaps. Remember, safety should always be paramount in all electronic design and handling activities.

